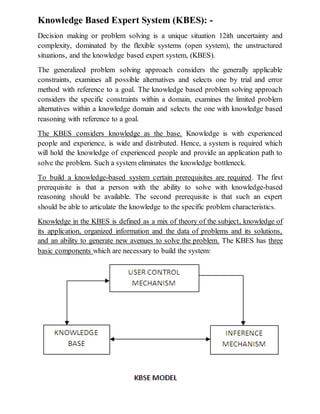
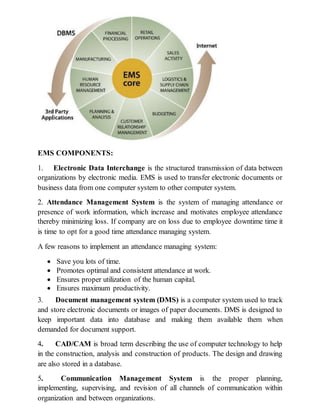
This document provides an overview of decision support systems (DSS), including what they are, how they differ from management information systems, their components and characteristics, types of decisions they support, and examples of DSS tools and models. A DSS is an interactive IT system that helps managers make semi-structured or unstructured decisions. It uses databases, models, and software to analyze large amounts of internal and external data and support decision-making at all management levels. DSS can incorporate various tools like spreadsheets, solvers, rules, and more to help evaluate alternatives, identify problems, and recommend or identify optimal solutions.