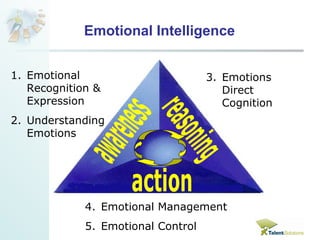
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance in the workplace. It defines EI as the capacity to effectively perceive, express, understand and manage emotions in a professional manner. The document outlines a five dimensional model of EI and describes each dimension. It then discusses research finding that higher EI is related to less stress, better teamwork, relationships, performance, leadership and job satisfaction. The document concludes by providing suggestions for how organizations can develop the EI of their employees.