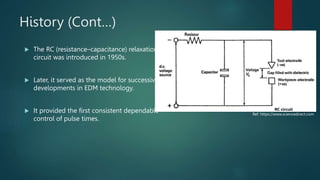
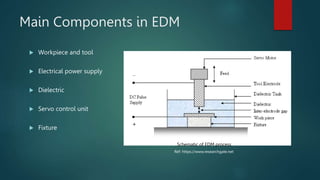
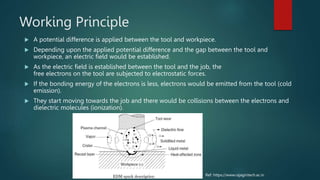
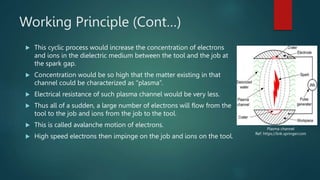
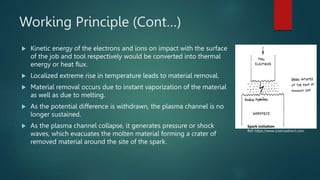
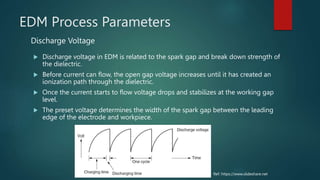
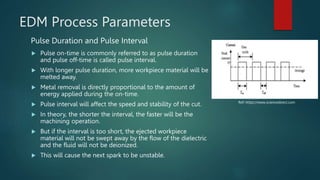
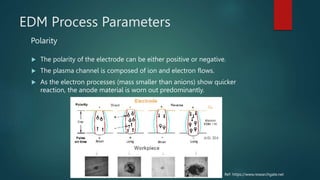
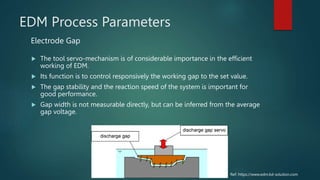
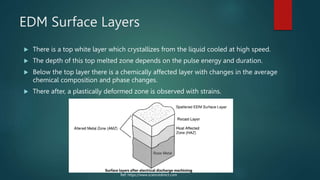
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a machining process that uses electrical discharges to erode material from a conductive workpiece. It was pioneered in the 1940s and uses a tool and workpiece submerged in a dielectric fluid. An electric current is applied between the tool and workpiece, causing electric sparks that melt and vaporize small amounts of material. Key parameters that affect the process include discharge voltage, current, pulse duration and polarity. EDM allows machining very hard materials and complex shapes regardless of hardness, and provides a high-quality surface finish.