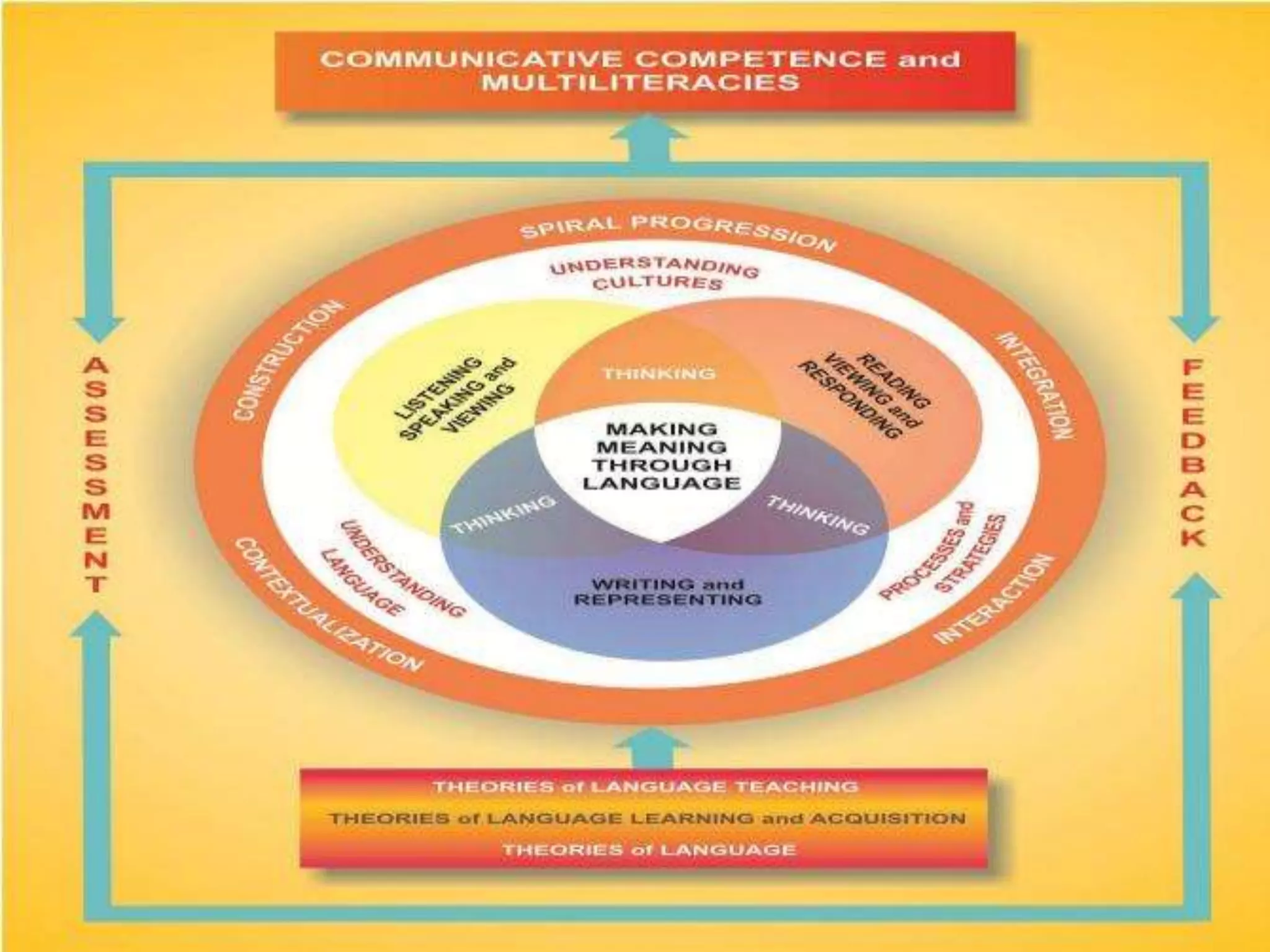
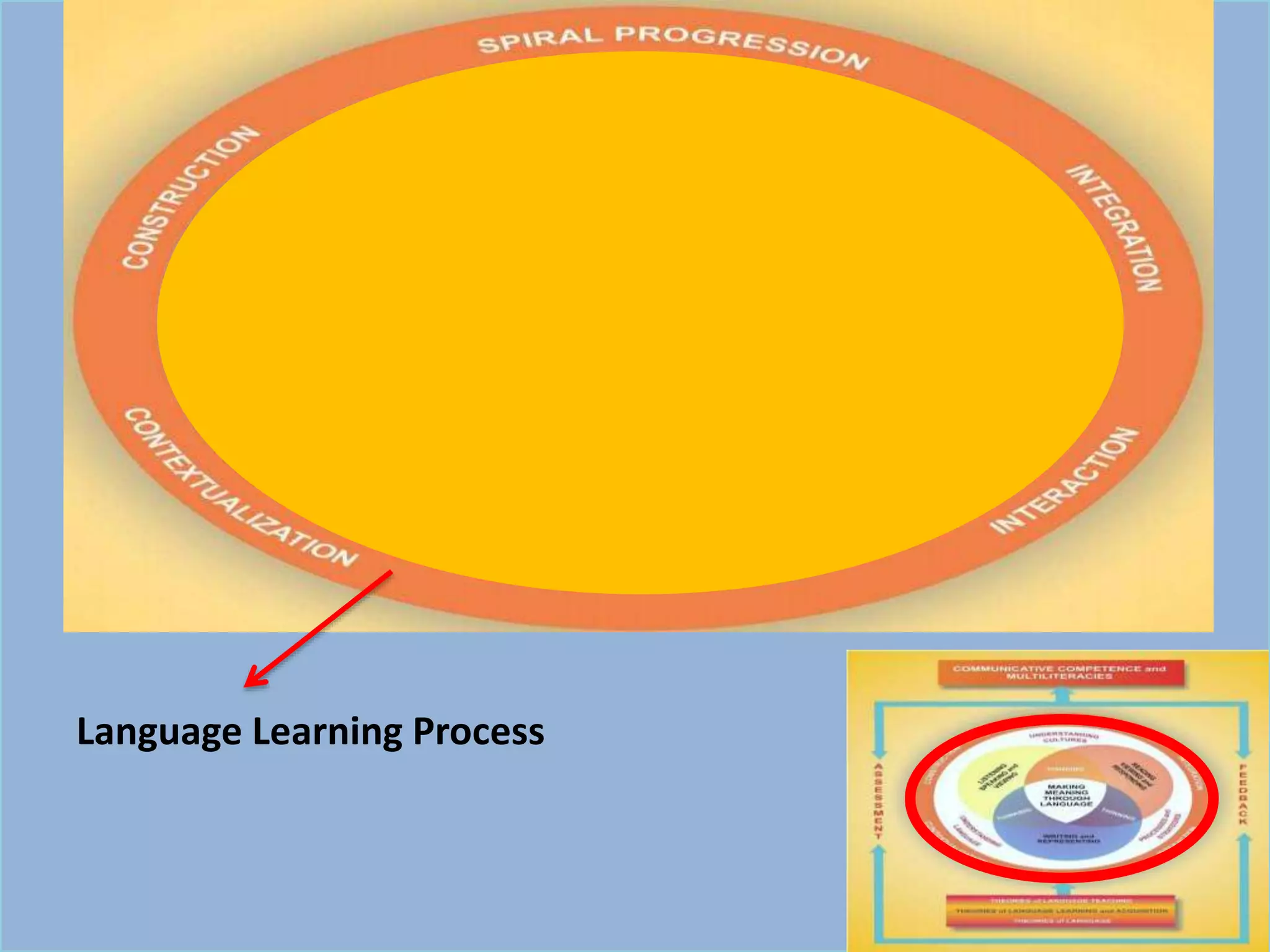
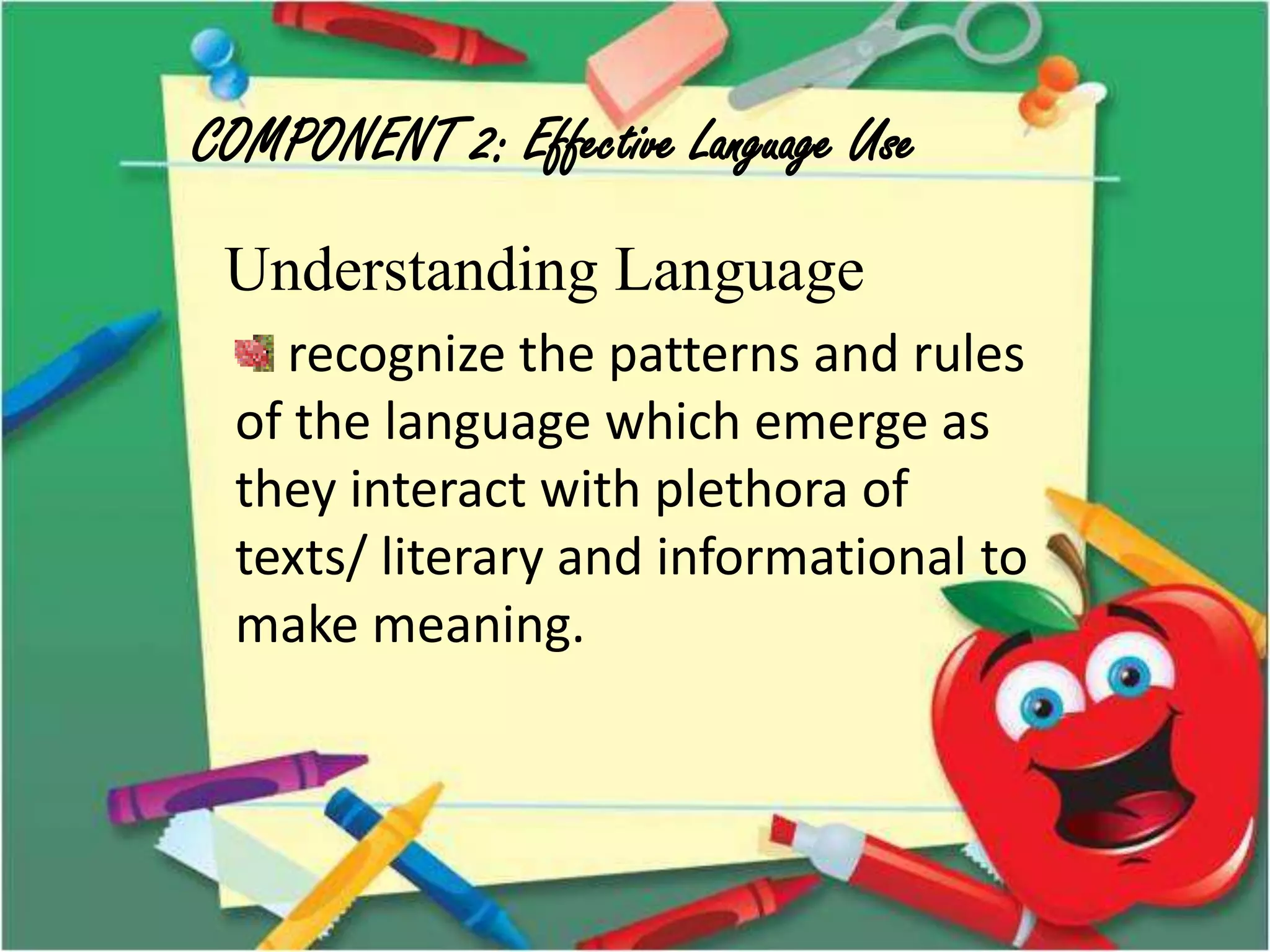
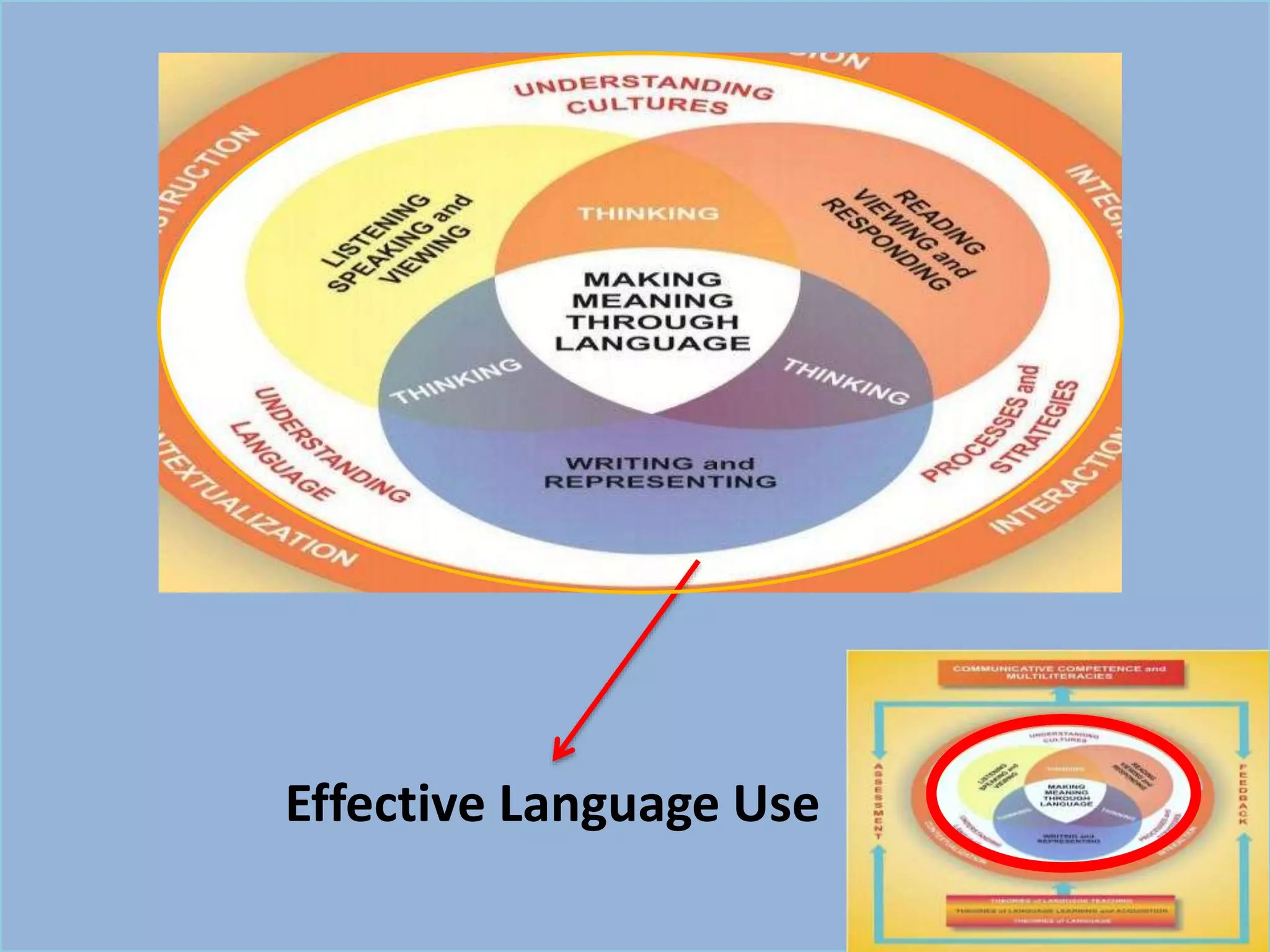
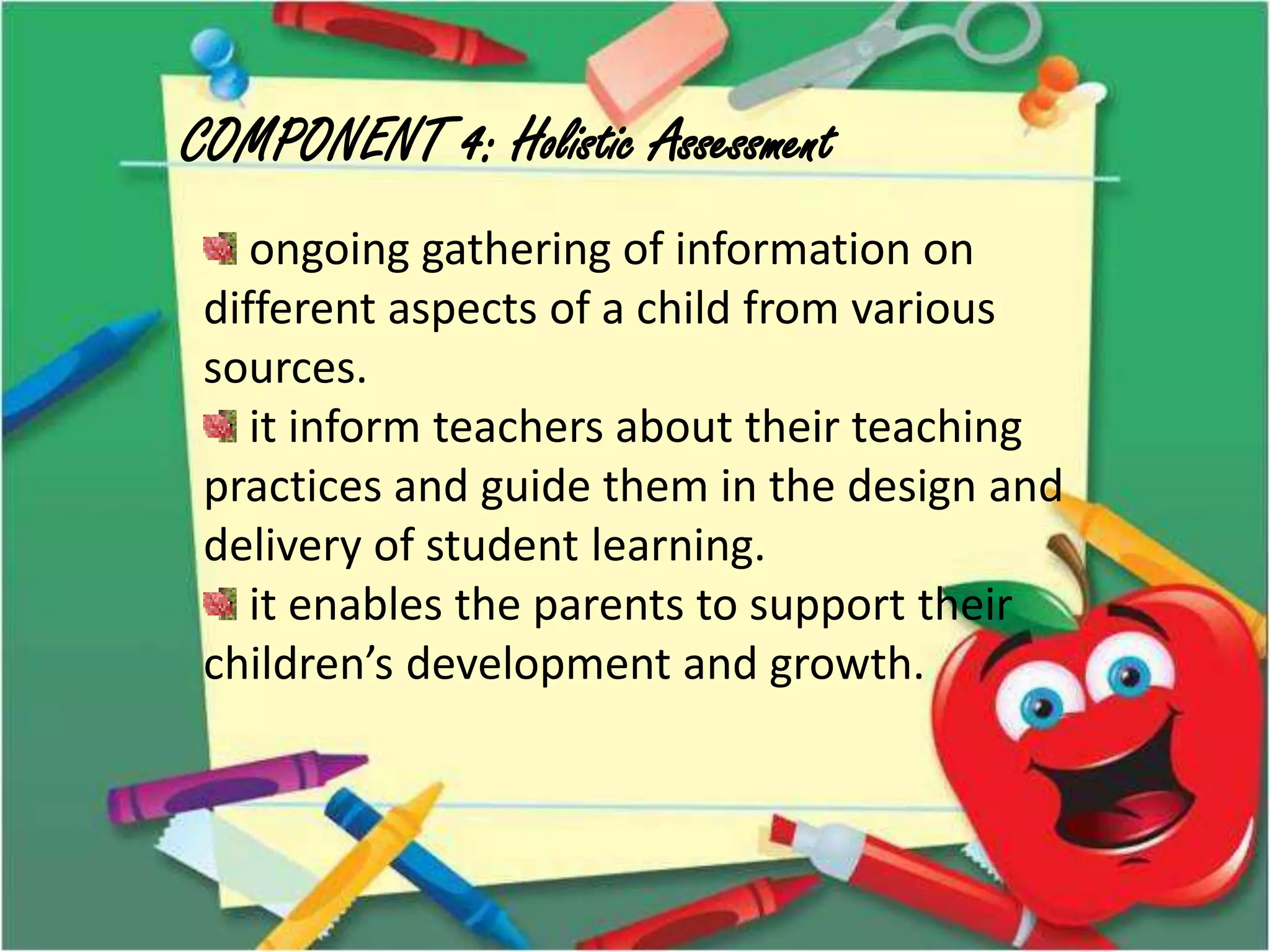
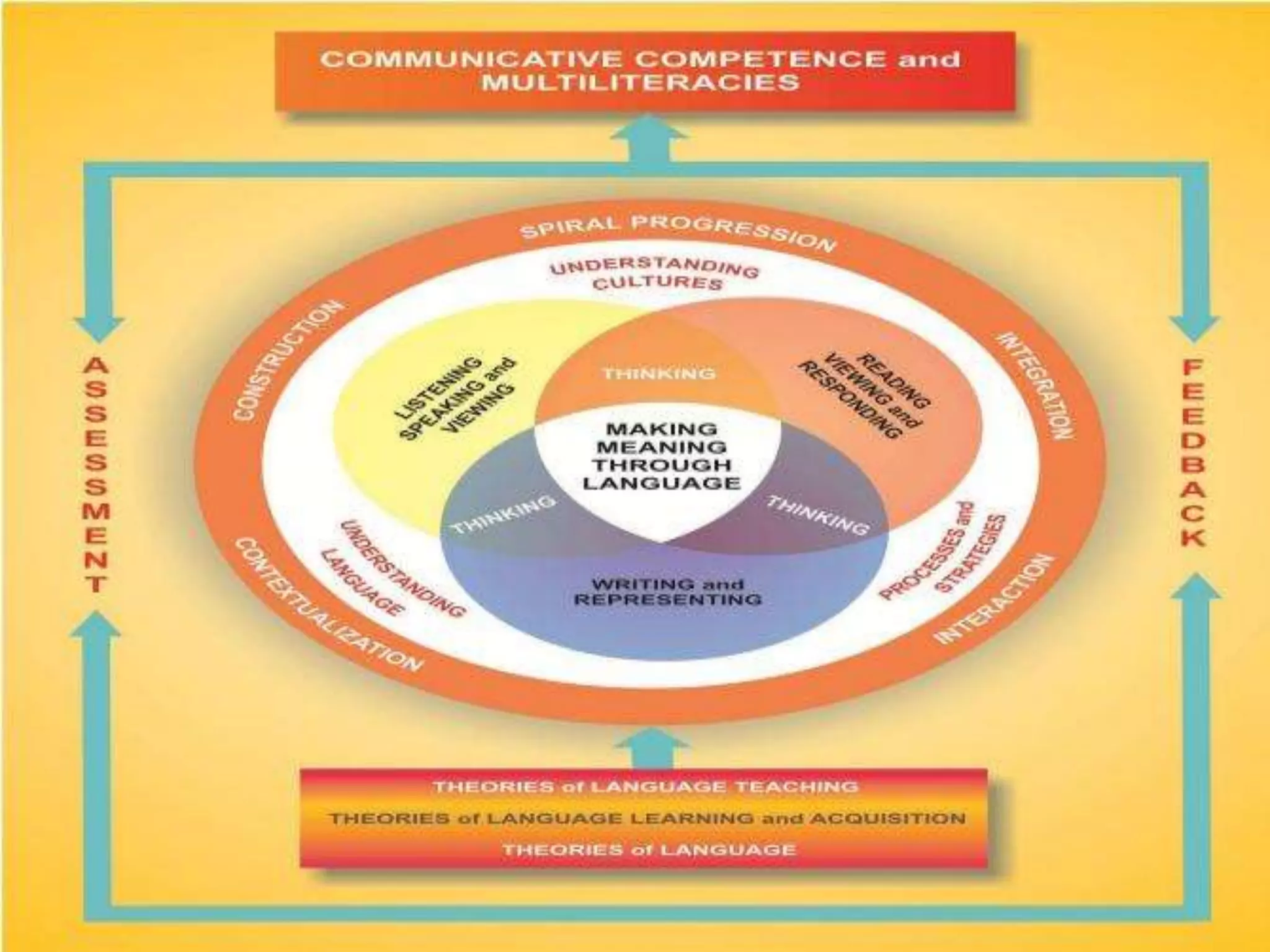
The document outlines a conceptual framework for education with 4 components: 1) language learning process using techniques like spiral progression and learner-centeredness, 2) effective language use including understanding cultures and language, 3) making meaning through language using oral/written communication macro-skills, and 4) holistic assessment with characteristics like proximity to performance and a holistic view of language.