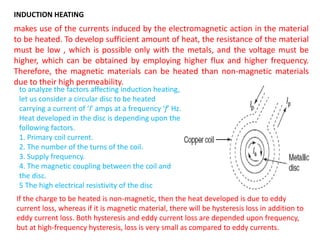
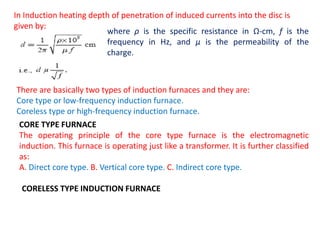
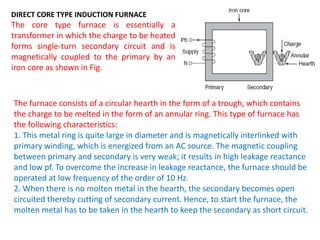
High-frequency heating uses electromagnetic energy to rapidly heat materials through induction or dielectric methods. Induction heating induces currents in conductive materials like metals to generate heat, while dielectric heating heats insulating materials. Induction furnaces can heat magnetic materials more than non-magnetic due to higher permeability. Core type furnaces operate like transformers, using an iron core to magnetically couple the primary and secondary coils. Direct core furnaces form a large metal ring secondary that is heated within a circular hearth. They require low frequency operation below 10Hz to reduce leakage reactance and pinch effects in the molten metal.