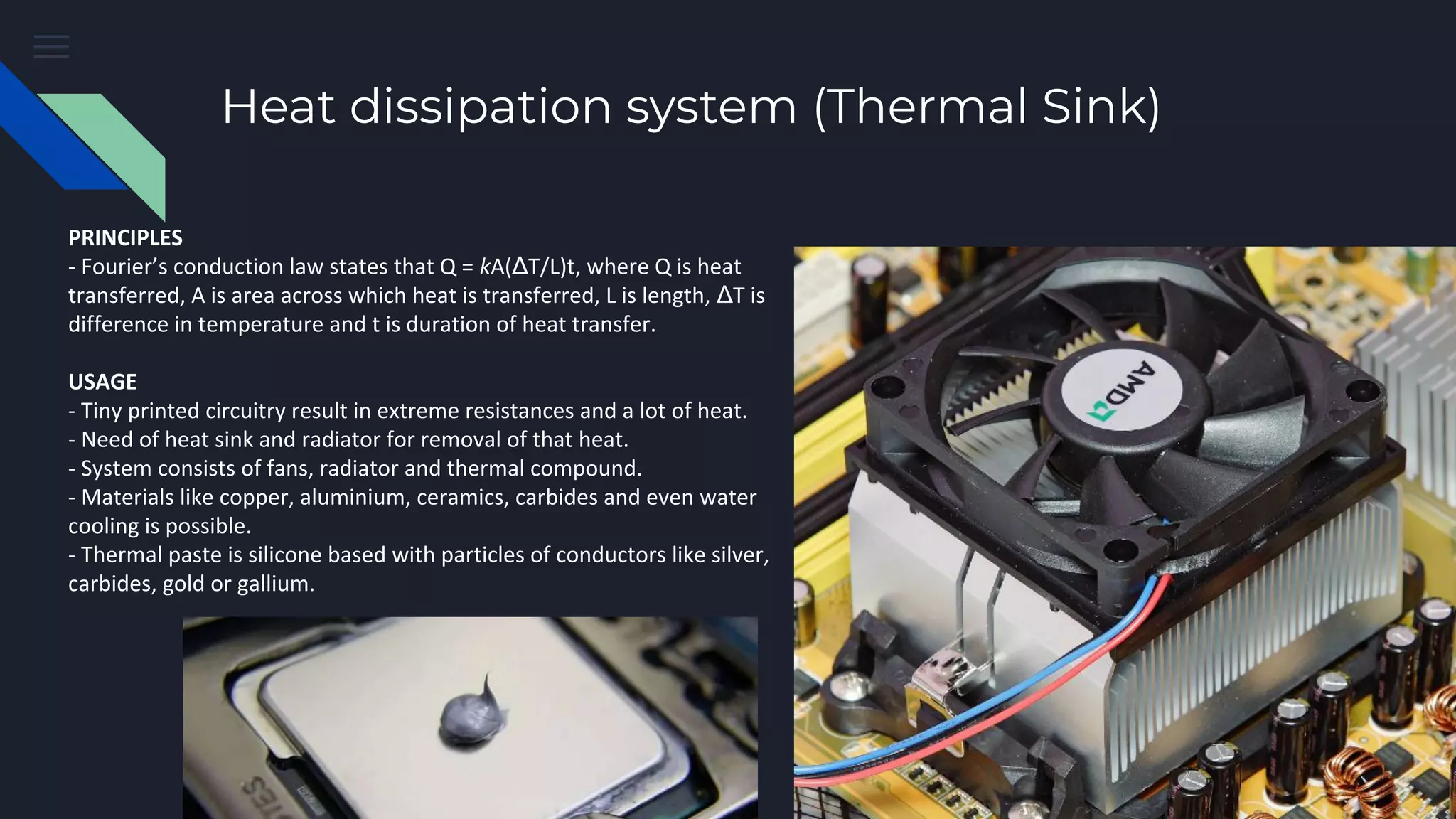
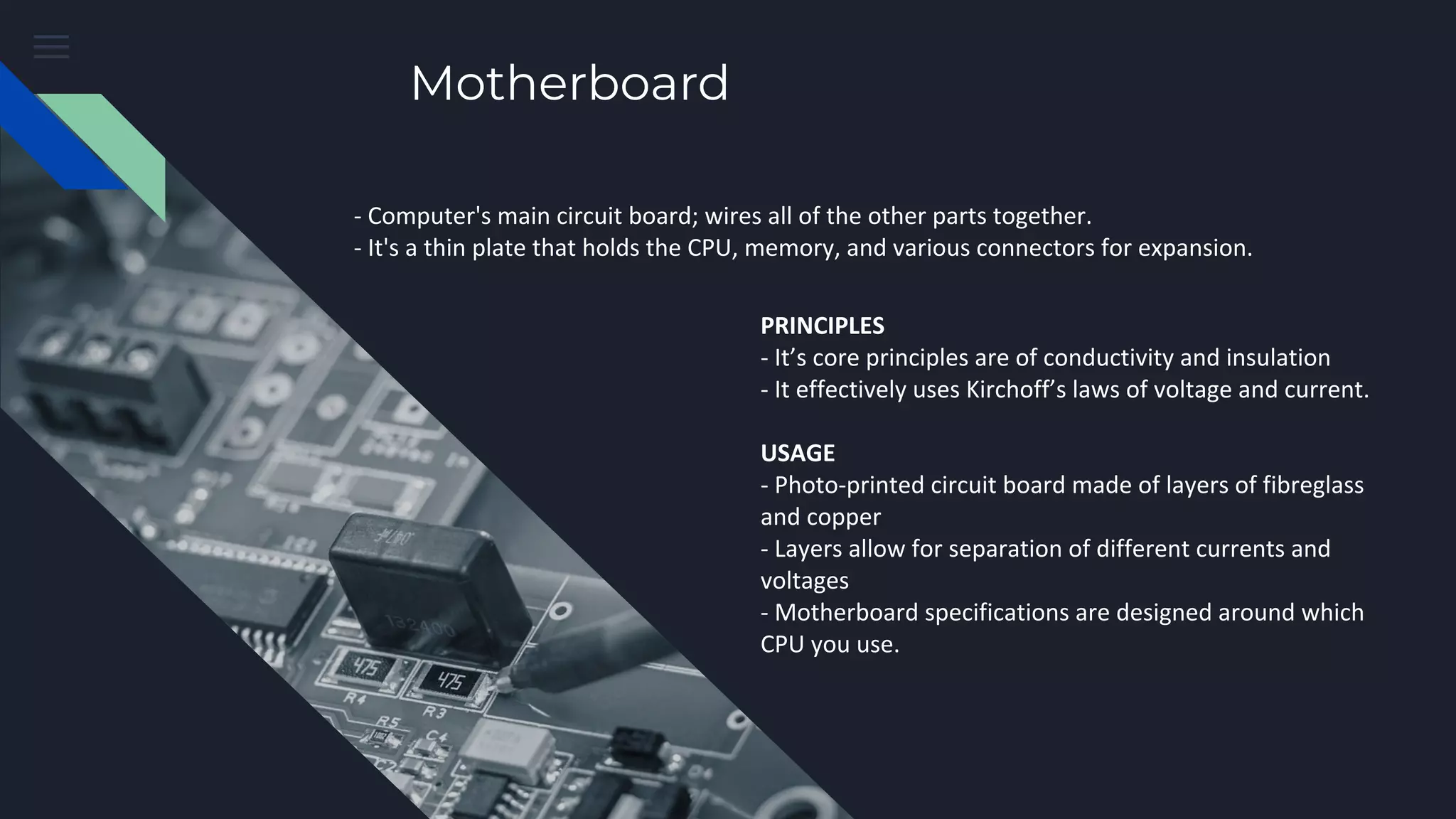
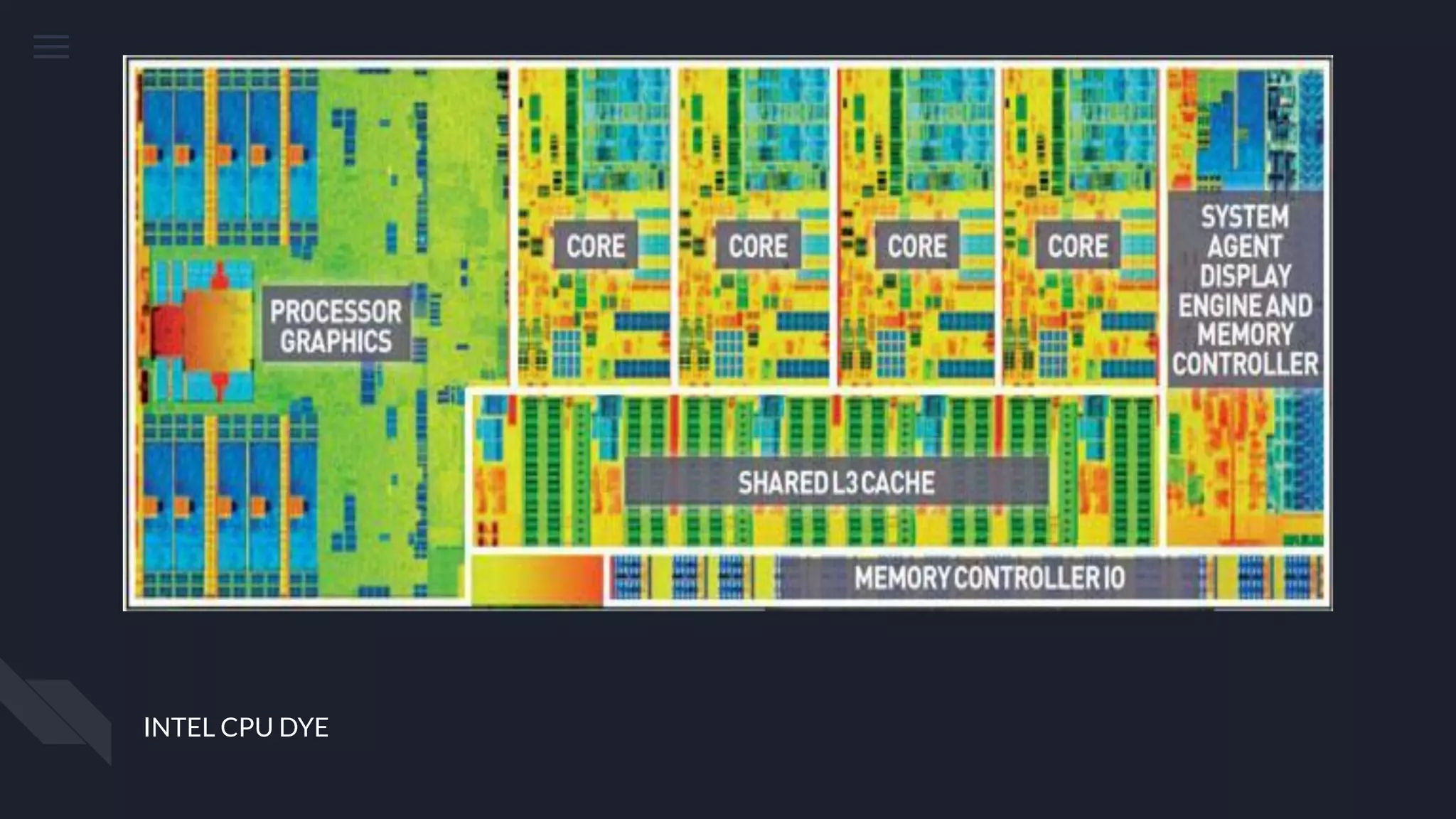
This document provides an overview of the key components inside a desktop computer and their functions. It discusses the housing/shielding, heat dissipation system, motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard drive, and power supply unit. For each component, it describes the basic principles of operation and how they are used within a computer system. All of the parts must work together harmoniously for the computer to function properly.