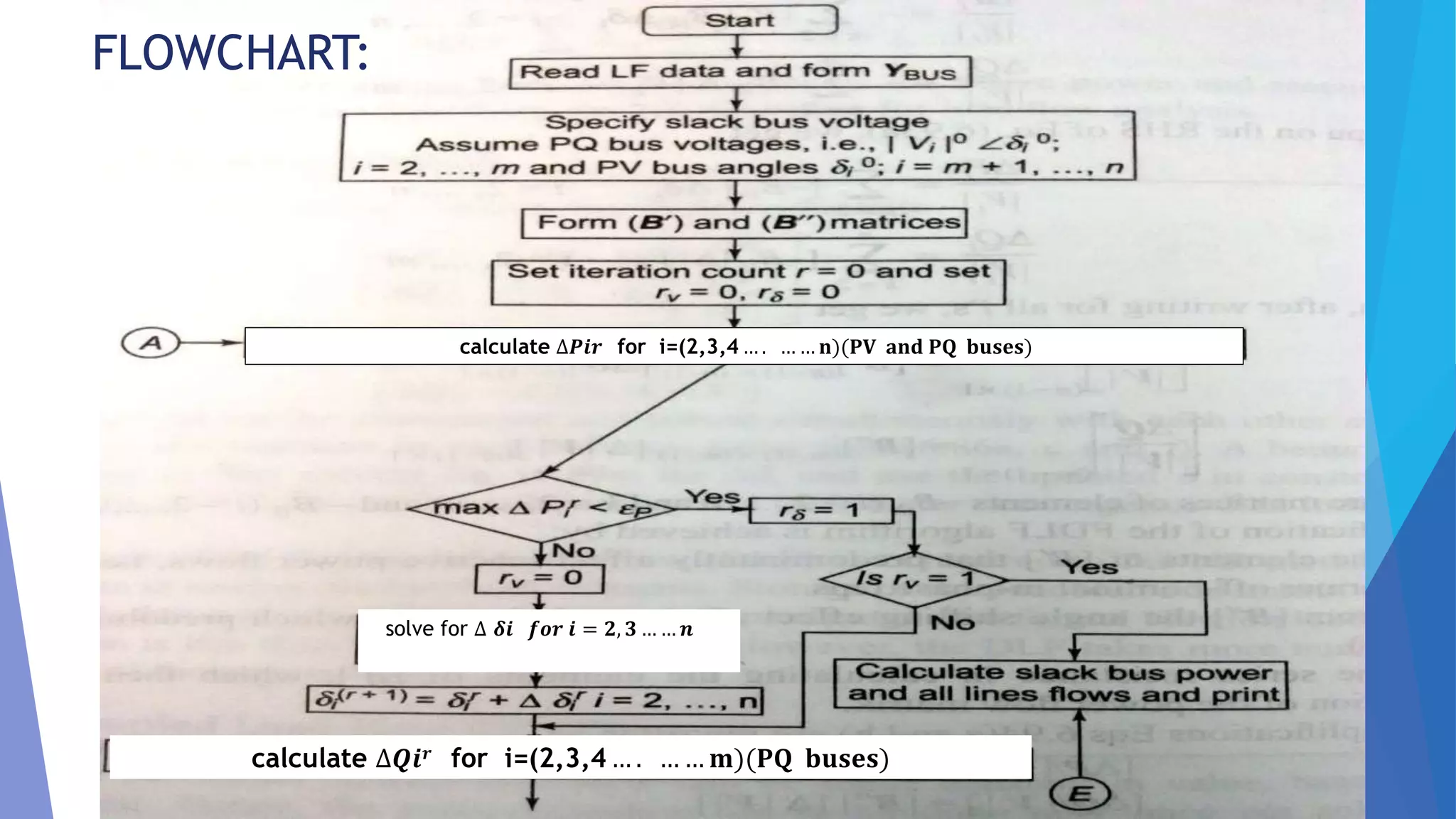
The document discusses the Fast Decoupled Load Flow (FDLF) method for solving load flow problems. FDLF is based on the Newton-Raphson method but further simplifies the load flow equations by assuming that active power changes are more sensitive to voltage angle changes and reactive power changes are more sensitive to voltage magnitude changes. This allows the Jacobian matrix to be separated into two square submatrices related to voltage angle and magnitude. FDLF requires fewer iterations than Newton-Raphson, has higher reliability, and is faster and uses less storage. The method is physically justifiable and can be used in optimization studies involving multiple load flow solutions.