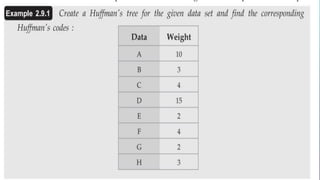
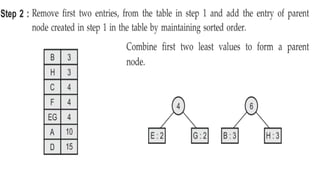
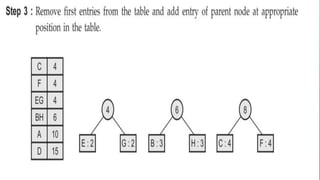
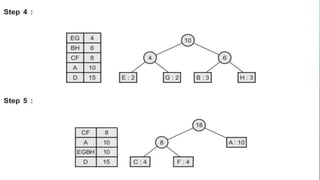
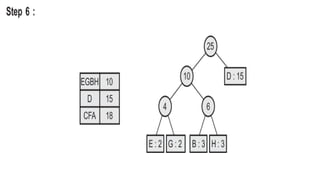
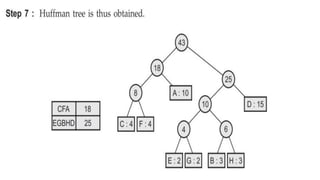
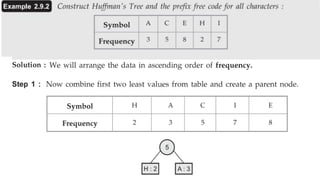
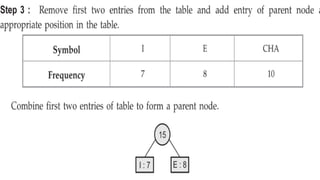
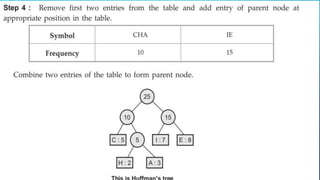
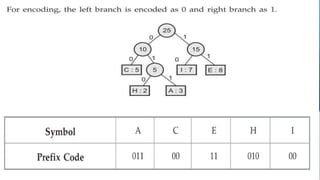
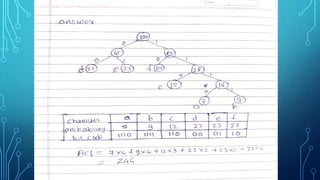
This document provides an overview of Huffman coding and Huffman's algorithm. It discusses how Huffman coding works by assigning variable length binary codes to characters based on their frequency, with more common characters getting shorter codes. It then explains Huffman's algorithm, which builds the Huffman tree by recursively combining the two least frequent nodes until a full binary tree is constructed, and codes are assigned based on paths in the tree. Examples of its applications in data compression are also given.










![HUFFMAN CODING
• Huffman (C)
• 1. n=|C|
• 2. Q ← C
• 3. for i=1 to n-1
• 4. do
• 5. z= allocate-Node ()
• 6. x= left[z]=Extract-Min(Q)
• 7. y= right[z] =Extract-Min(Q)
• 8. f [z]=f[x]+f[y]
• 9. Insert (Q, z)
• 10. return Extract-Min (Q)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsapresentetionhuffmantree-220416095908/85/DSA-Presentetion-Huffman-tree-pdf-11-320.jpg)