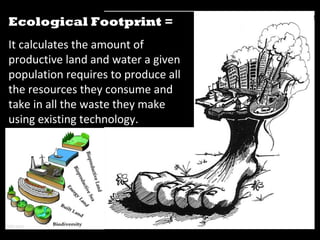
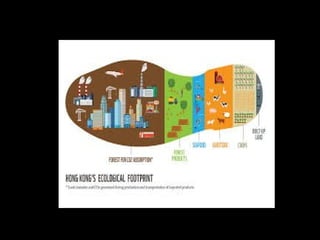
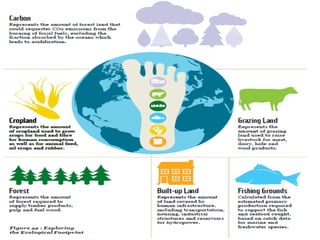
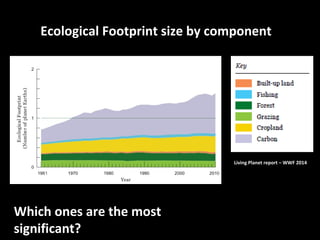
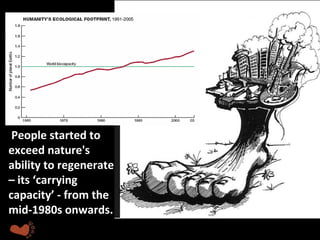
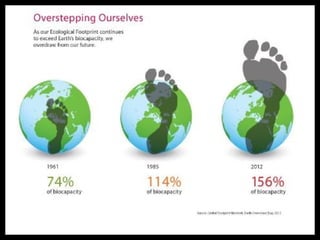
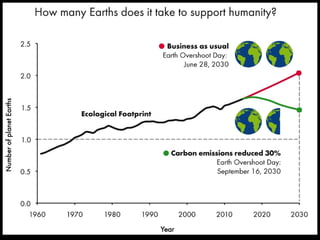
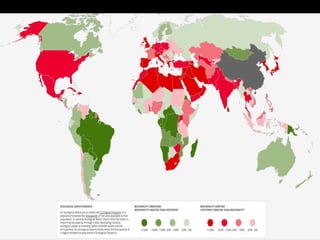
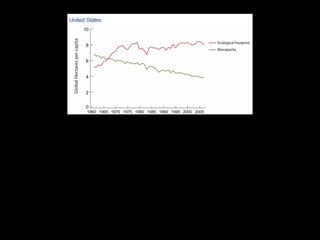
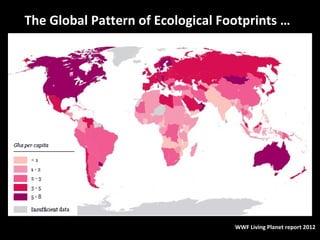
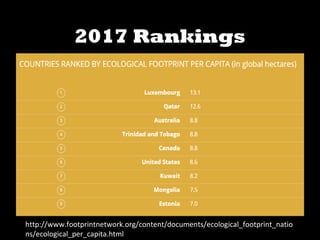
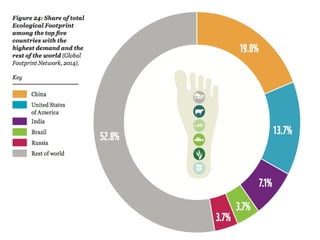
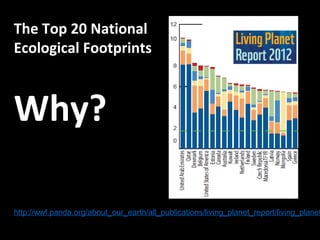
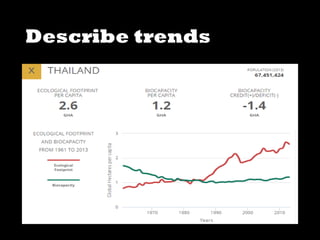
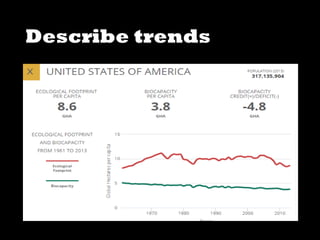
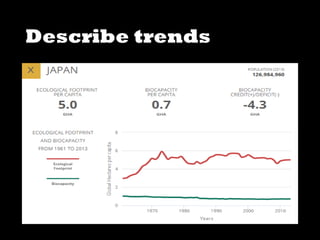
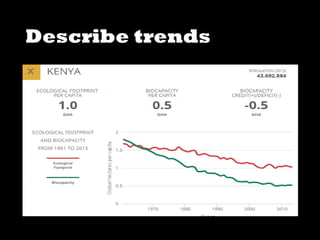
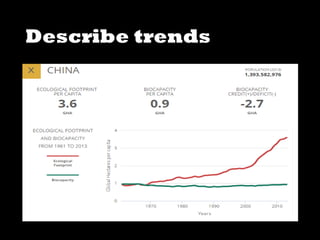
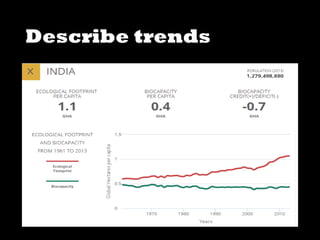
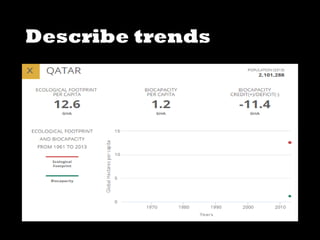
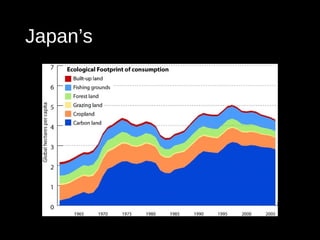
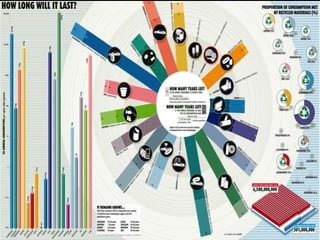
This document discusses ecological footprints and how to measure them. An ecological footprint calculates the amount of productive land and water required to support a population based on its consumption and waste production using current technology. The document notes that global footprints exceeded the Earth's carrying capacity in the mid-1980s. It provides ecological footprint sizes for various countries, with the highest footprints belonging to Qatar, the USA, and Australia.