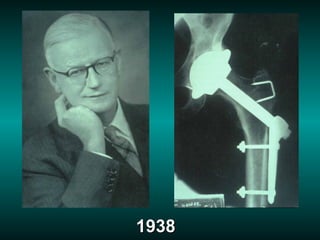
1. Total hip arthroplasty has evolved significantly since its origins in the late 1800s through improvements in materials, designs, fixation methods, and surgical techniques.
2. Cementless fixation and improved bearing surfaces have led to improved implant survivorship and reduced osteolysis.
3. Current areas of focus include minimizing wear through novel bearing surfaces and coatings, inhibiting the cellular response to wear debris, and improving surgical techniques through minimal access approaches and computer navigation.