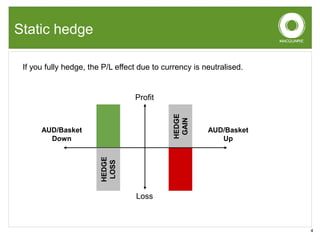
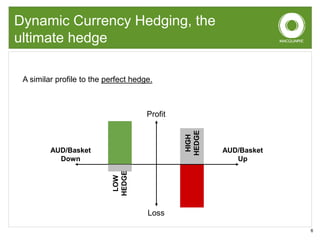
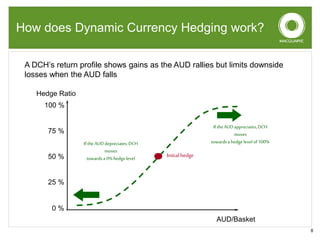
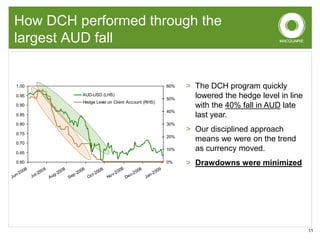
This document discusses dynamic currency hedging (DCH) as a strategy to protect overseas assets from currency risk. It notes that accurately forecasting currency movements is very difficult, with experts often missing the mark. DCH aims to hedge currency risk while allowing upside participation by adjusting hedge levels in response to currency fluctuations using forward contracts. This results in an option-like profile that limits losses when the home currency falls while capturing gains when it rises. The document provides examples showing how DCH outperformed static hedging and unhedged approaches during a period of large Australian dollar depreciation by quickly lowering hedge levels.