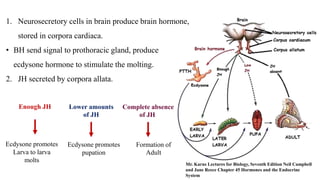
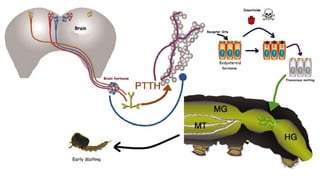
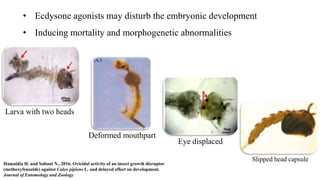
The document discusses ecdysone receptor agonists and their role in insect development, including molting and reproduction. It highlights the function of hormones like ecdysone and juvenile hormone, emphasizing their impact on larva development and metamorphosis. Specific chemical compounds such as methoxyfenozide are mentioned for their targeted effects against certain pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects.