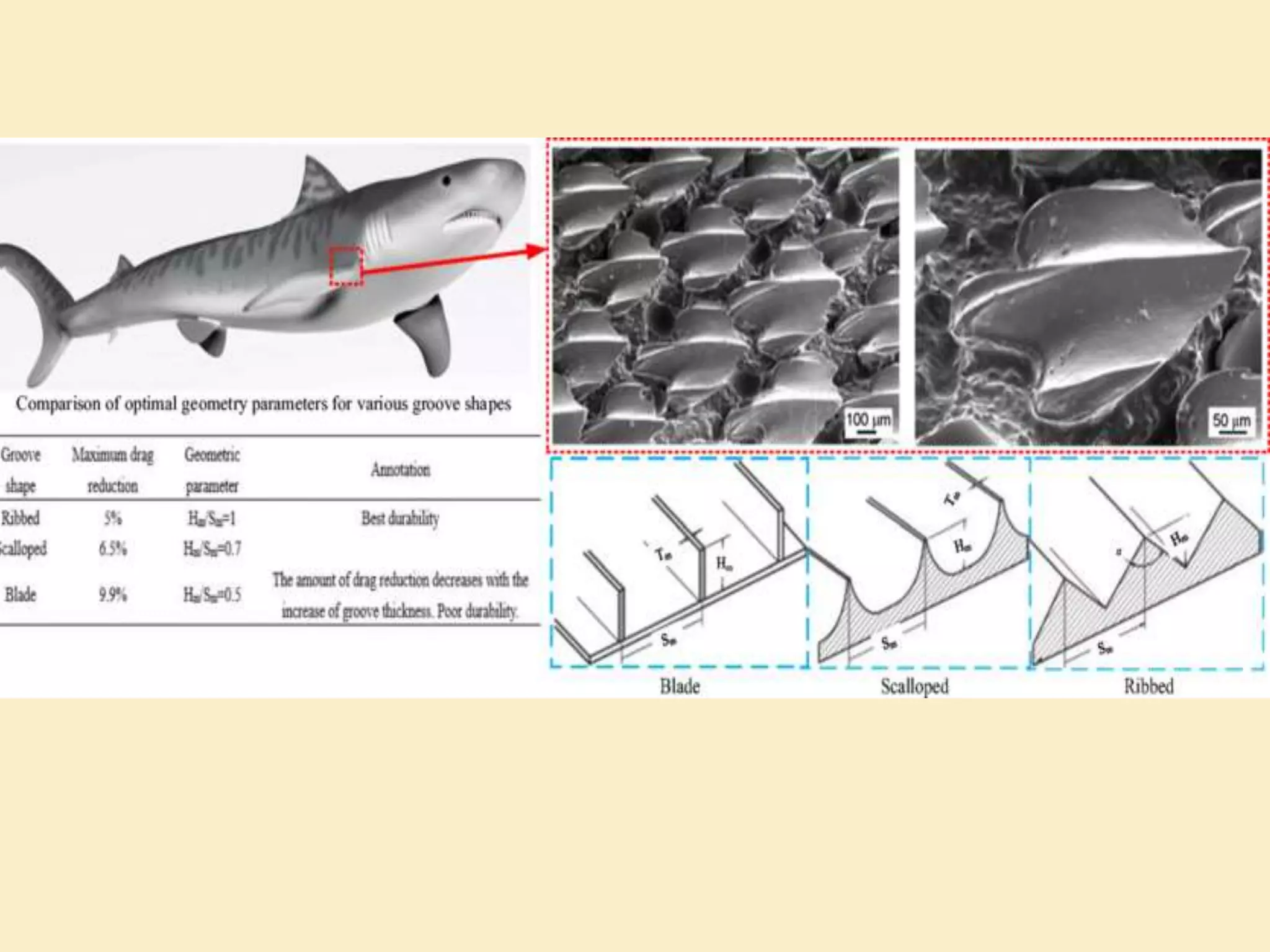
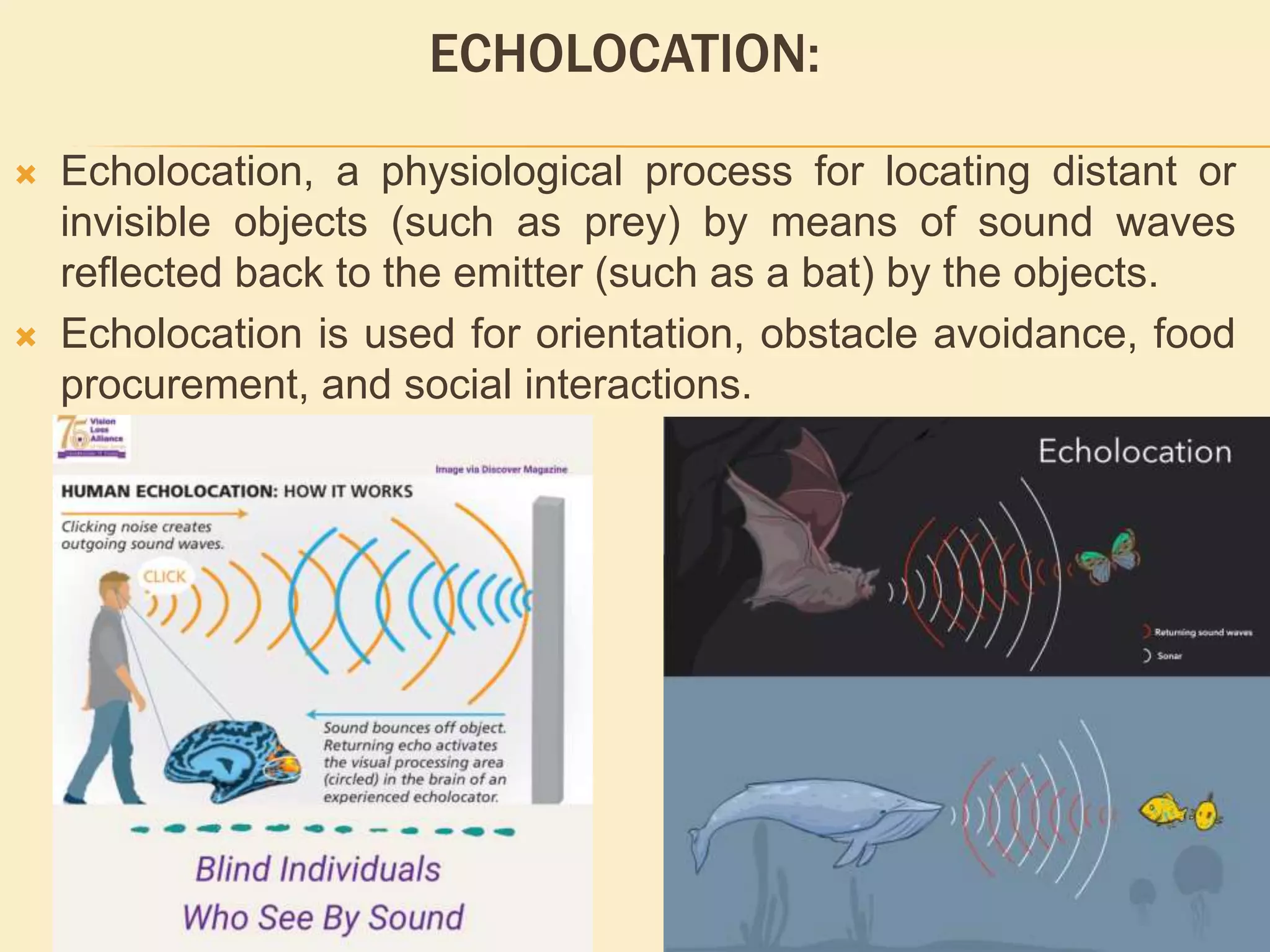
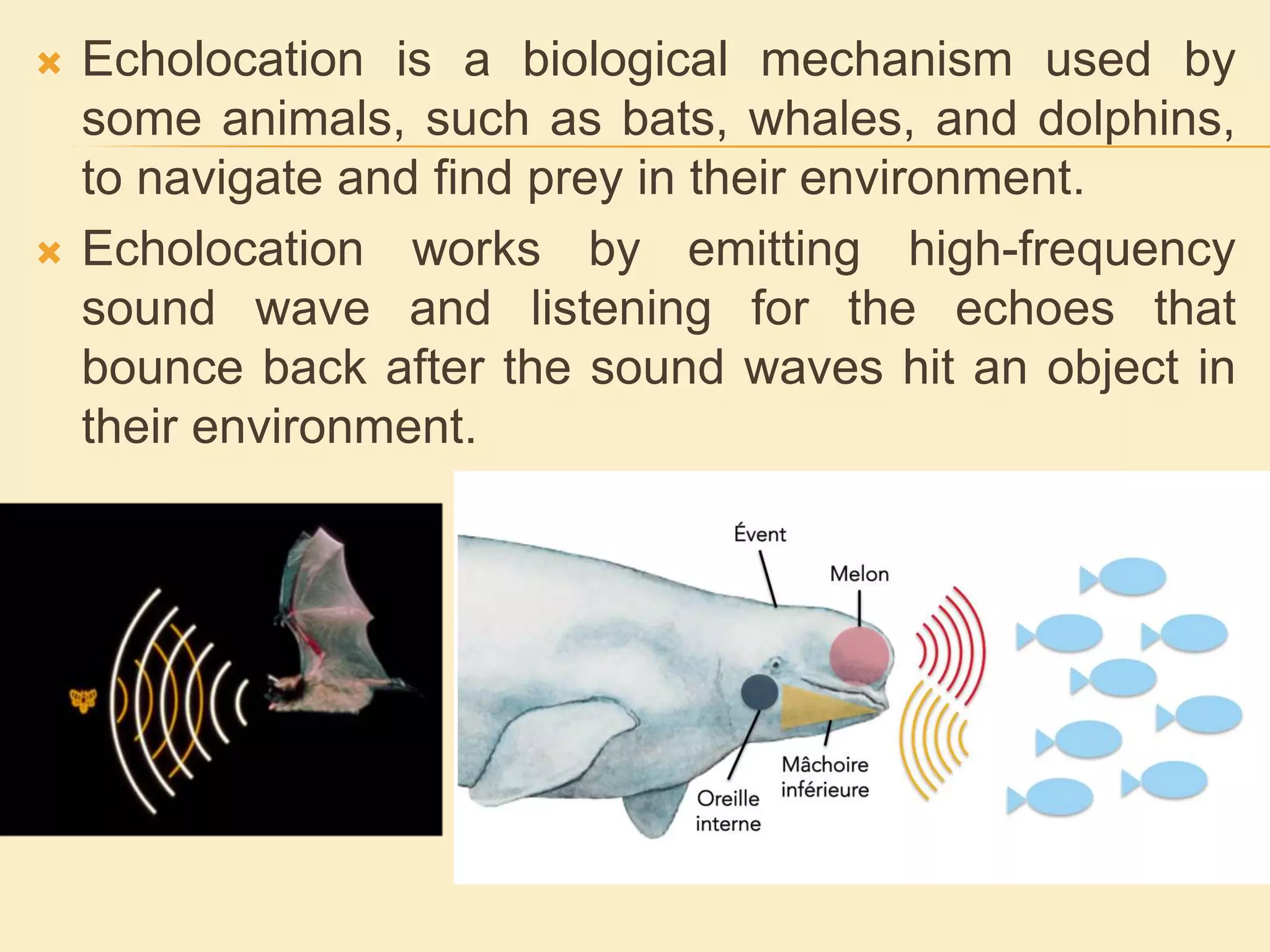
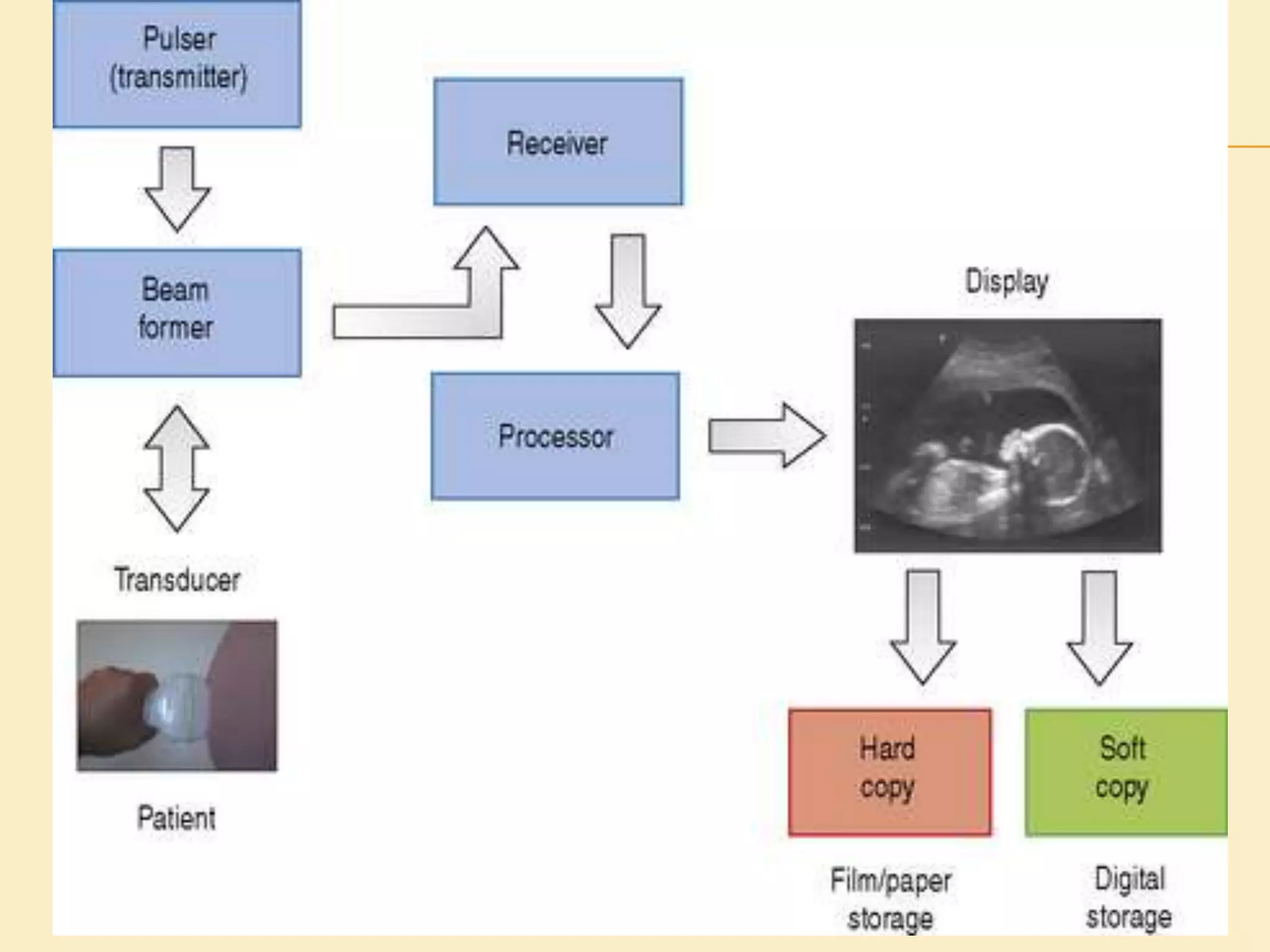
Ultrasonography uses the biological mechanism of echolocation to produce medical images. It works by emitting high-frequency sound waves from a transducer and receiving the echoes produced when the waves bounce off internal organs and tissues. The echoes are converted into real-time images that are displayed to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions in a non-invasive manner, such as monitoring fetal development or detecting tumors. The principles of ultrasonography are based on how sound waves travel through different body tissues and analyzing the echoes received.