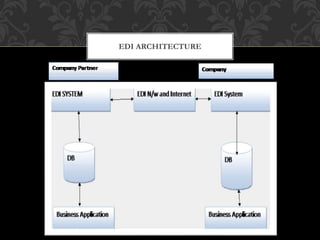
The document discusses e-commerce, including its processes, security threats, benefits, and challenges. It covers electronic data interchange (EDI), virtual organizations, and electronic payment systems, detailing their structures and functions. Additionally, it touches on e-governance, emphasizing the role of information and communication technology in enhancing government services to citizens and businesses.