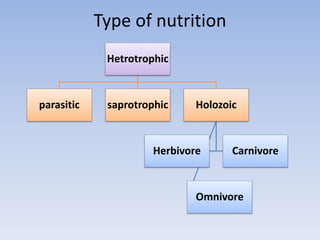
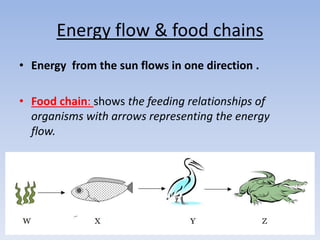
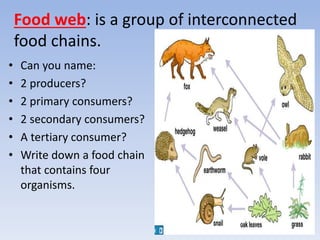
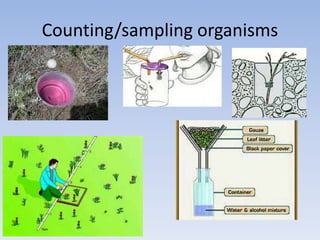
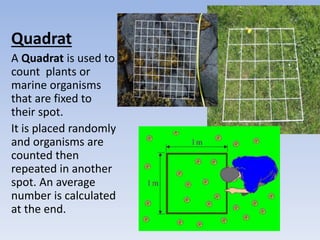
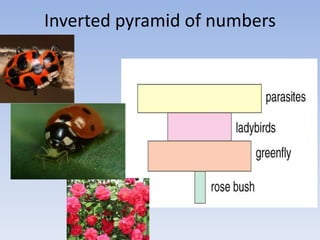
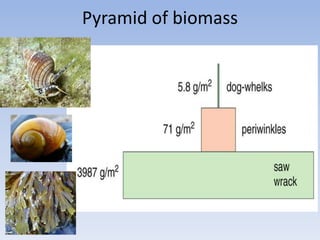
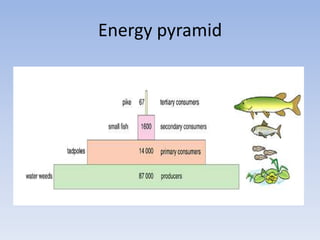
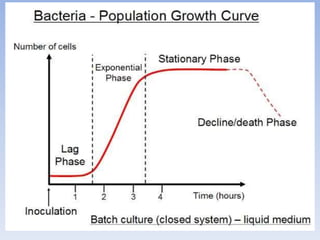
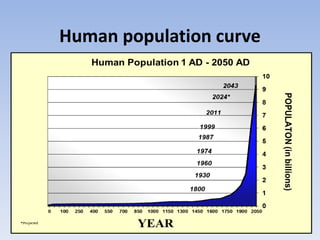
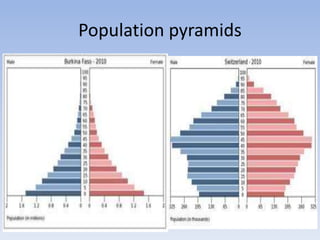
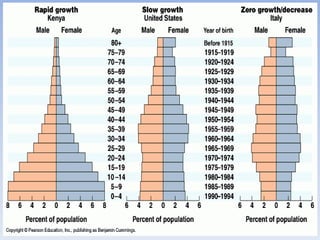
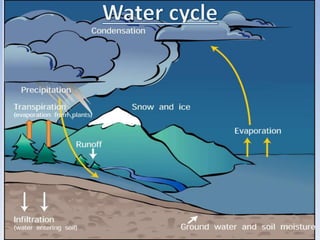
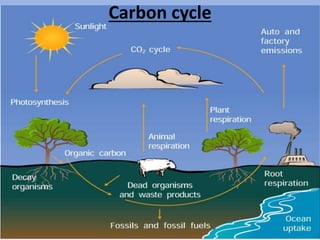
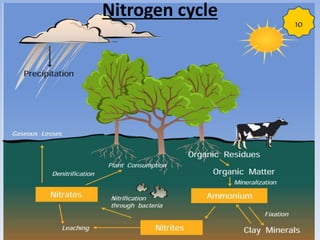
This document provides an overview of key concepts in ecology, including definitions of important terms like habitat, environment, adaptation, camouflage, mimicry, predator, prey, producer, consumer, food chain, and food web. Examples are given of adaptations like camouflage in stick insects and mimicry in Viceroy butterflies. Methods for sampling populations are described, such as using quadrats, pitfall traps, and Tullgren funnels. Diagrams illustrate population pyramids, energy pyramids, population curves, and factors affecting population size. The carbon and nitrogen cycles are also summarized.