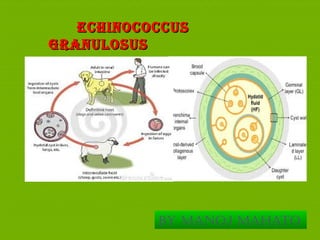
Echinococcus granulosus is a tapeworm that causes hydatid cysts in humans. It is most common in temperate sheep-raising areas like South America, East Africa, and central Russia. The highest prevalence is seen in Kenya. Humans typically become infected by ingesting E. granulosus eggs from sheep dog feces. The adult tapeworm lives in the small intestine of dogs. Eggs are passed in dog feces and can infect sheep. If humans ingest the eggs, the larvae can develop into cysts in organs like the liver and lungs. Symptoms depend on the location and size of the cysts. Diagnosis involves examination of cyst fluid for scolices or serological tests. Treatment involves