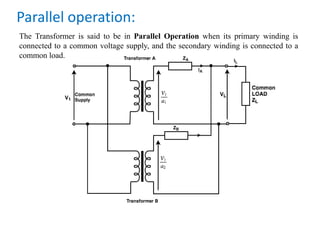
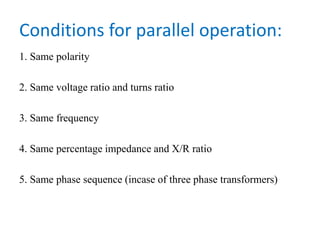
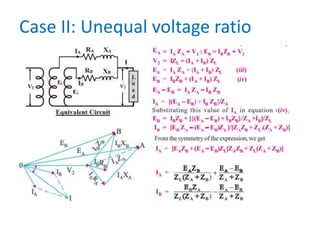
1. The document discusses parallel operation of transformers and auto transformers. Parallel operation connects multiple transformer primary windings to a common voltage supply and secondary windings to a common load. This allows for continuity of supply, operating at maximum capacity, and adjusting to load requirements.
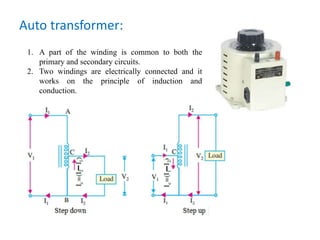
2. An auto transformer uses a common winding for both the primary and secondary circuits. This makes it cheaper and more efficient than an ordinary two-winding transformer but provides less isolation and can be damaged more easily by faults.
3. Auto transformers are used as starters for induction motors, to provide a small boost to correct voltage drops, and for voltage regulation in power transmission and distribution systems.