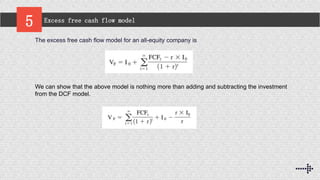
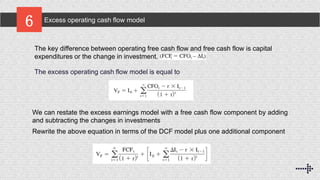
The excess free cash flow model, excess operating cash flow model, and excess earnings model are all valuation methods that are equivalent to discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation under consistent implementation. They discount excess accounting earnings or residual income instead of excess free cash flows. The key difference between the models is how changes in working capital, accruals, and capital expenditures are treated. Specifically, the excess earnings model can be restated as the DCF model plus components related to changes in investments and accruals.