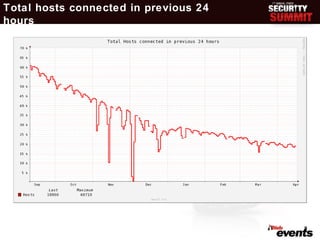
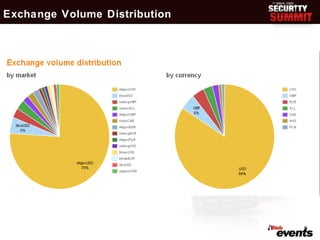
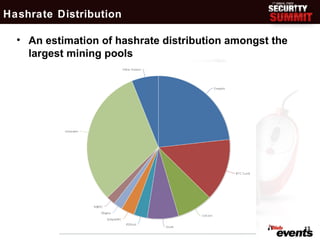
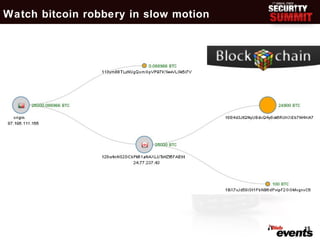
This document discusses the evolution of digital cash and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It outlines the goals and concerns of a cashless society, provides background on early digital cash systems, and describes how Bitcoin introduced a decentralized digital currency using cryptography. The document reviews Bitcoin statistics and applications, discusses security issues and regulatory concerns, and considers Bitcoin's potential future prospects as an independent digital currency.