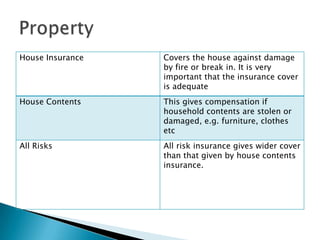
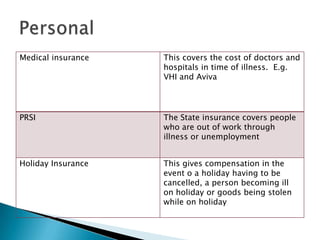
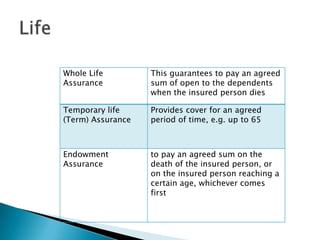
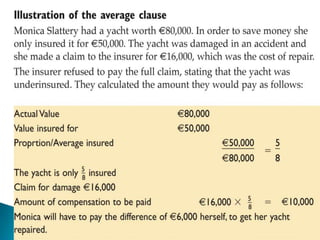
Insurance protects individuals and businesses from financial loss by paying compensation for damage to or loss of valuable property and assets. It works by pooling risks among many policyholders, so that the costs of claims made by a few are shared among all. There are important principles that govern insurance, such as insurable interest, utmost good faith, indemnity, contribution, subrogation and average clauses.