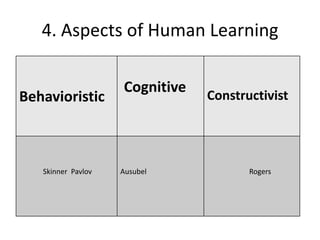
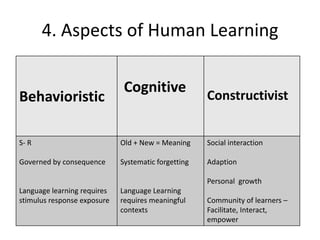
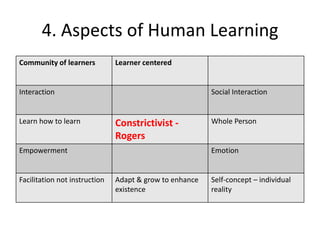
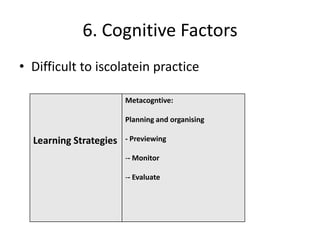
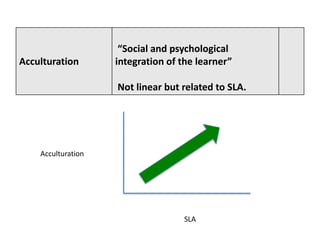
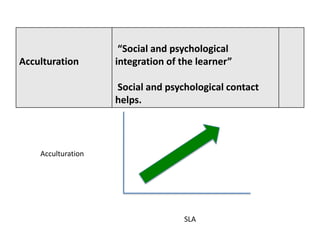
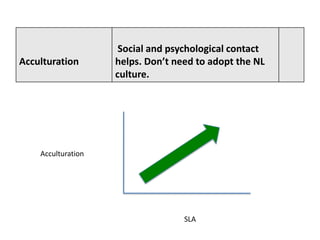
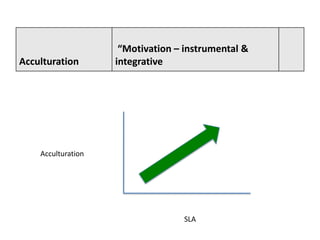
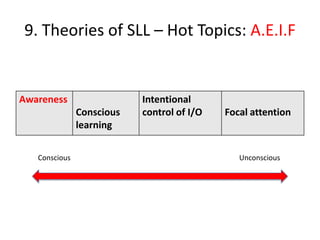
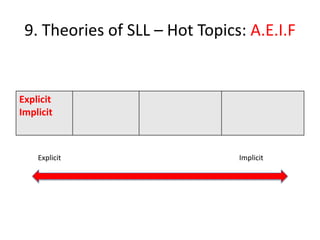
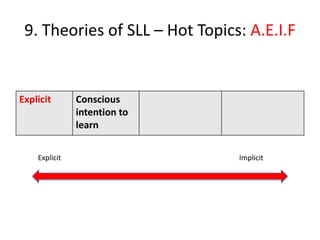
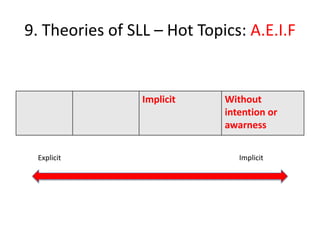
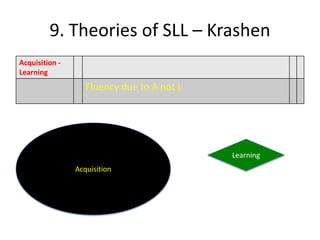
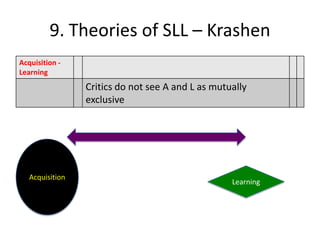
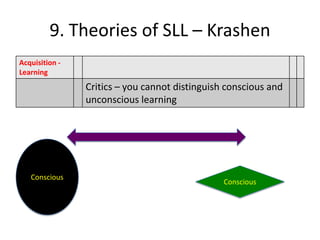
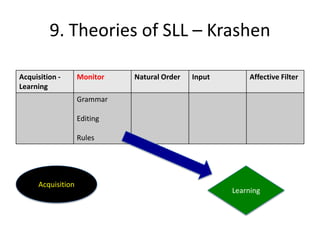
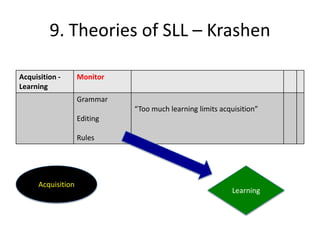
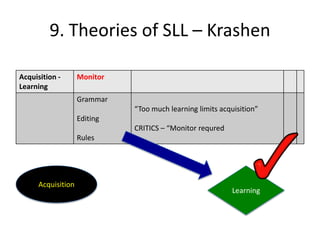
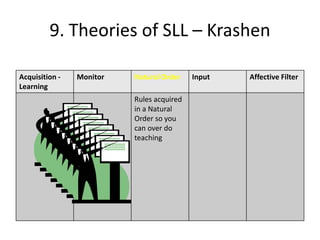
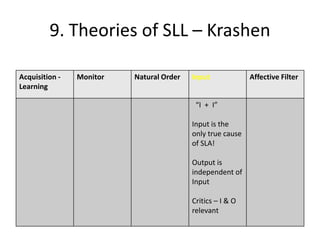
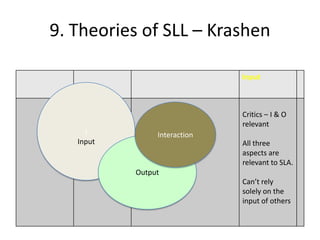
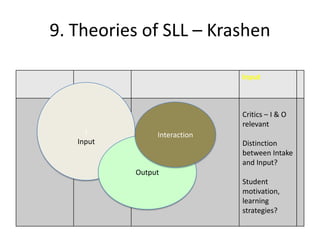
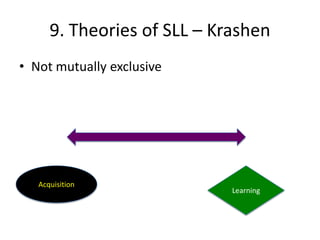
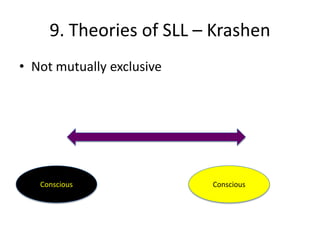
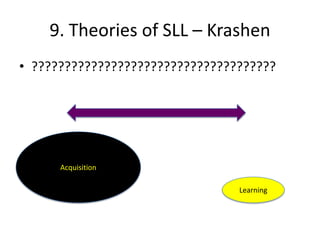
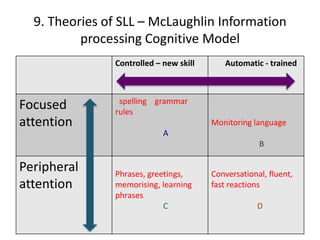
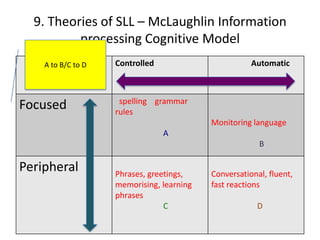
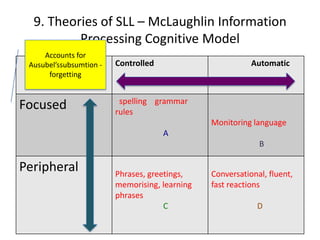
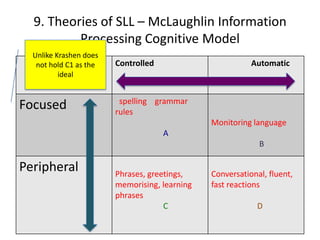
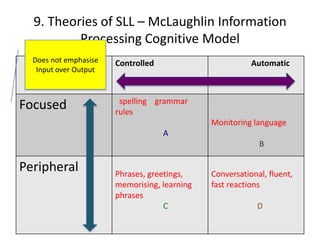
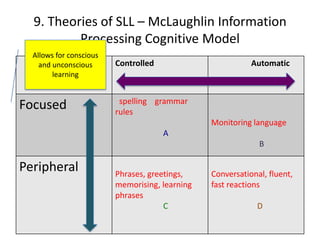
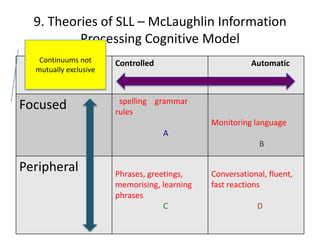
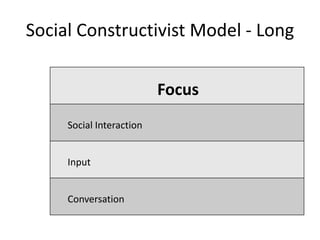
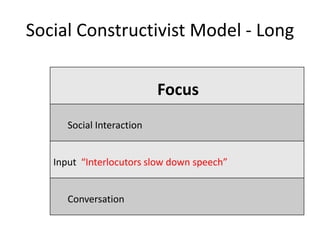
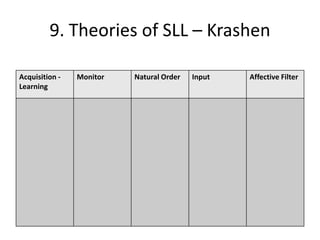
The document discusses various theories of first language acquisition including behaviorism, nativism, and functionalism. It also covers theories of second language learning and compares similarities and differences between first and second language acquisition. Various language teaching methods are outlined such as Total Physical Response, The Natural Approach, the Audiolingual Method, and Community Language Learning. Factors involved in the learning process from cognitive, metacognitive, and socio-affective perspectives are also summarized.