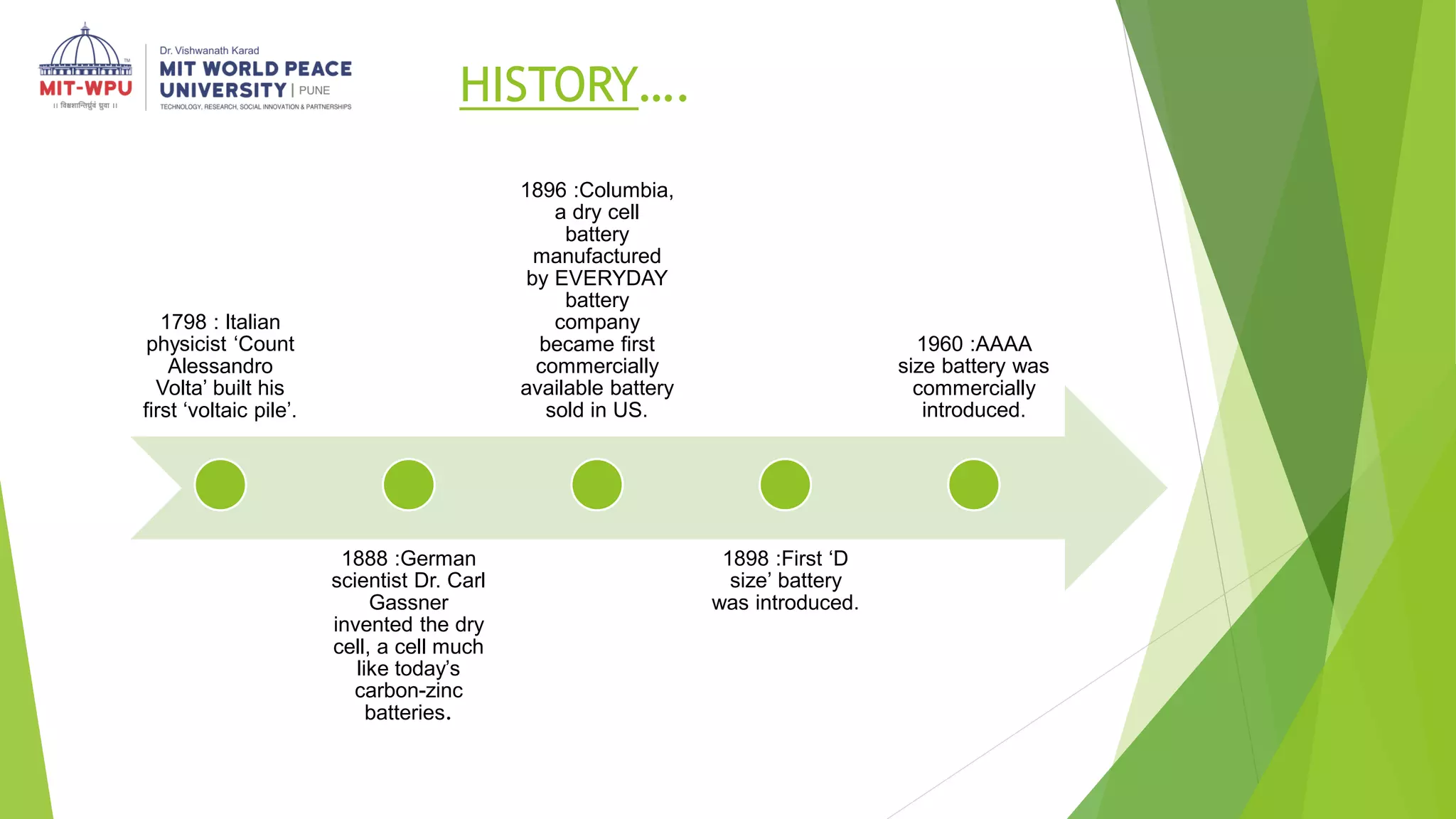
A dry cell is a type of battery that converts chemical energy into electrical energy, was developed in 1886, and is widely used in portable devices. It consists of a zinc container and a carbon rod, utilizing a moist paste of ammonium chloride as the electrolyte. Various types of dry cells, including zinc-carbon, alkaline, lithium, mercury, and silver oxide cells, serve different applications but can pose risks if mishandled.