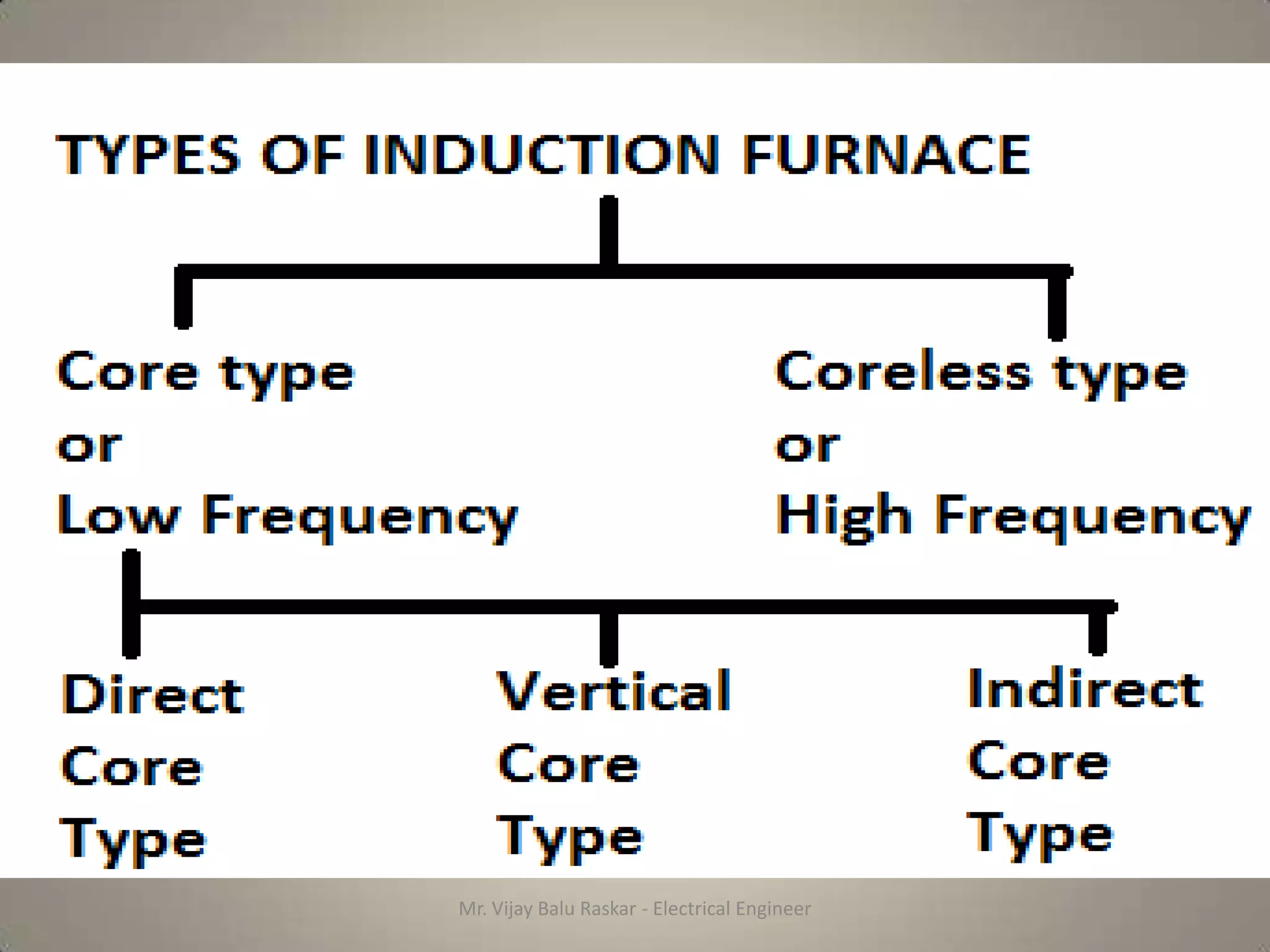
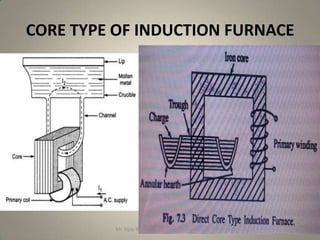
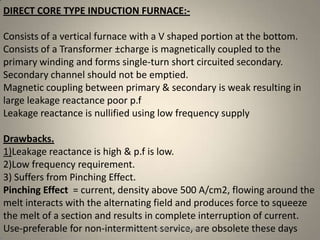
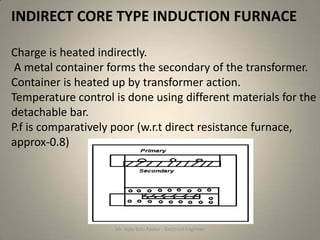
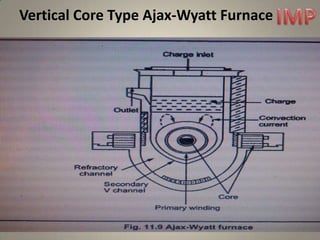
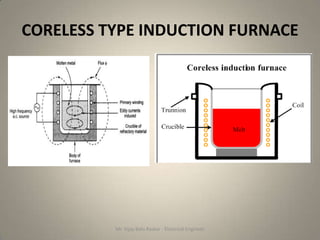
The document discusses different types of induction furnaces, including direct core type, vertical core type (Ajax-Wyatt), and coreless type furnaces. It explains their basic constructions and operating principles. The vertical core type furnace (Ajax-Wyatt) aims to eliminate the limitations of direct core type furnaces by using a V-shaped design that helps prevent discontinuity in the secondary circuit. Coreless furnaces have no iron core and use high frequency supply to induce eddy currents directly in the charge for heating.