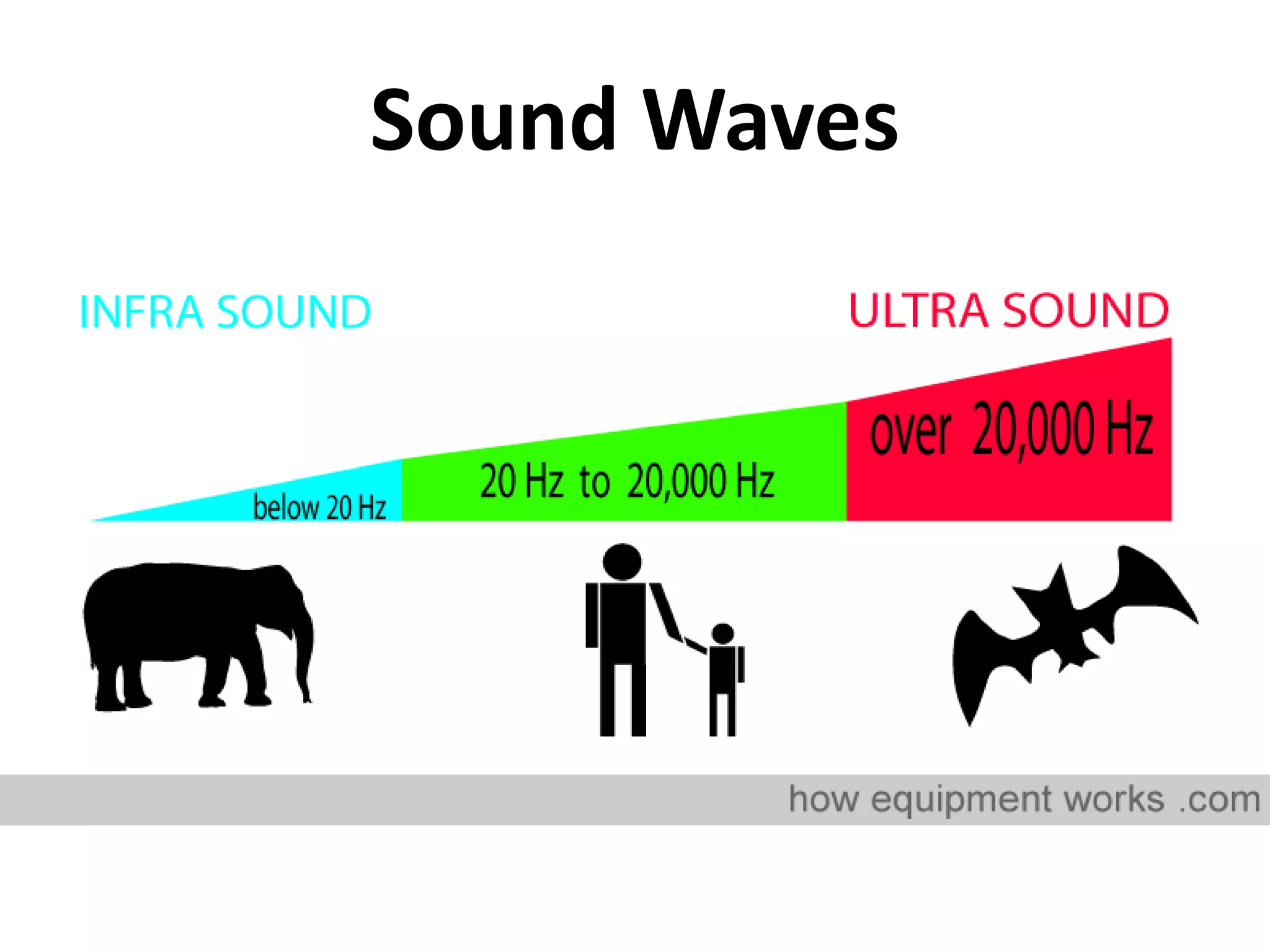
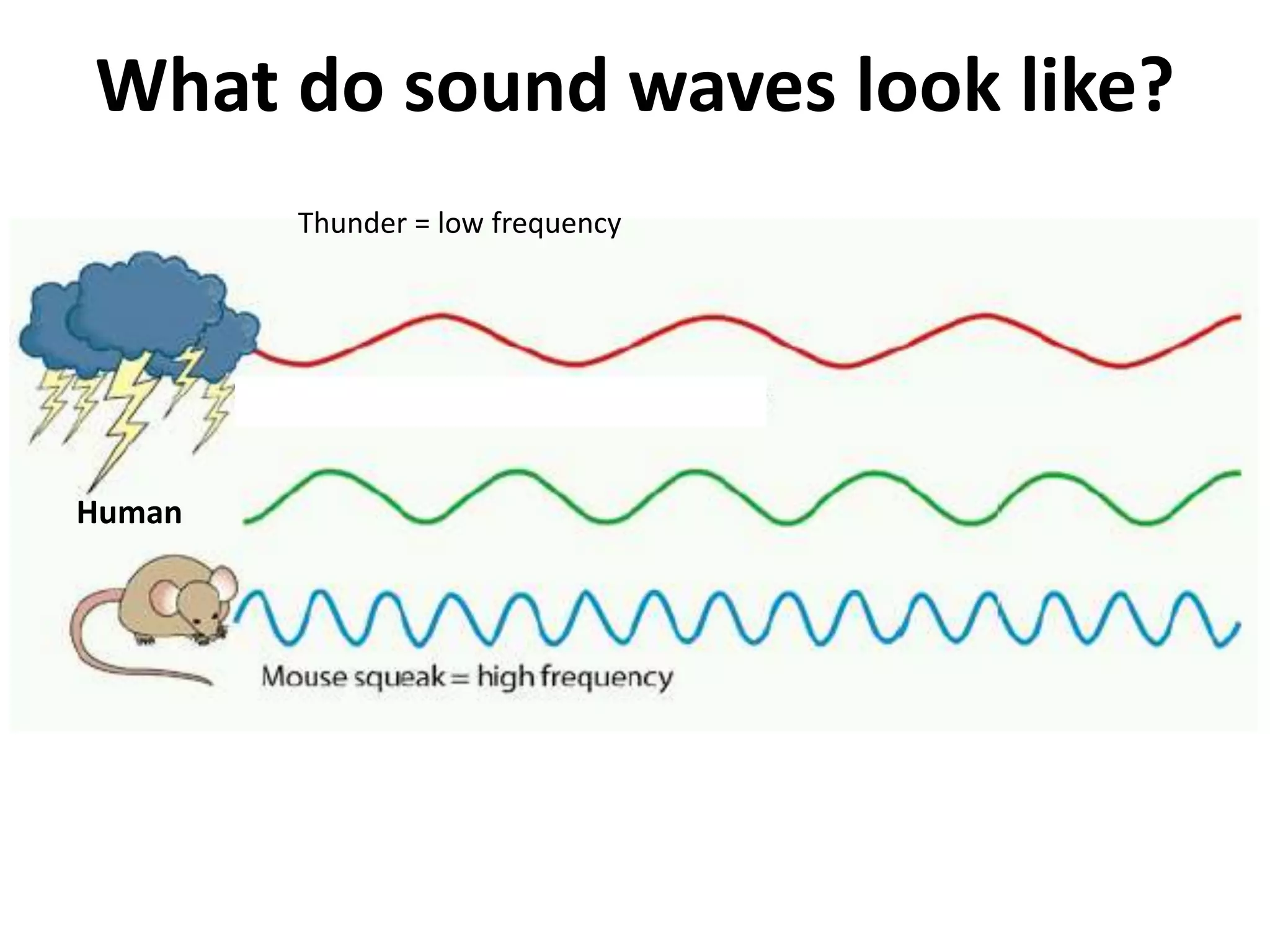
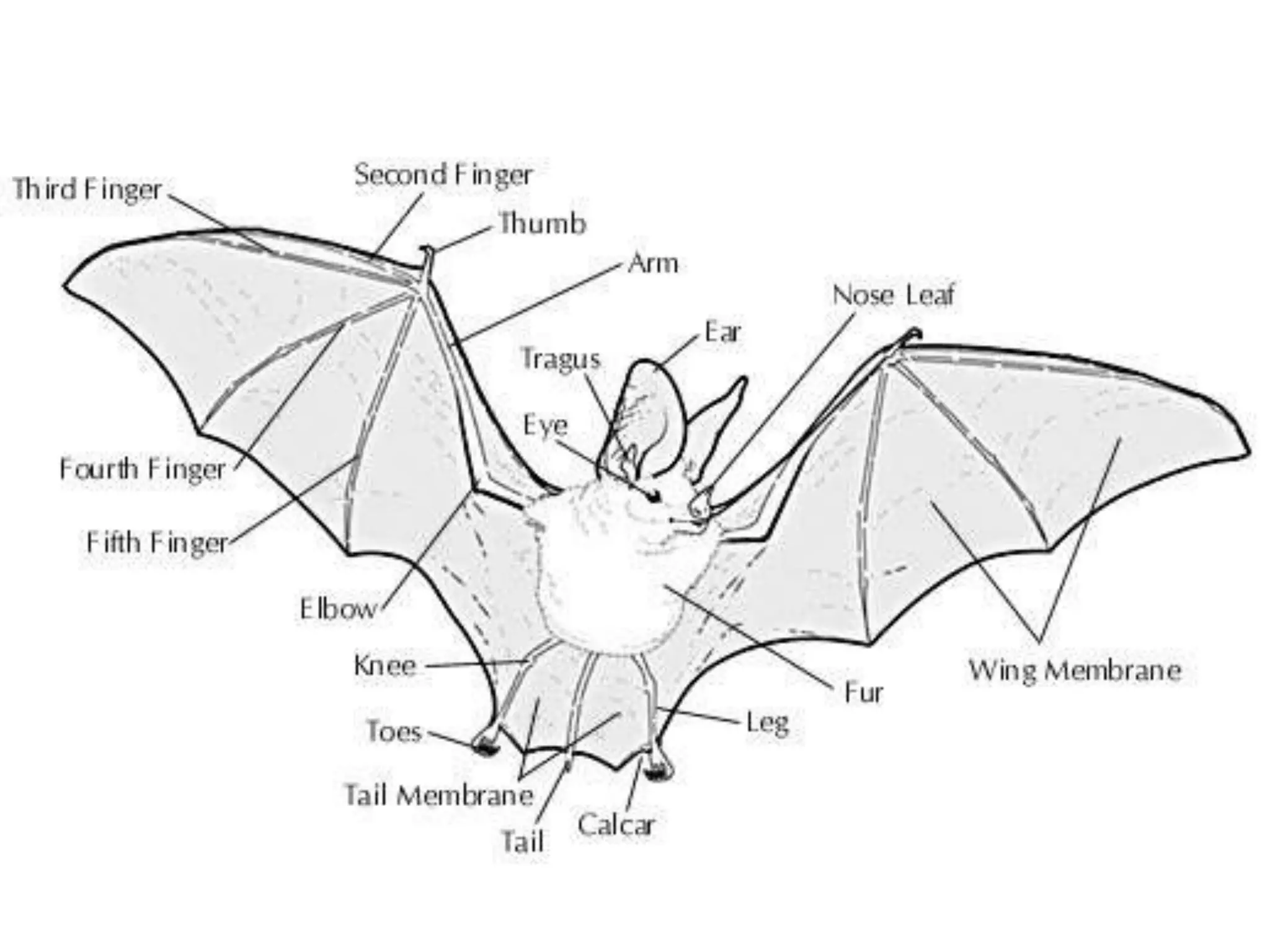
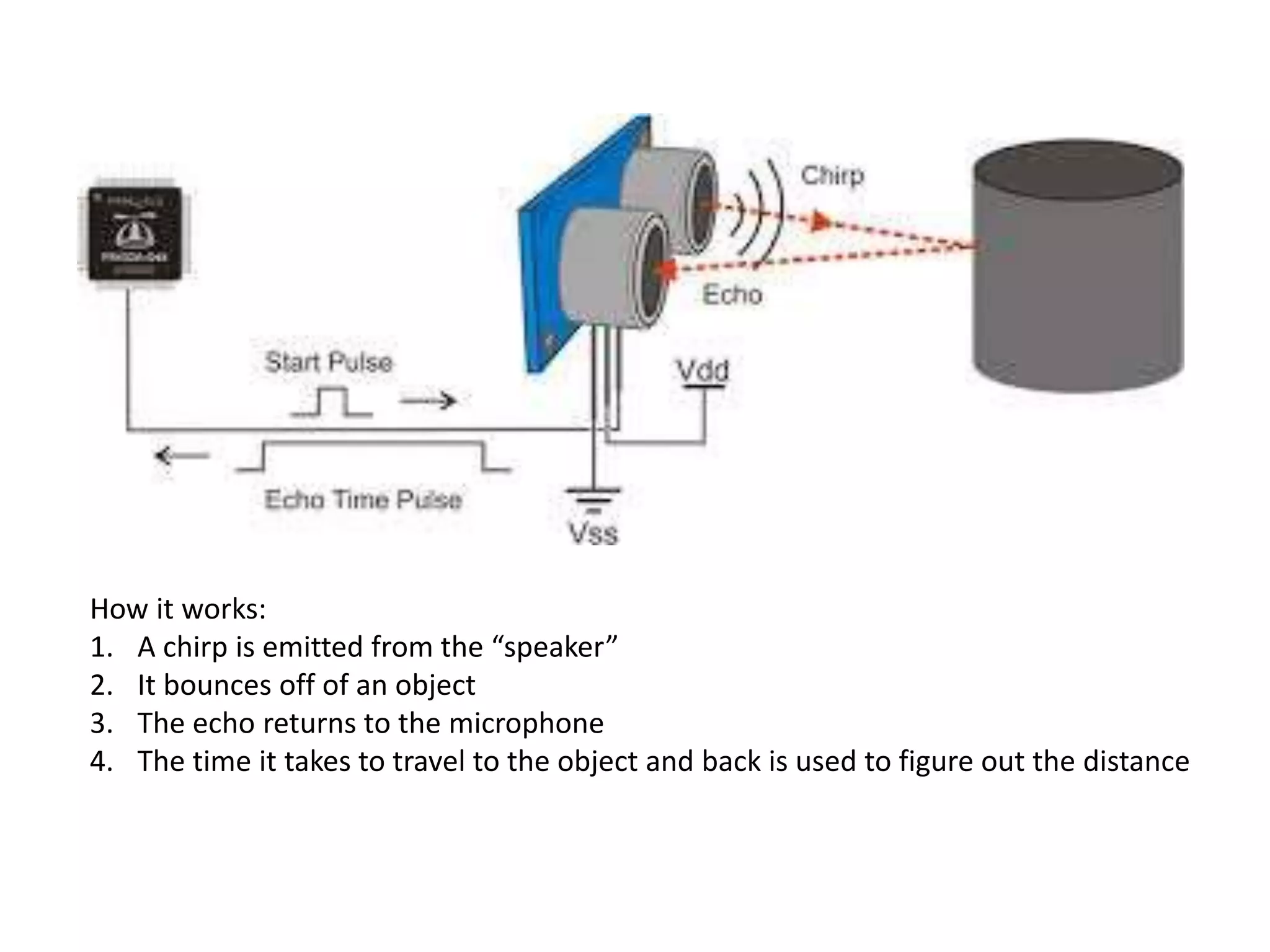
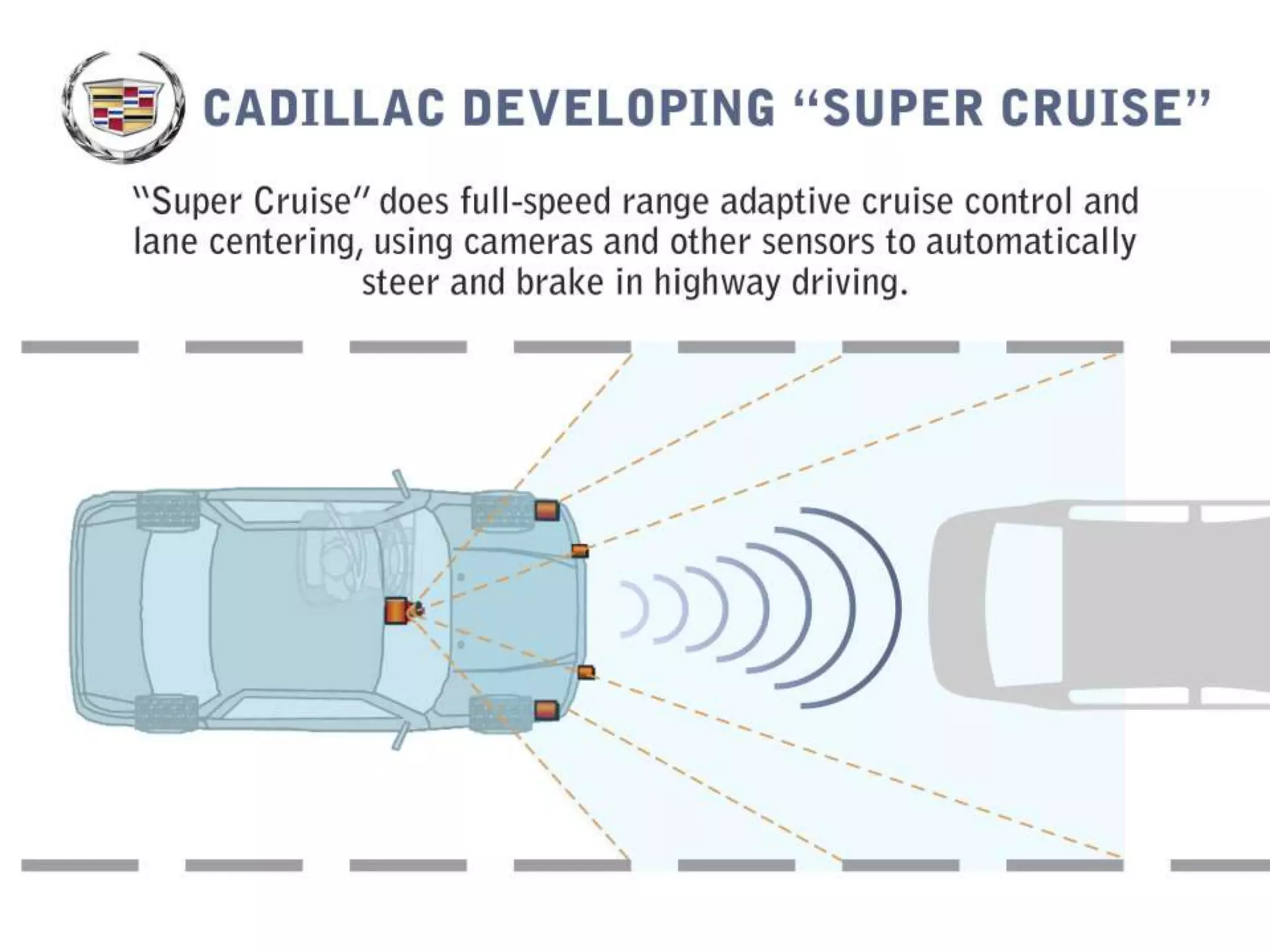
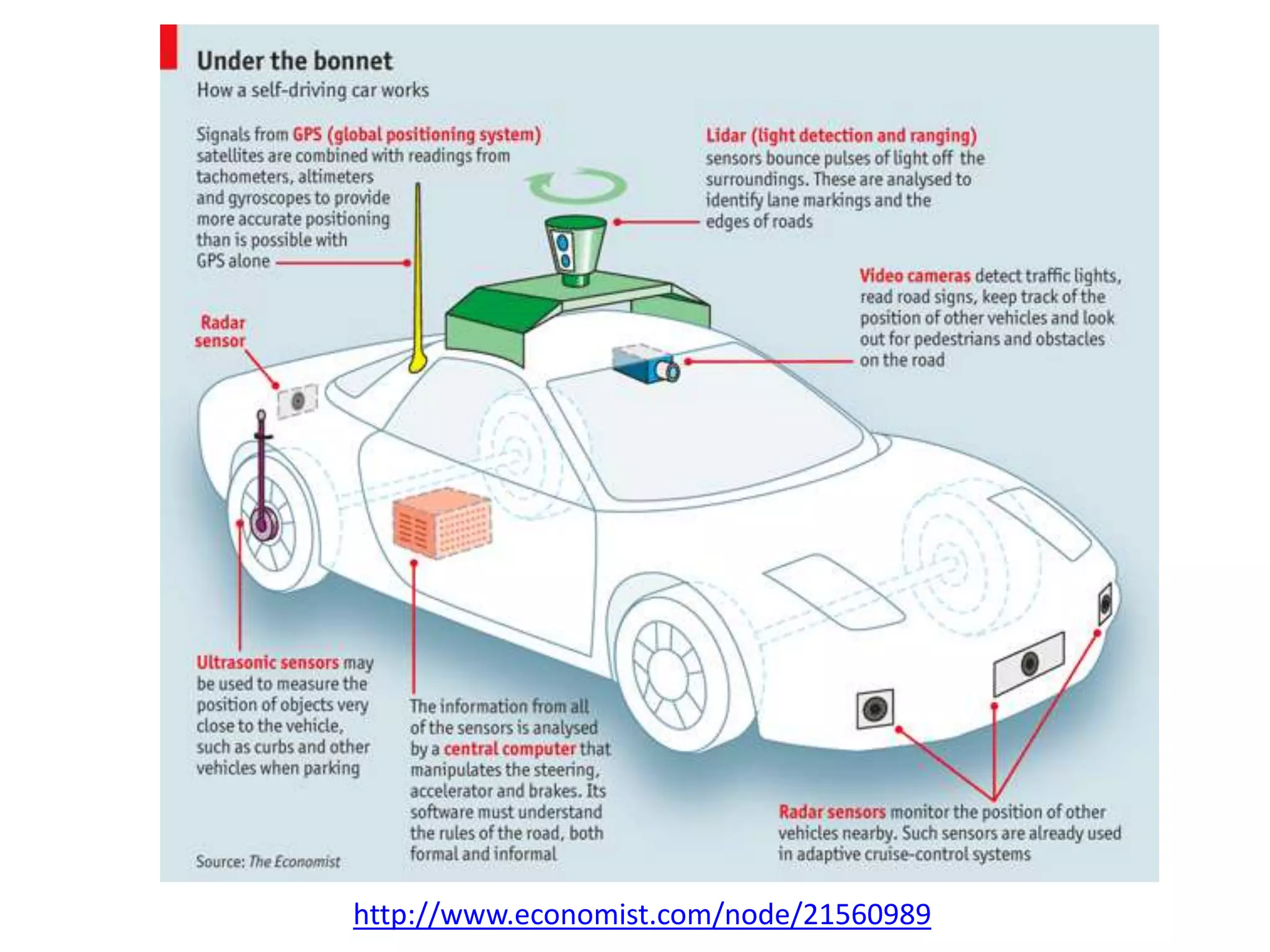
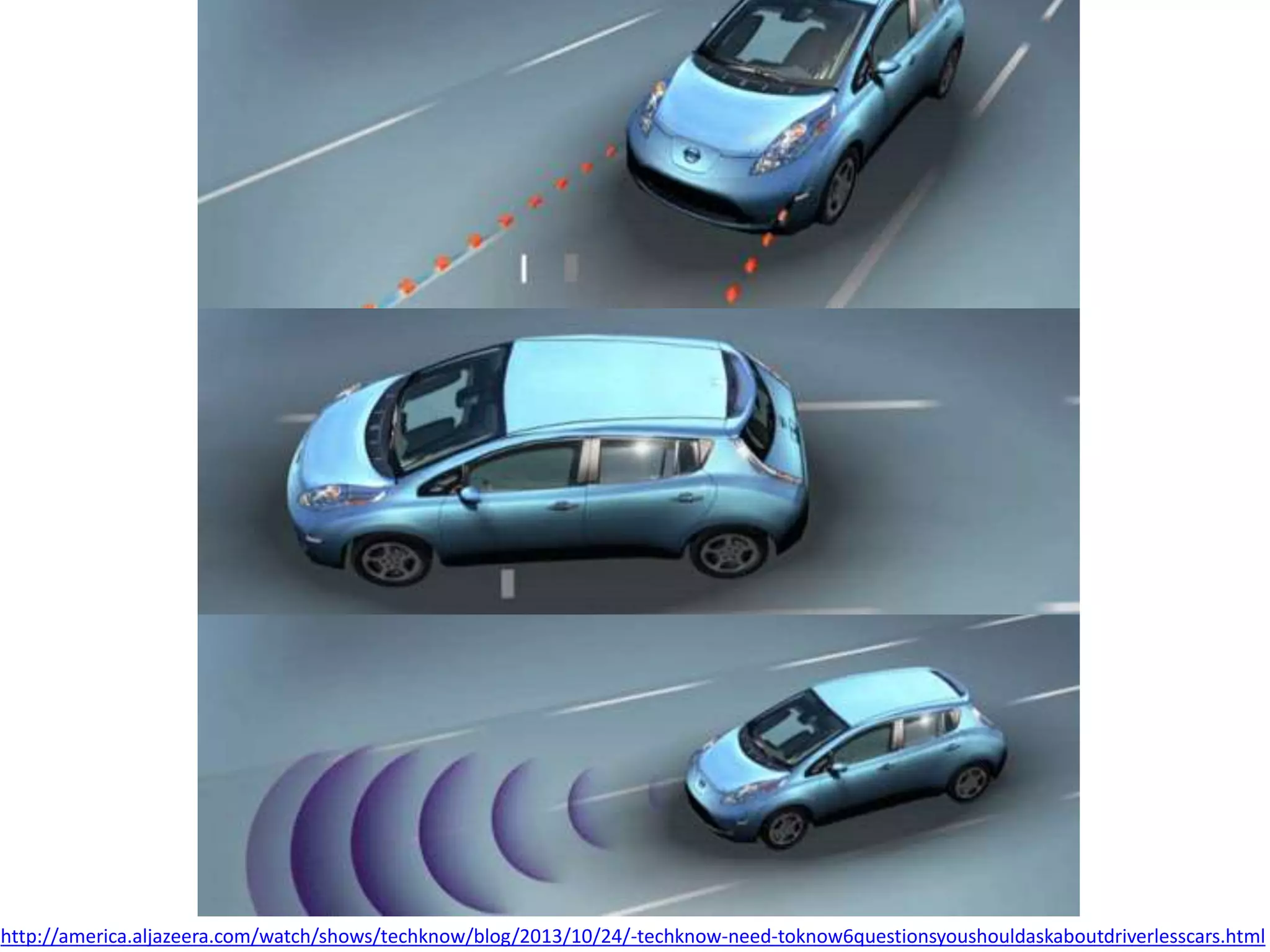
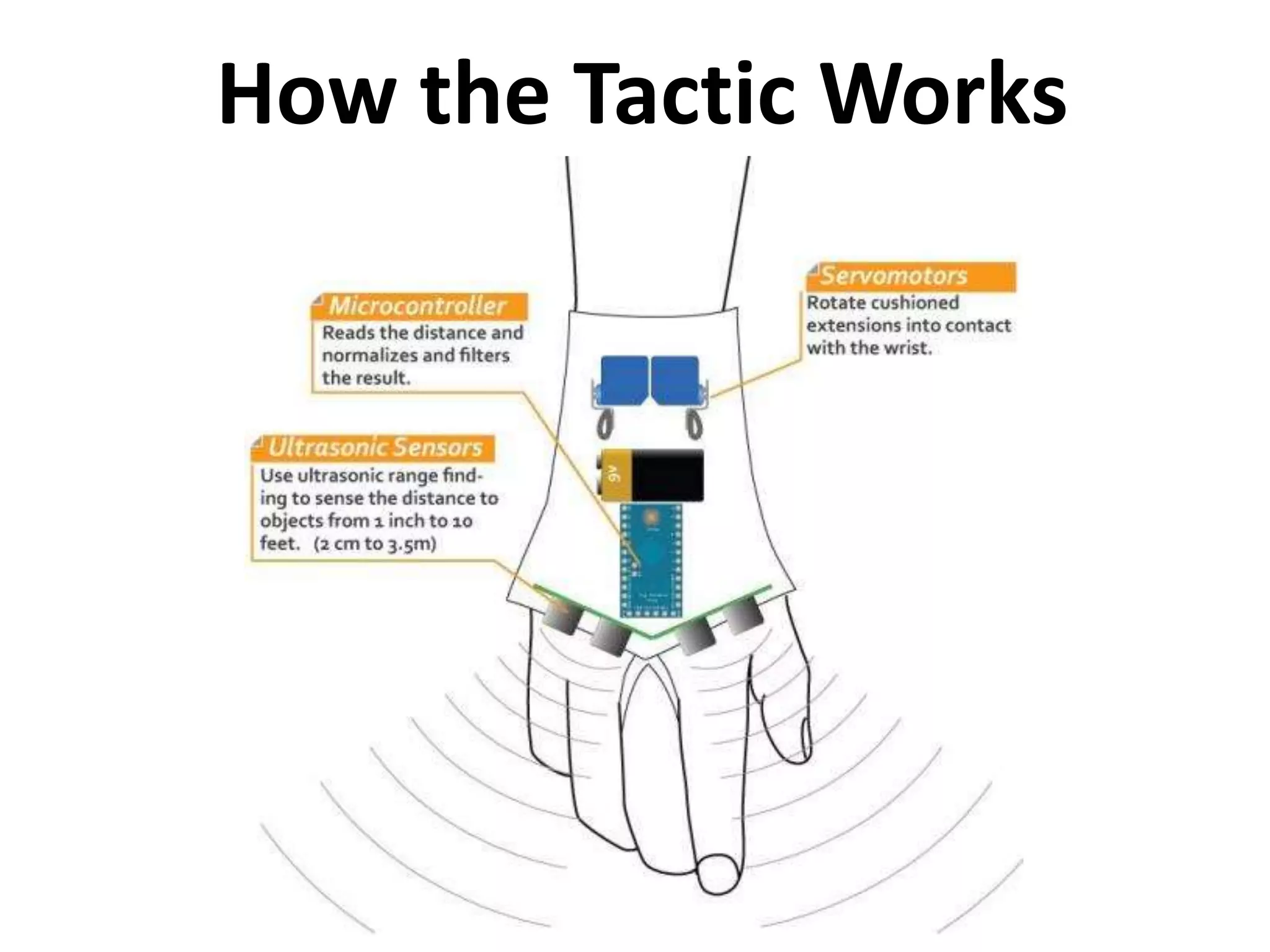
The document discusses how echolocation and ultrasound are used by various animals and humans. It explains that bats, dolphins, and some insects use echolocation to locate objects by emitting sounds and interpreting the echoes. Applications of these principles by humans are also summarized, including using ultrasound for robotics, driverless cars that rely on sensors like radar and sonar, and assistive devices for the blind such as one that converts distance readings to pressure on the wrist. The story of Ben Underwood, who learned to use echolocation to navigate as a blind person, is also briefly described.