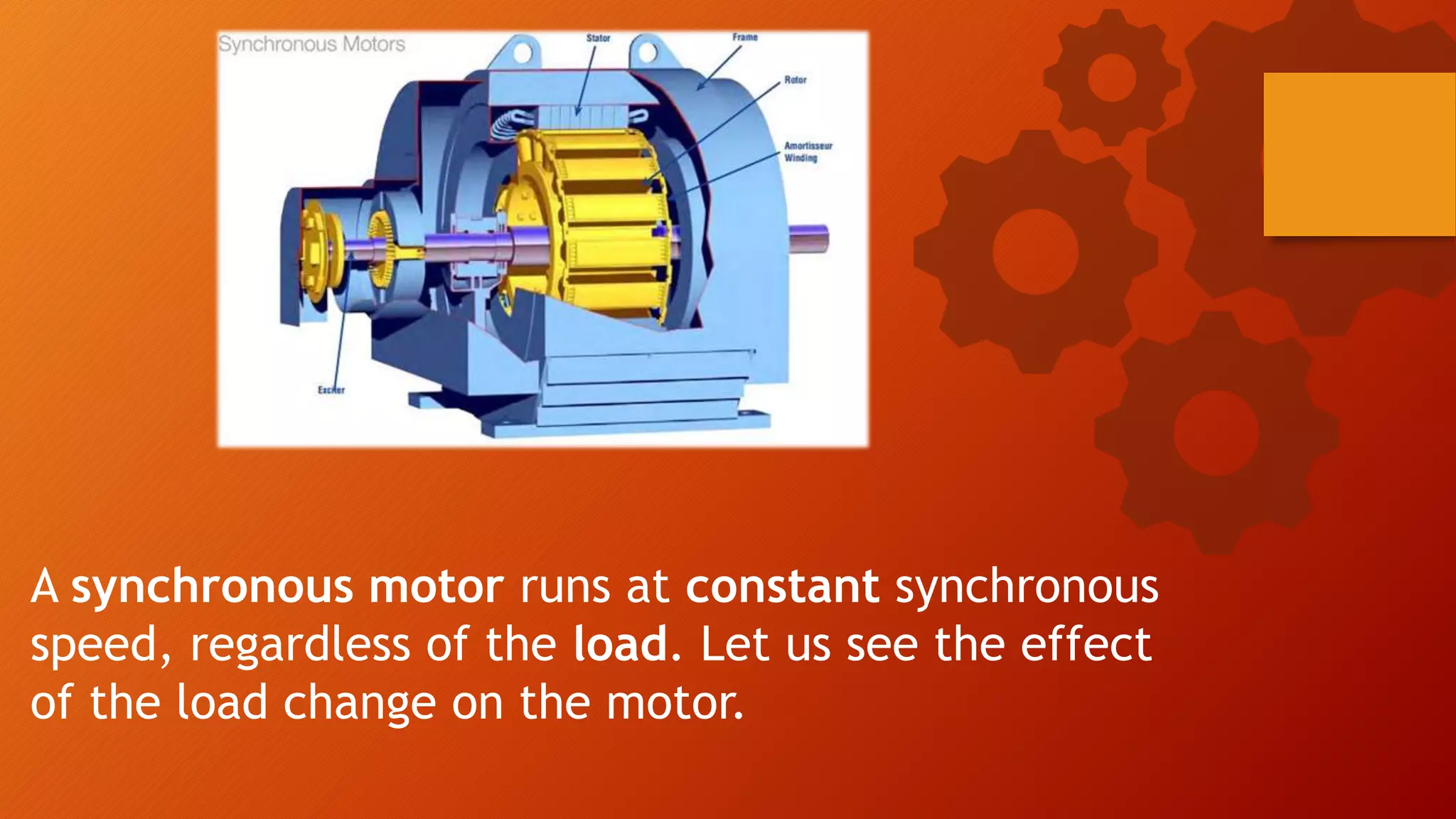
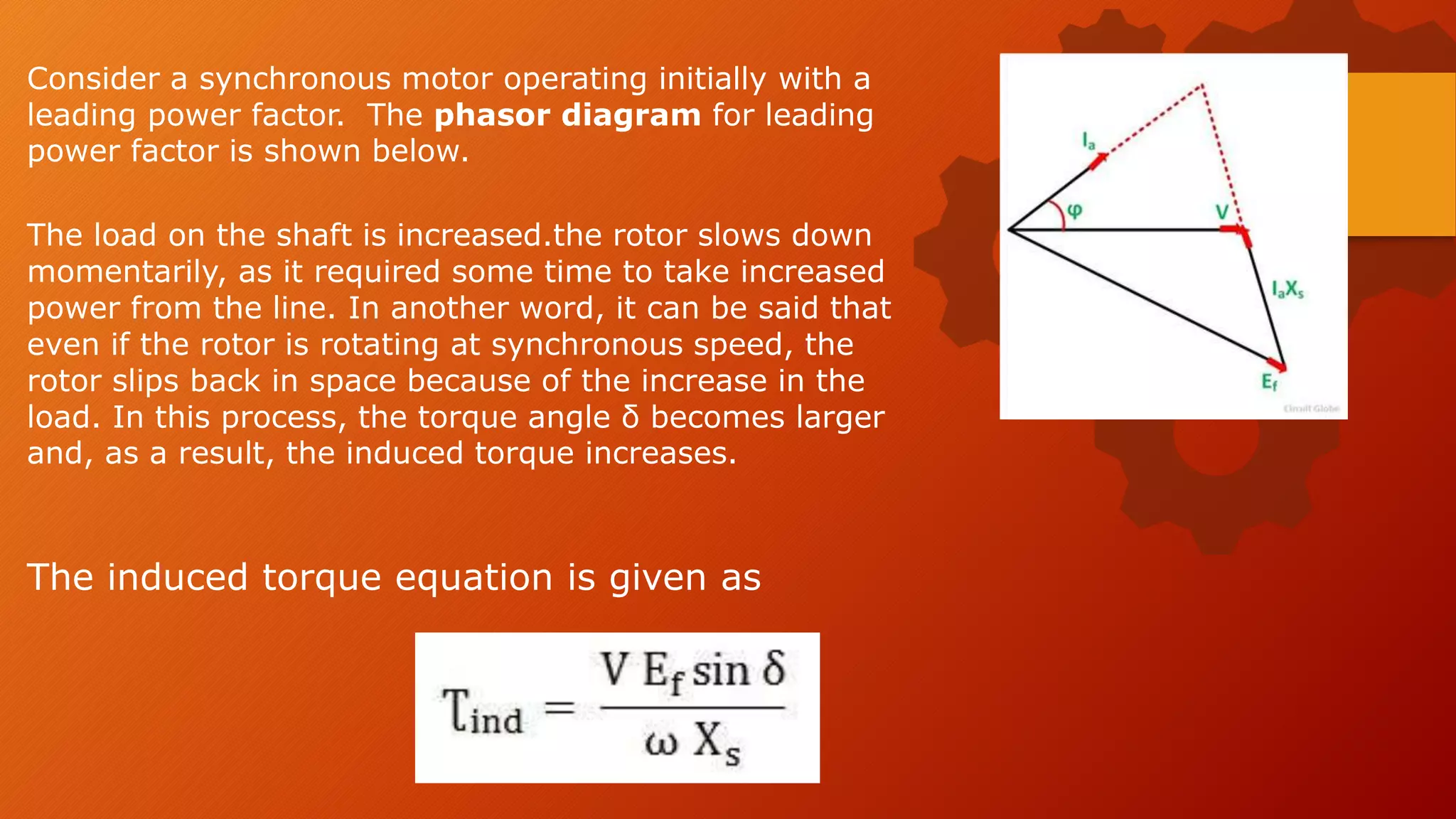
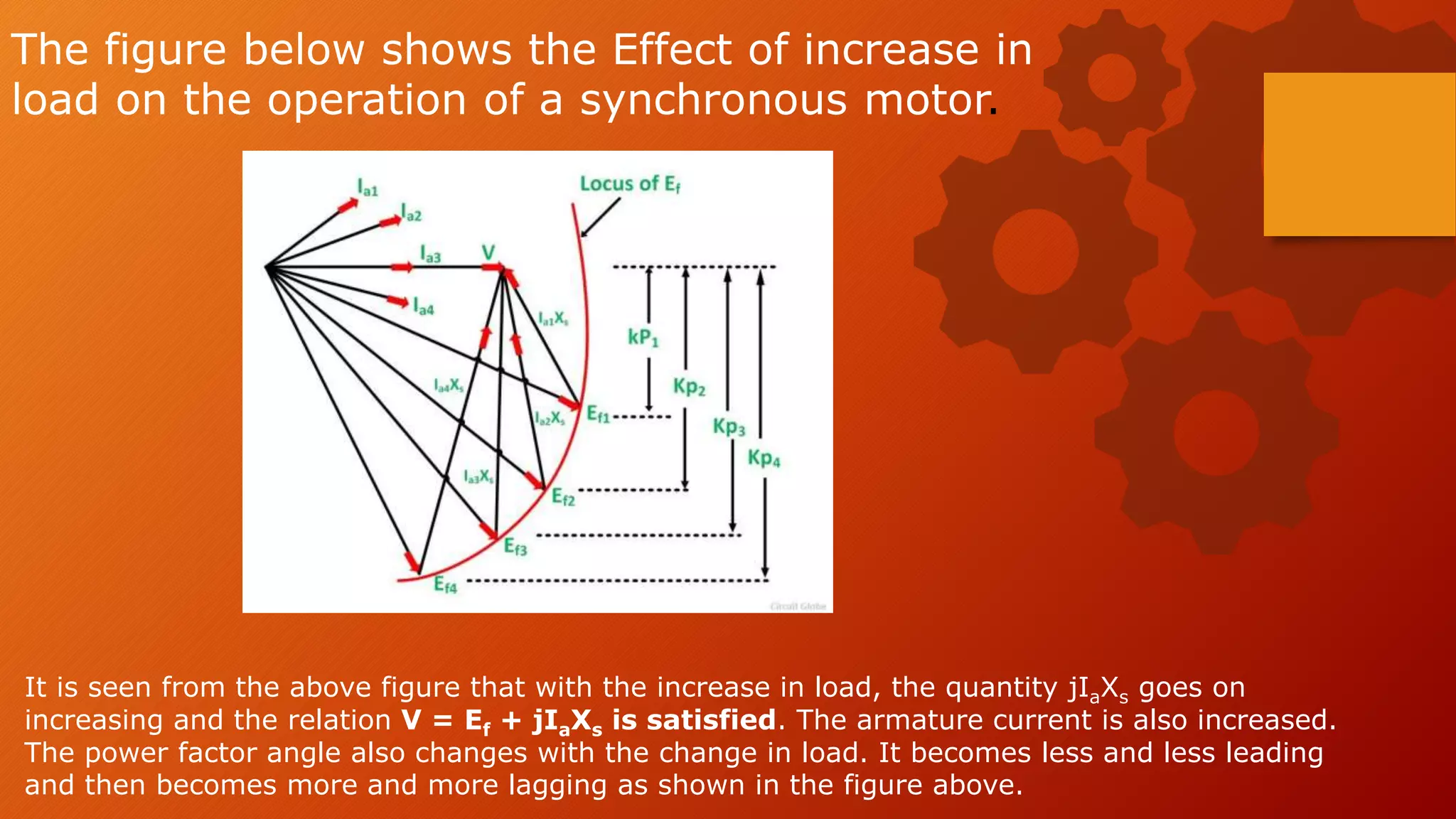
When the load on a synchronous motor is increased:
1. The motor continues to run at synchronous speed.
2. The torque angle increases to develop more torque to handle the increased load.
3. The armature current drawn from the supply increases to provide the additional torque while the excitation voltage remains constant.