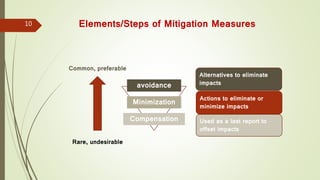
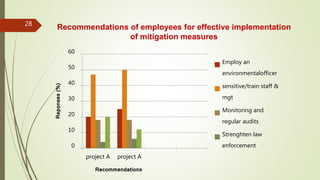
The presentation discusses environmental protection measures, focusing on mitigation strategies to manage environmental impacts across various projects. It outlines objectives for mitigation, types of measures, and implementation strategies, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices in infrastructure development. Case examples highlight the importance of careful decision-making regarding airport expansions and the agricultural sector in Nepal, weighing economic and environmental costs.