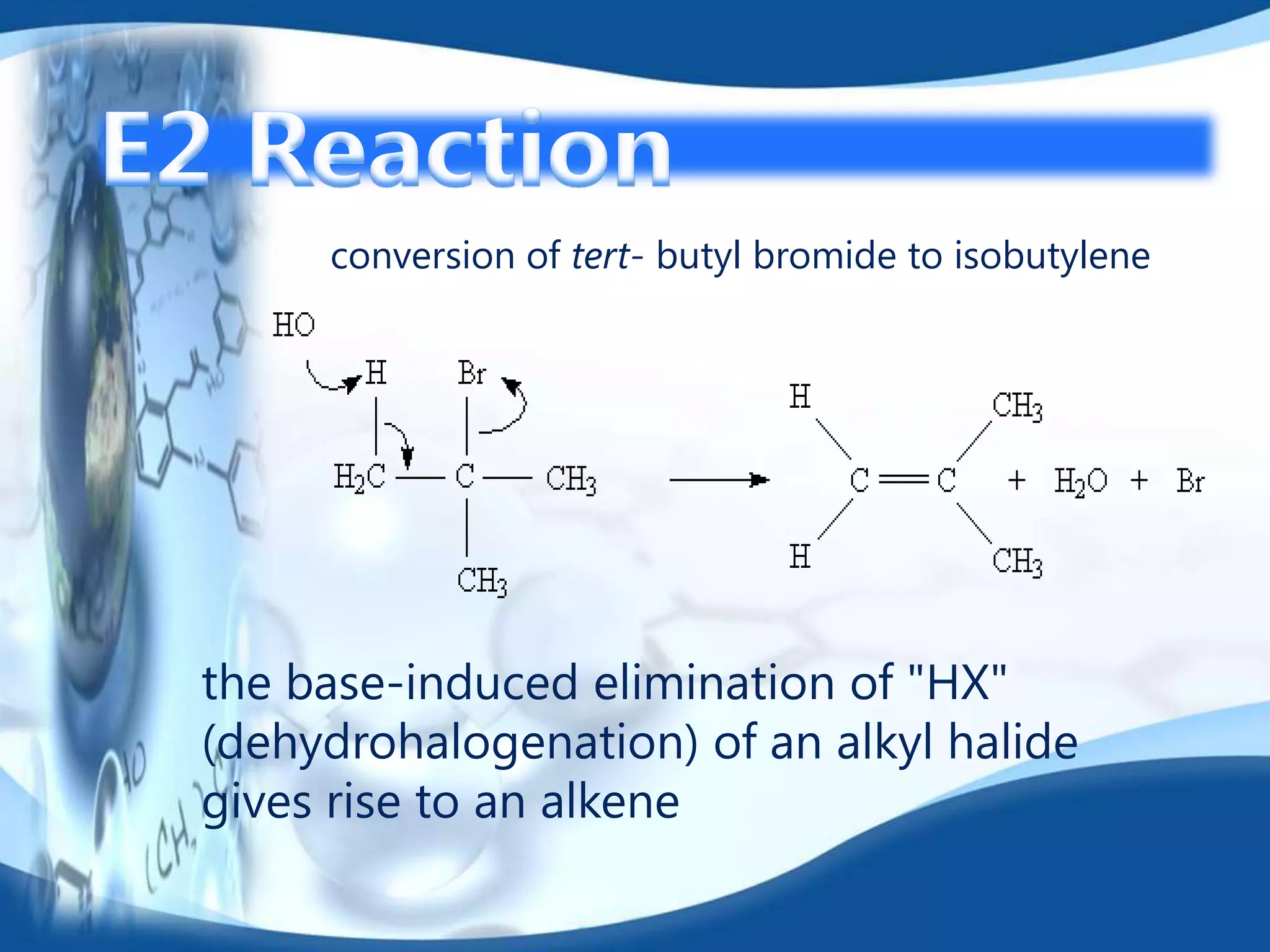
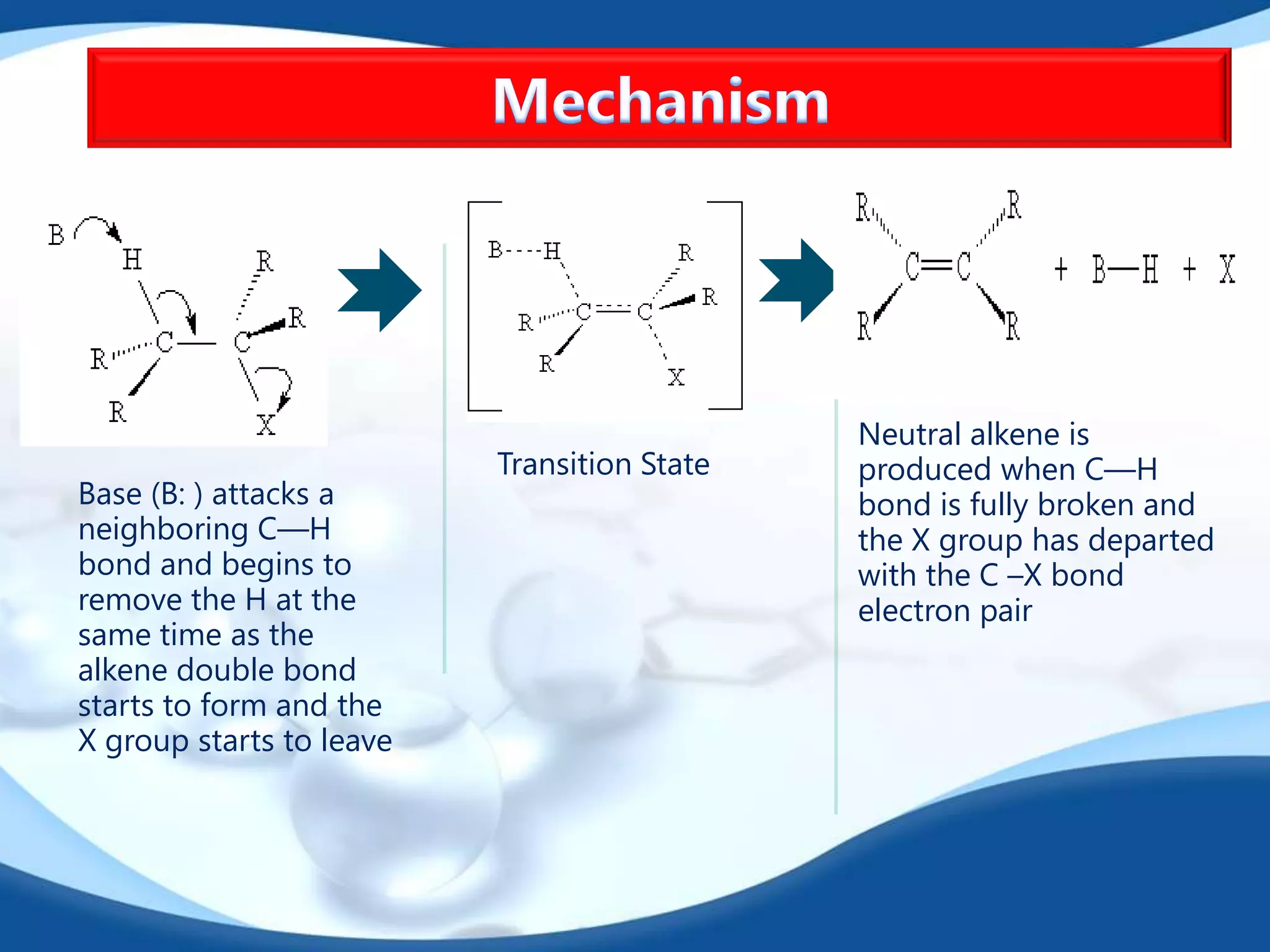
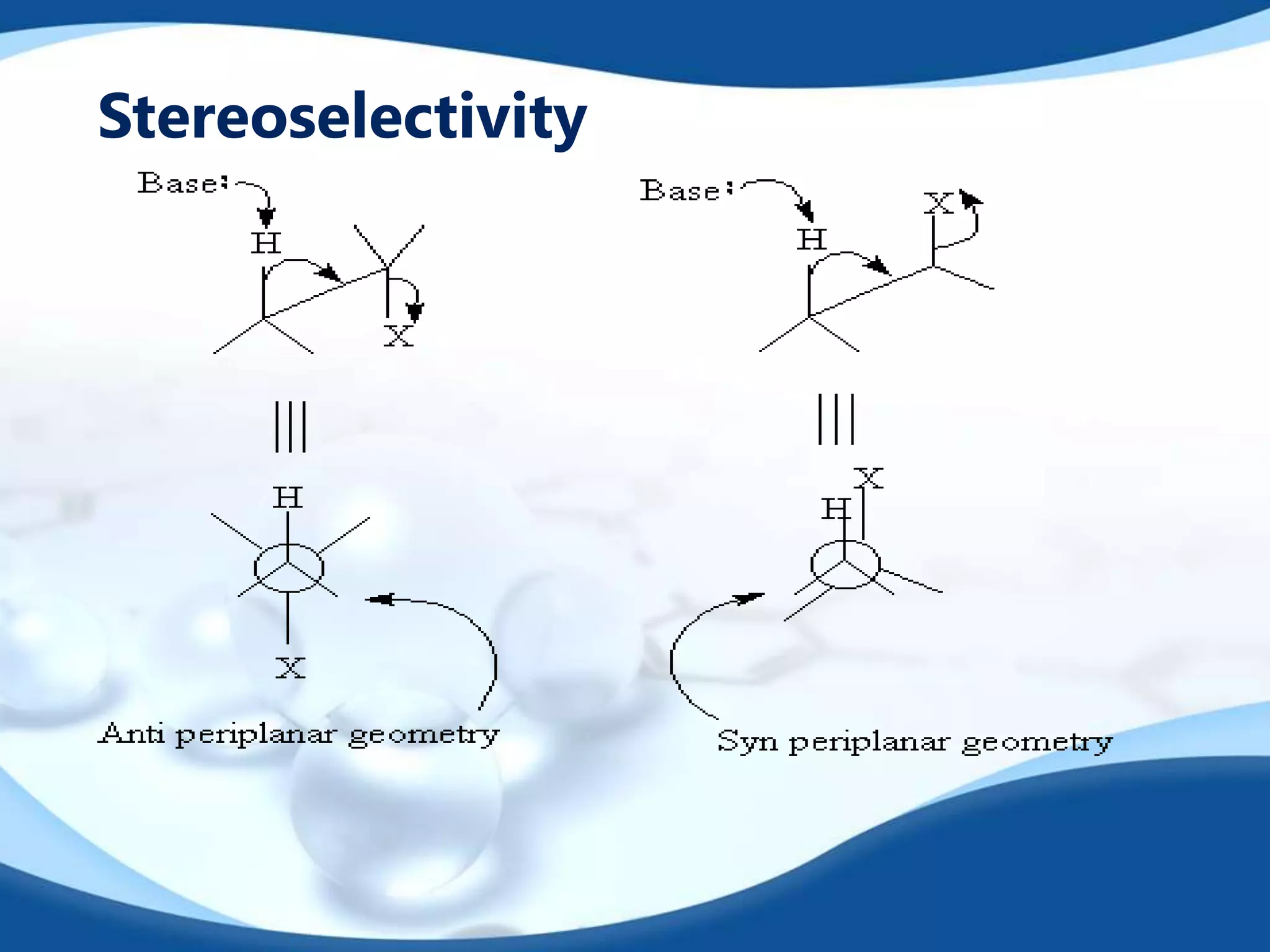
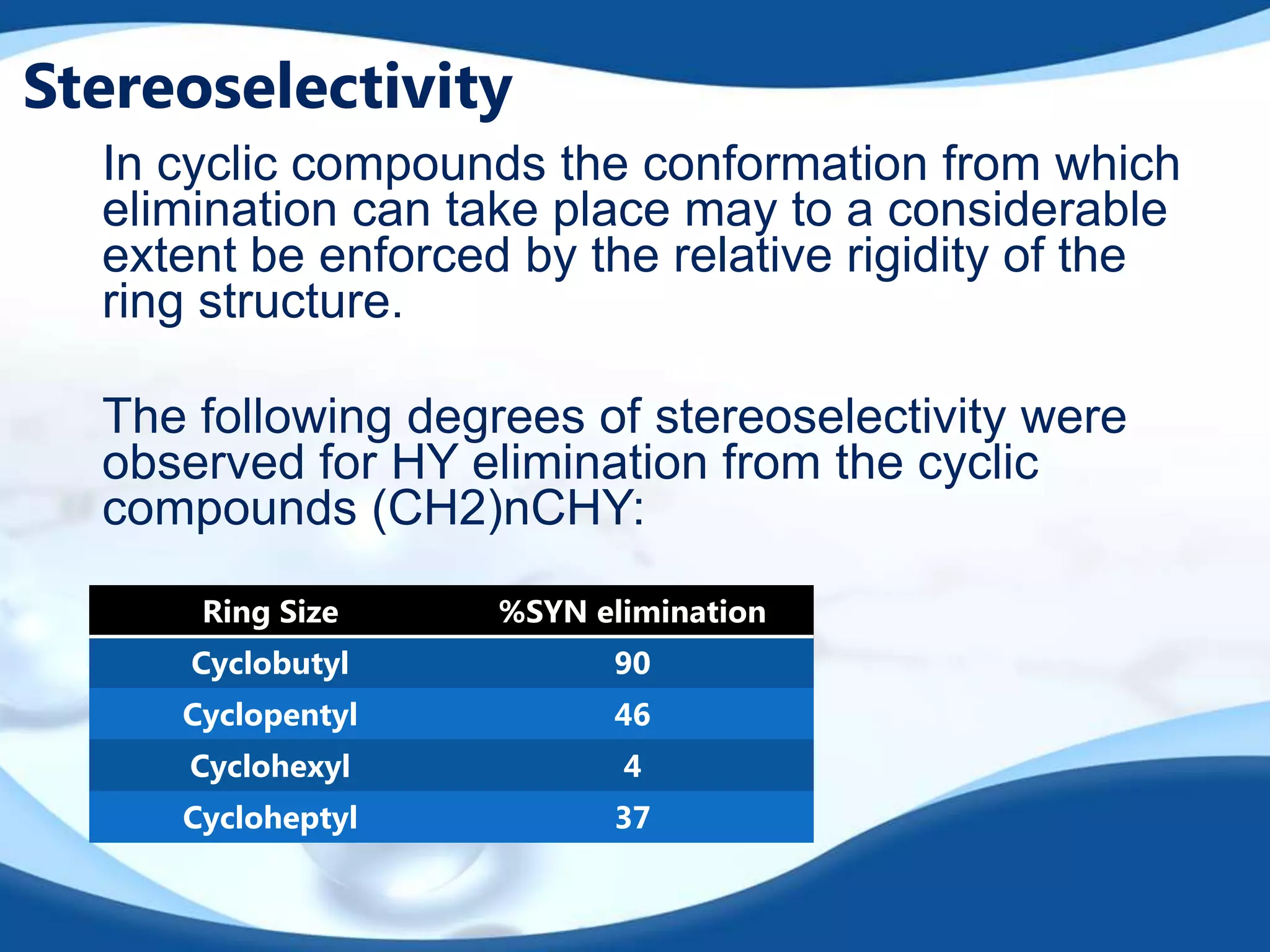
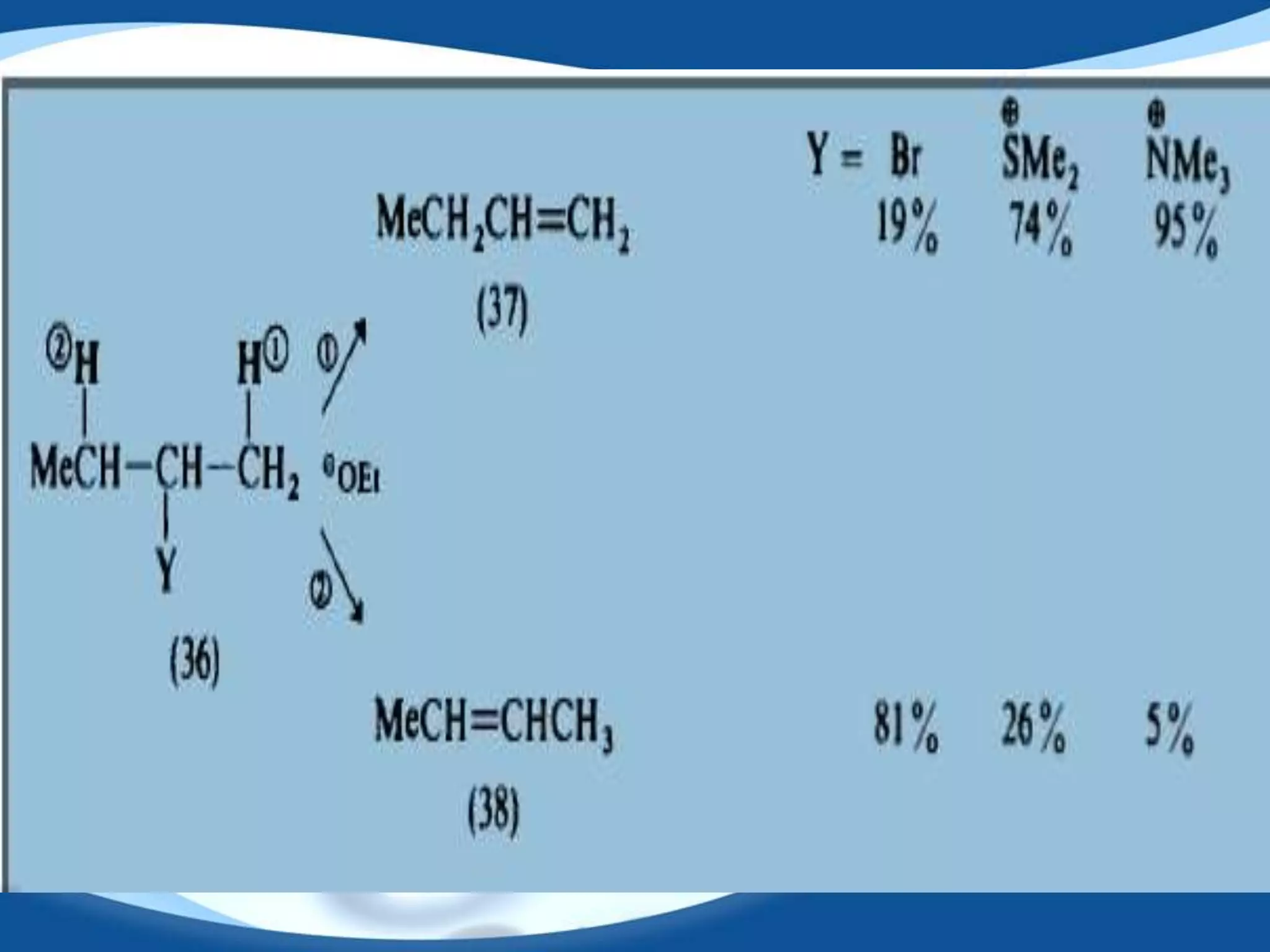
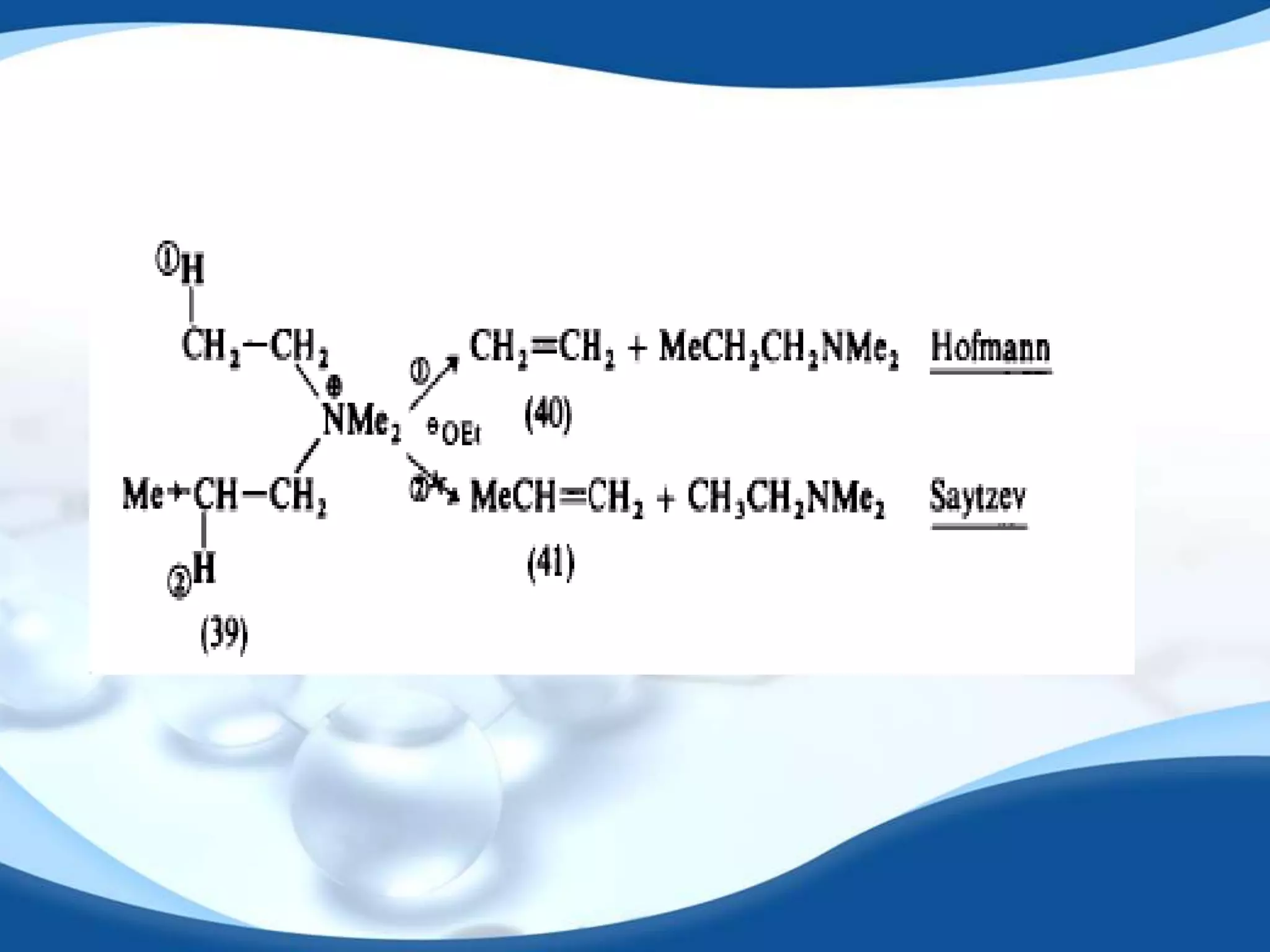
The E2 reaction mechanism involves the base-induced elimination of a hydrogen and halide atom from an alkyl halide, forming an alkene product. The reaction proceeds through a concerted bimolecular transition state where the C-H bond breaks as the C-X bond forms. Stereoselectivity is determined by whether the anti or syn orientation is preferred. Cyclic compounds exhibit varying degrees of stereoselectivity depending on ring size. The orientation of the double bond in the product can be predicted by either Hofmann or Saytzev rules based on the stability of the carbocation intermediate.