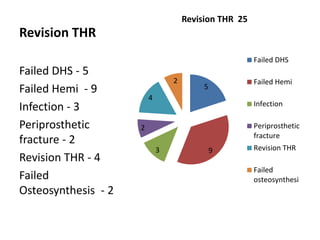
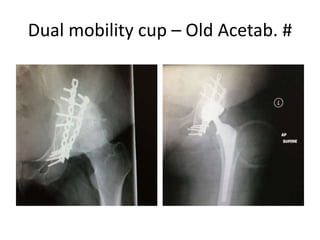
This document summarizes the experience with dual mobility cups at Khoula Hospital. It discusses that dual mobility cups are effective at reducing dislocation rates in high-risk patients such as those over 65, with prior hip surgery, neurological disorders, or revision THR. The document then provides details of 47 cases at Khoula Hospital using dual mobility cups, finding a low 2% dislocation rate. It concludes that dual mobility cups provide good early results in high-risk patients in Oman and can reduce dislocation compared to conventional THR.