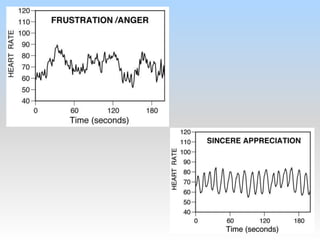
The document discusses effective communication in the workplace, focusing on the impact of emotions and common negative feelings such as anger, guilt, fear, jealousy, and apathy. It provides strategies for managing and embracing these emotions through a structured approach known as 'TEARS of HOPE,' which involves teaching, expressing, accepting, re-appraising, and seeking social support. Overall, the workshop aims to enhance emotional intelligence and promote positive interactions in professional settings.