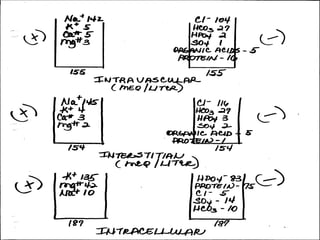
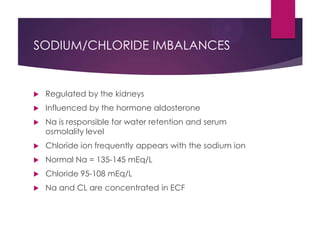
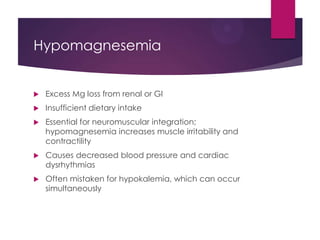
This document discusses electrolyte imbalances, including sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, and magnesium. For each electrolyte, it covers normal levels, causes of imbalances, signs and symptoms, diagnostic findings, and treatment approaches. Key points include the roles of electrolytes in nerve impulse transmission, acid-base balance, and other bodily functions. Major imbalances discussed are hyponatremia, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hypercalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypermagnesemia.