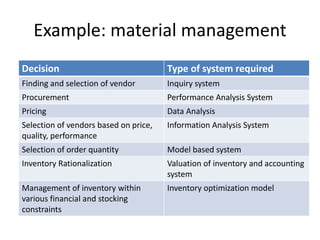
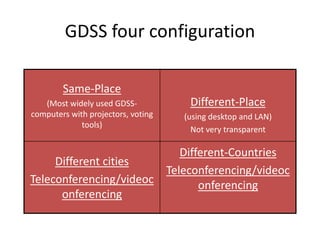
Herbert Simon proposed a 4-phase model of problem solving: intelligence, design, choice, and review. Decision making involves either programmed or non-programmed decisions. Decision support systems (DSS) provide interactive support for semi-structured and unstructured decisions through queries, models, and reports without making the final decision. A DSS collects data, allows for group work, and can incorporate artificial intelligence. Common DSS models include behavioral, management science, and operations research models. Group decision support systems (GDSS) facilitate group problem solving through individual workstations, facilitation software, and aggregation of ideas, comments, and votes.