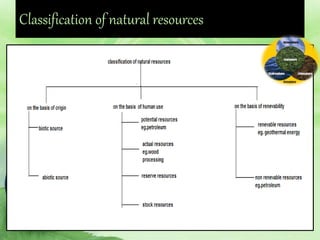
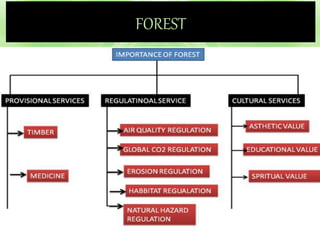
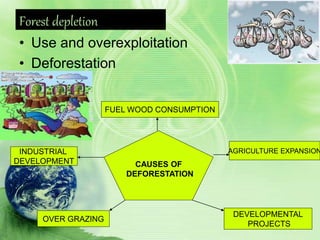
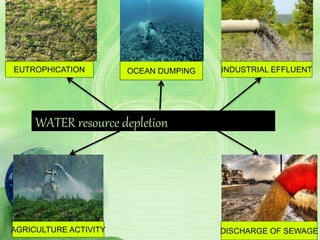
Natural resources include materials from the environment that are valuable to humans such as forests, water, and minerals. Humans use natural resources through either consumptive use, which reduces the available supply, or non-consumptive use, which does not. Overuse and mismanagement of natural resources can harm the environment through deforestation, water depletion, and depletion of mineral resources. Proper management of natural resources involves legislative protections, sustainable practices, and developing alternative resources.