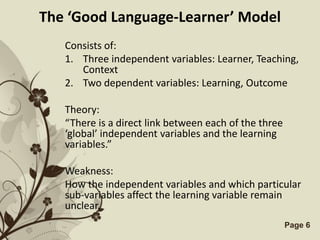
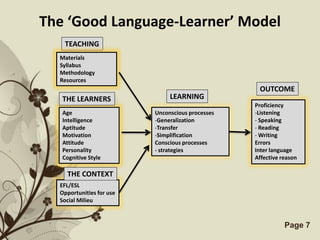
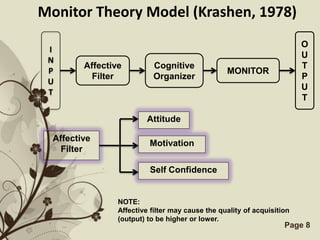
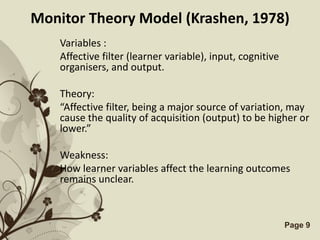
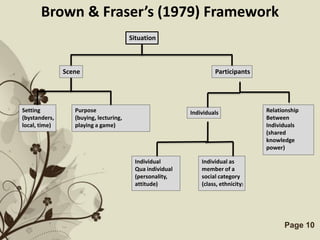
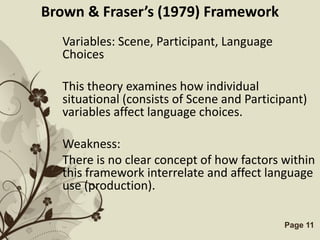
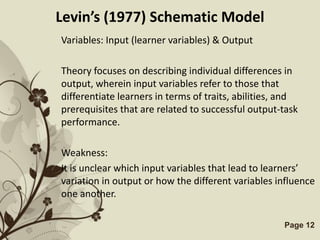
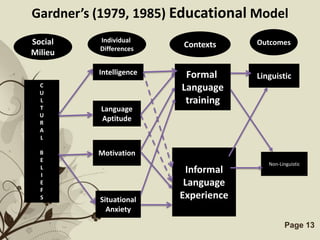
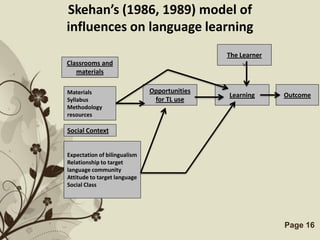
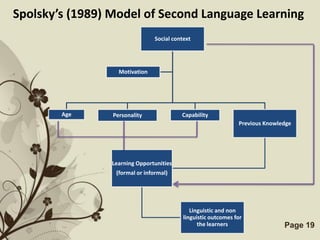
The document discusses several models that examine the relationship between individual differences and language learning. It summarizes models that view individual variables as independent factors affecting learning outcomes, as well as models that see the variables as interdependent. The models covered include the Good Language Learner model, Monitor Theory model, Brown and Fraser's framework, Levin's schematic model, Gardner's educational model, Skehan's model of influences, and Spolsky's model of second language learning. The document also lists several individual difference factors that may affect Computer-Assisted Language Learning outcomes.