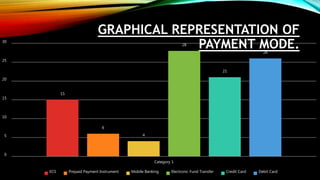
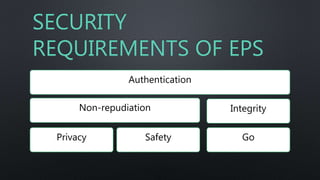
This document discusses electronic payment systems. It defines electronic payment systems as financial exchanges that take place online between buyers and sellers using digital payment methods backed by banks or intermediaries. It notes benefits of EPS like reduced costs, increased online commerce, and improved accuracy and security. It also discusses various electronic payment methods like credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, mobile banking, and electronic fund transfers. It outlines the process flows, security requirements, and risks associated with different electronic payment options.