Embed presentation








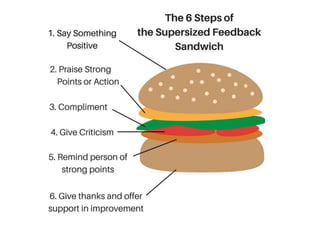

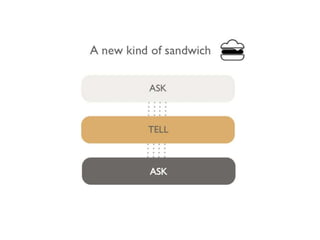
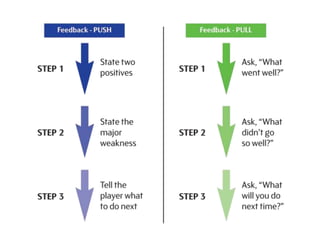
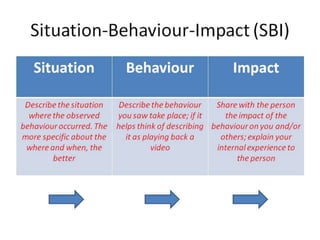
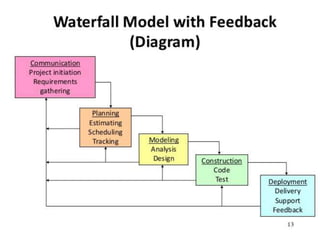

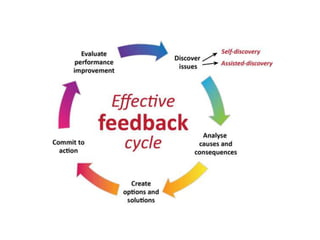
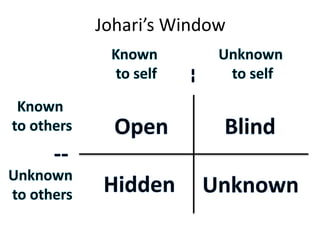
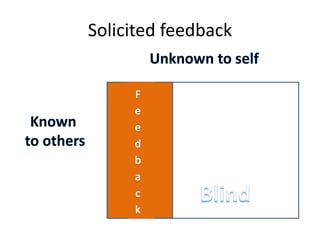
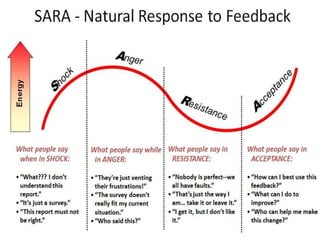
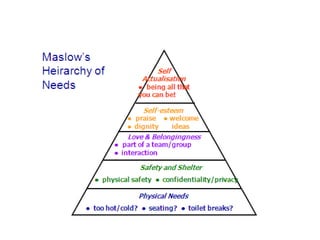



The document discusses feedback and how to give and receive it effectively. It defines feedback as information about a system's output that is used to modify future outputs. Feedback should (1) identify strengths and weaknesses, (2) focus on continuous quality improvement, and (3) be given privately as soon as possible on 2-3 key areas. When receiving feedback, one should listen carefully, assume a constructive intent, pause before responding, ask questions, and express thanks. Effective feedback uses criteria-based phrases, focuses on no more than two traits, and allows the recipient to apply the feedback in revised work.






















