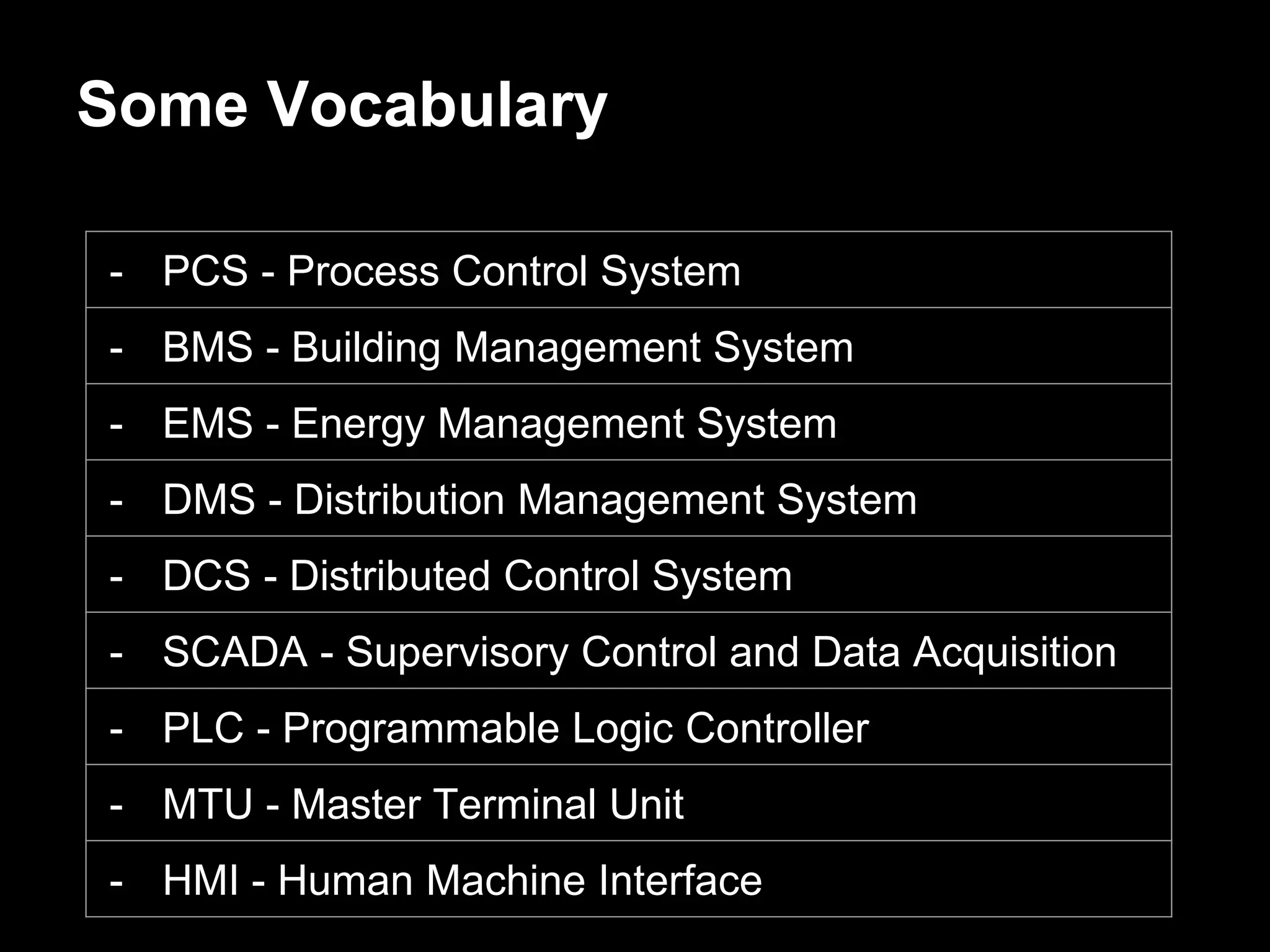
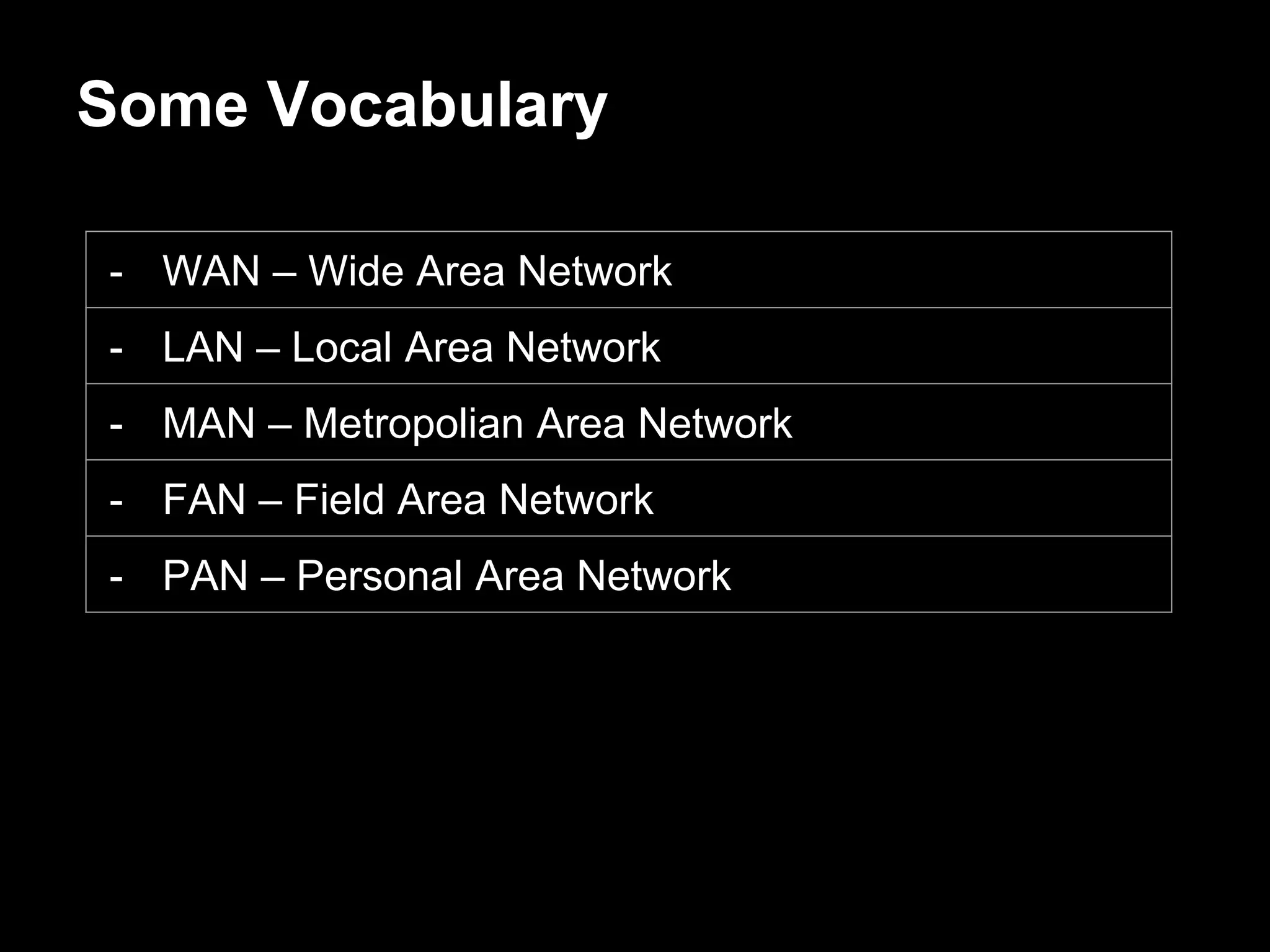
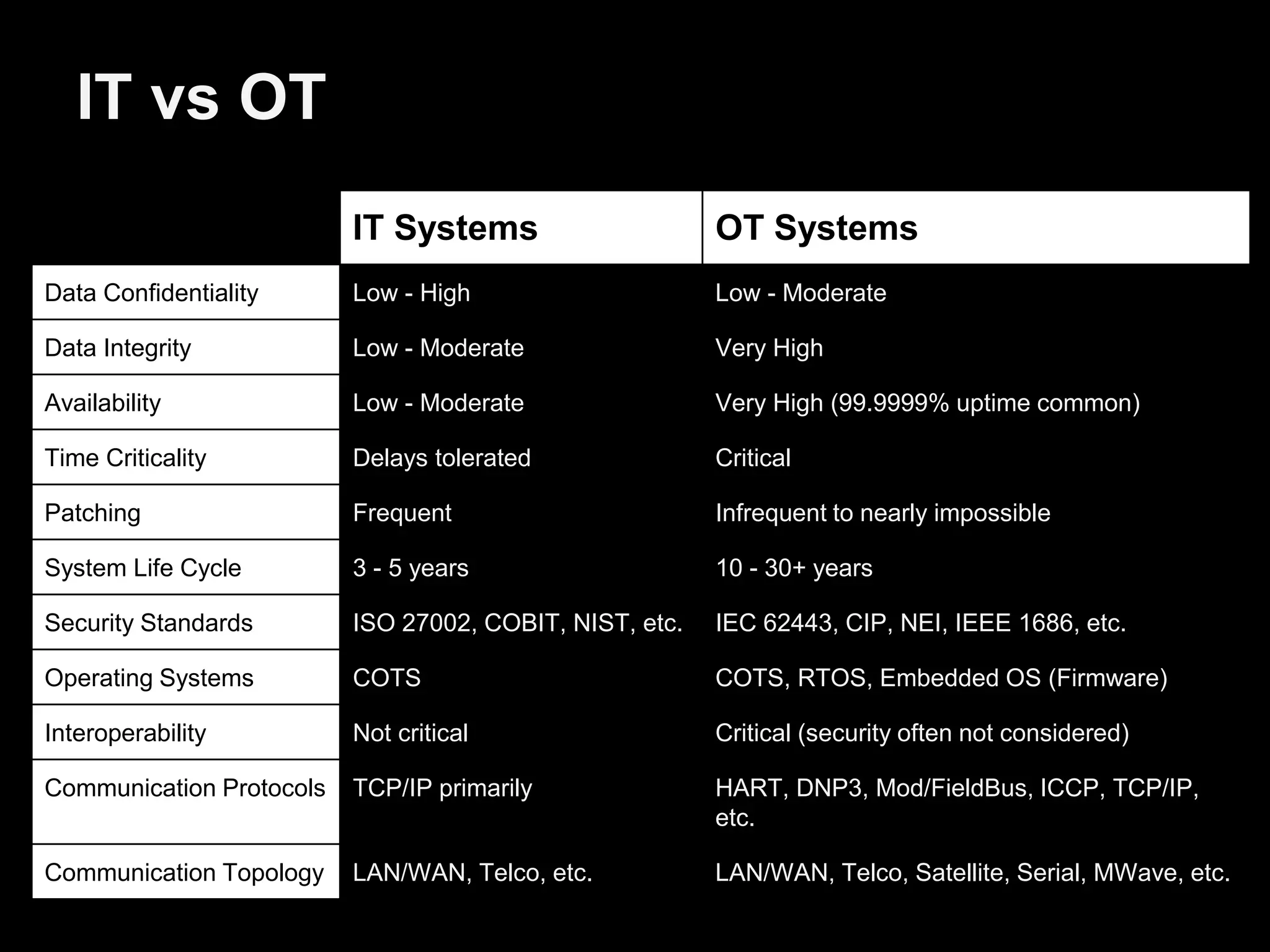
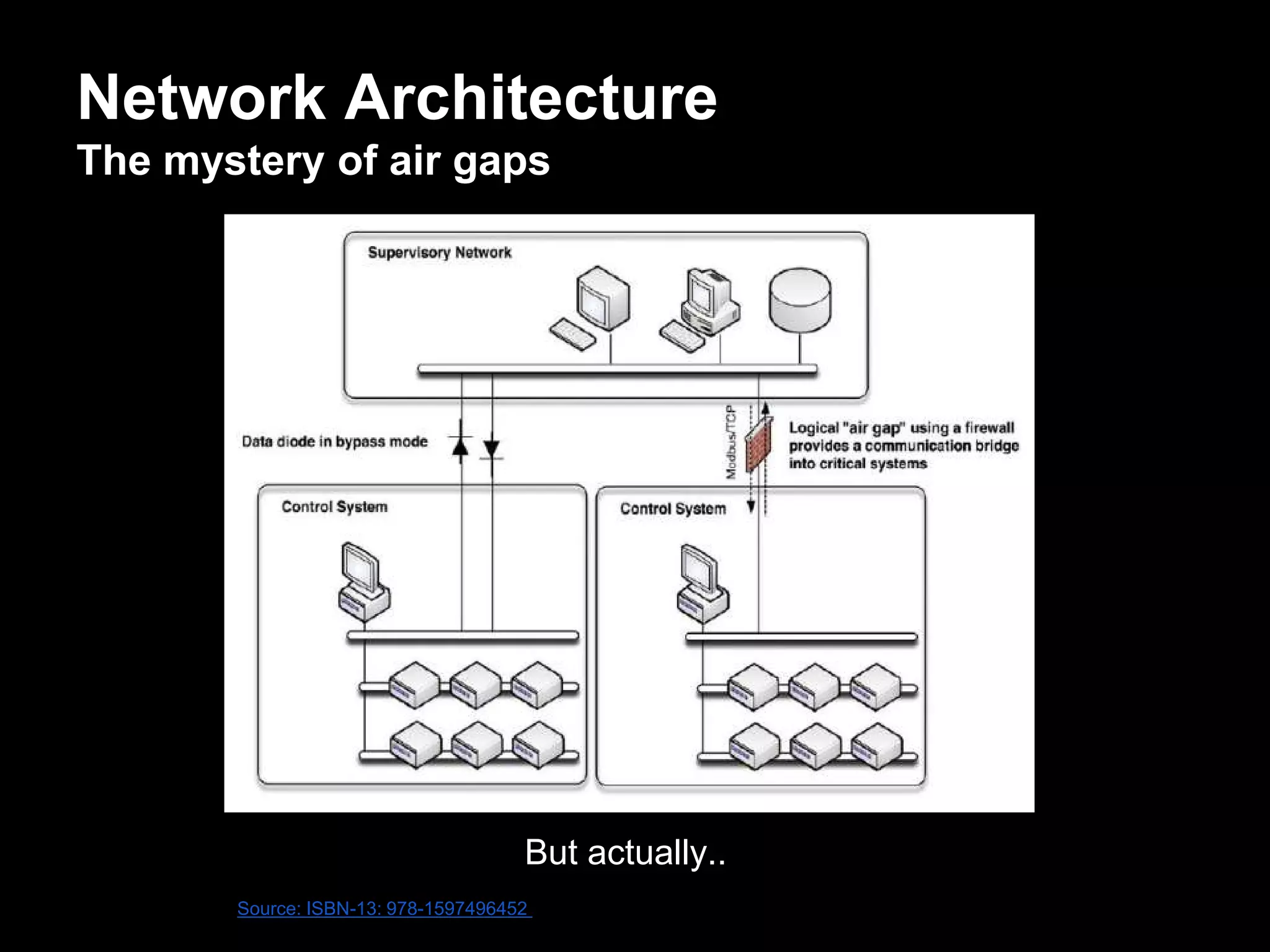
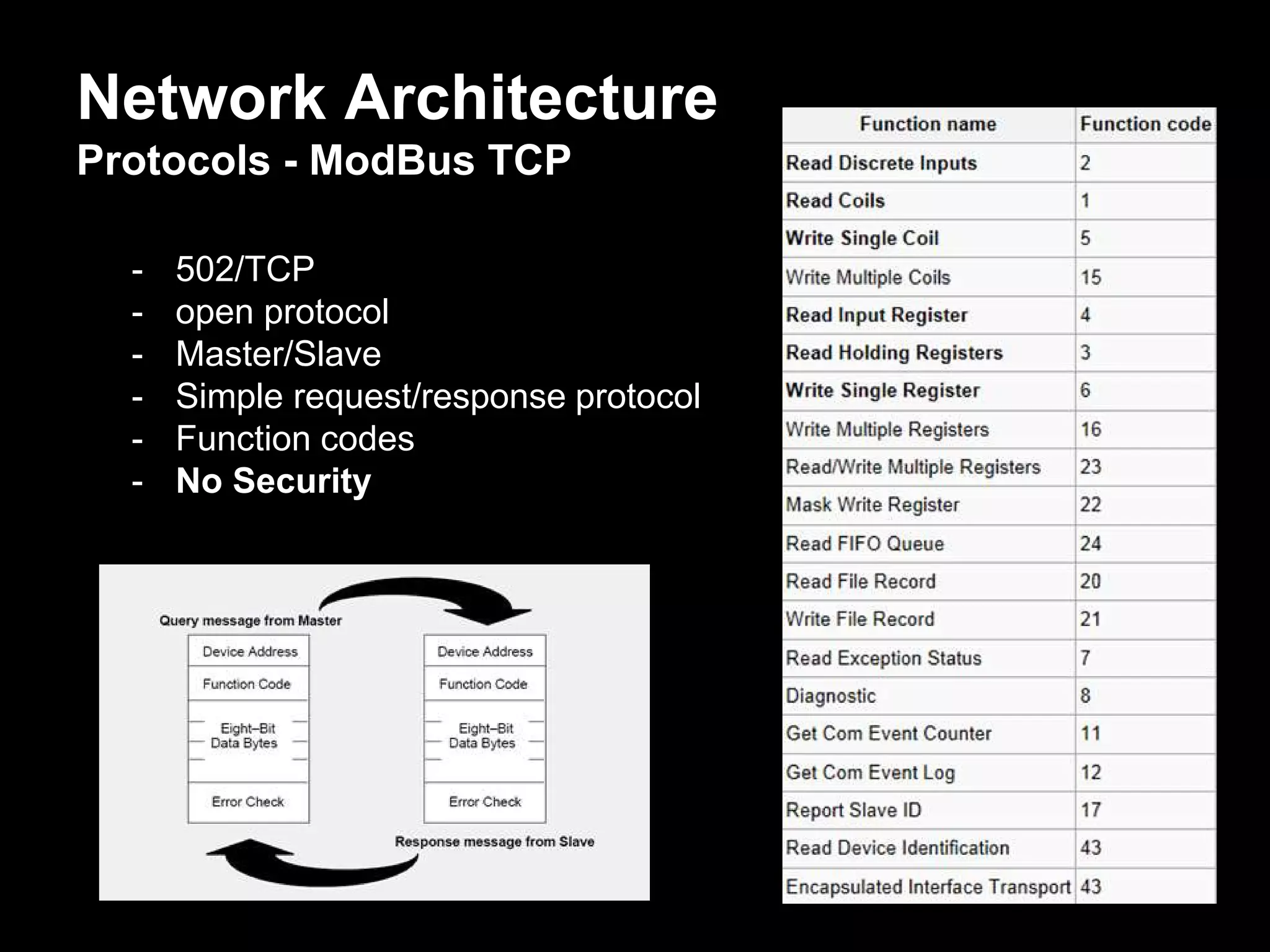
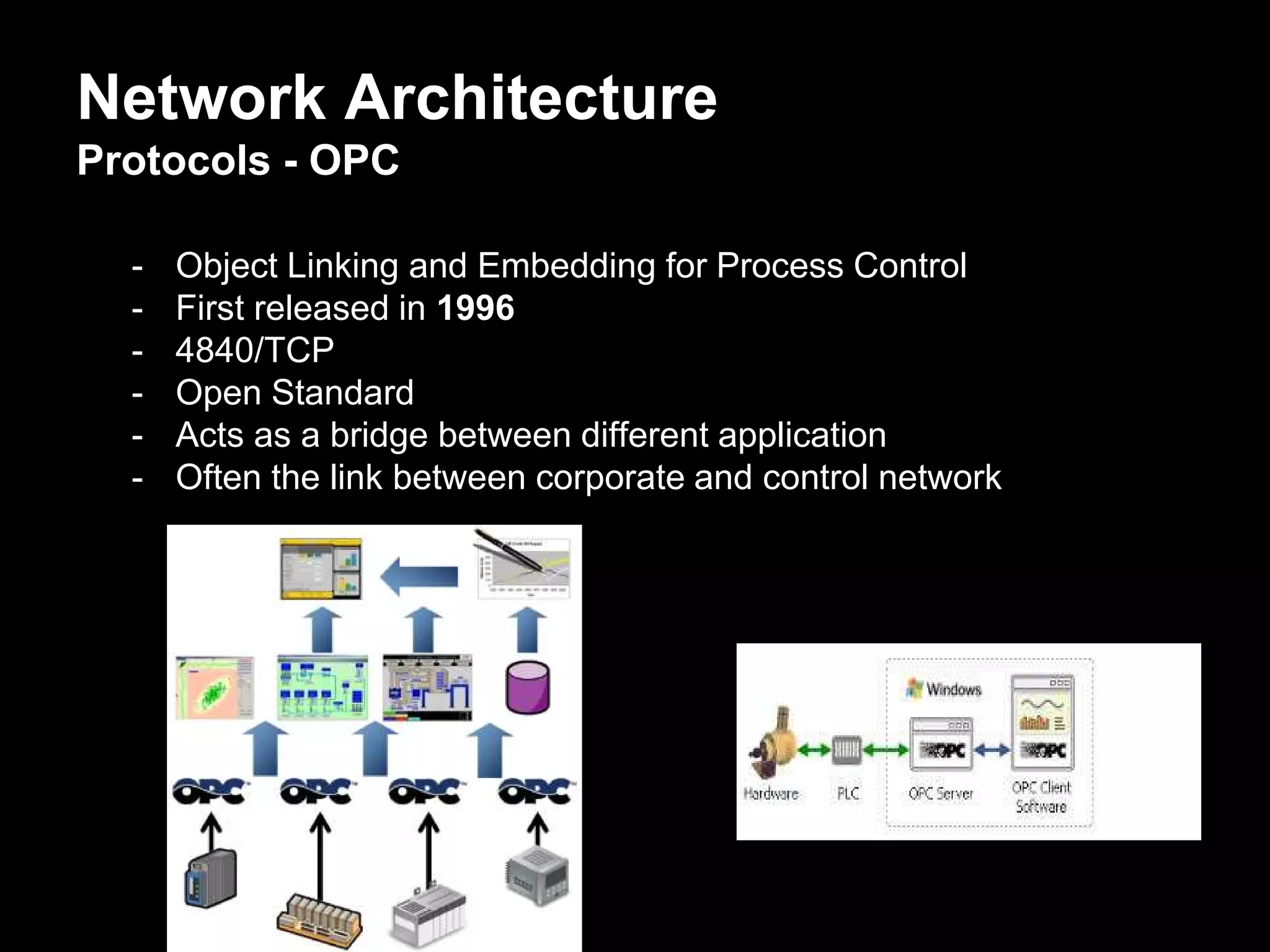
The document discusses the journey of understanding and securing operational technology (OT) and industrial control systems (ICS), highlighting the different types of risks associated with such systems, including human safety and environmental effects. It emphasizes the importance of security measures, system architecture, and common weaknesses in OT and ICS environments, urging collaboration among security, operations, maintenance, and IT teams. The necessity of compliance with various security standards, the challenges of patch management, and the need for an inventory of current security levels are also addressed.











![Operational Technology [OT]
Operational
Technology
Industrial
Control
Systems [ICS]
Network
Other
components
(apps,
systems)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejourneytoicsfinal-extended-150804235833-lva1-app6892/75/The-journey-to-ICS-Extended-12-2048.jpg)
















![Standards
- NERC CIP
- IEC 62443 (ISA99)
- IEEE 1686
- NIST SP800-82 rev 2
- Etc [link]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejourneytoicsfinal-extended-150804235833-lva1-app6892/75/The-journey-to-ICS-Extended-49-2048.jpg)
