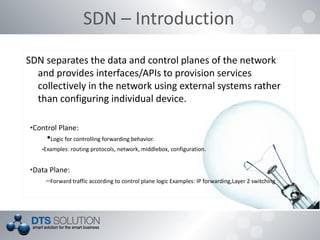
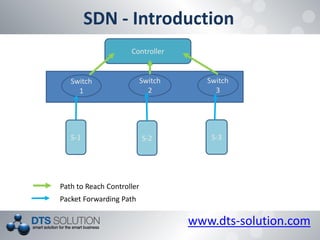
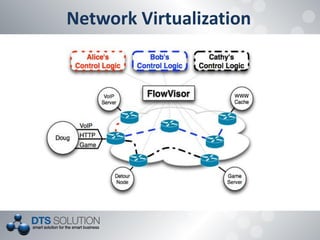
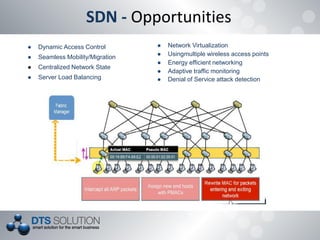
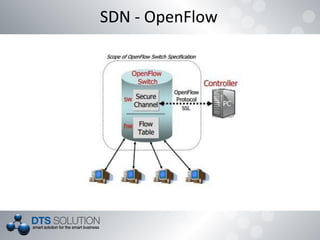
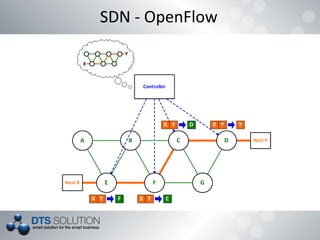
The document discusses software defined networking (SDN) and network virtualization. It explains that SDN separates the control plane and data plane, allowing network control through external systems rather than individual device configuration. Network virtualization decouples applications from hardware and allows for logical network topologies on the same physical infrastructure through resource isolation. OpenFlow is presented as a standard for SDN implementation, and tools like Open vSwitch, Mininet and OpenDaylight are discussed. Challenges around scalability, reliability and consistency with the separation of planes are also covered.