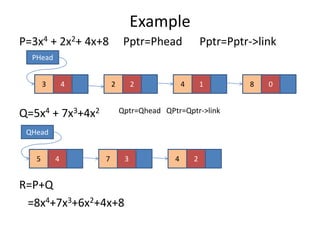
Linked lists are useful for dynamic memory allocation and polynomial manipulation. They allow for efficient insertion and deletion by changing only pointers, unlike arrays which require shifting elements. Linked lists can represent polynomials by storing coefficient, exponent, and link fields in each node. Polynomial addition using linked lists involves traversing both lists simultaneously and adding coefficients of matching exponents or duplicating unmatched terms into the new list.