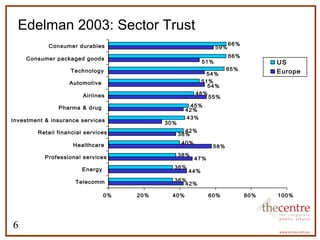
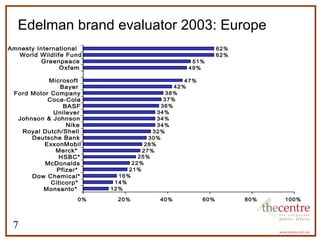
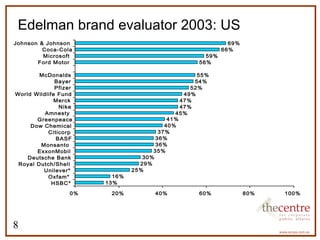
This document provides an overview of corporate social responsibility (CSR). It defines CSR and outlines the development of CSR in Australia. It discusses key drivers for businesses to engage in CSR such as enhancing reputation and improving community relationships. It also presents data on trust in different sectors and brands. Current trends in CSR are discussed along with examples of CSR programs and important aspects of internal CSR infrastructure.