Embed presentation
Downloaded 42 times




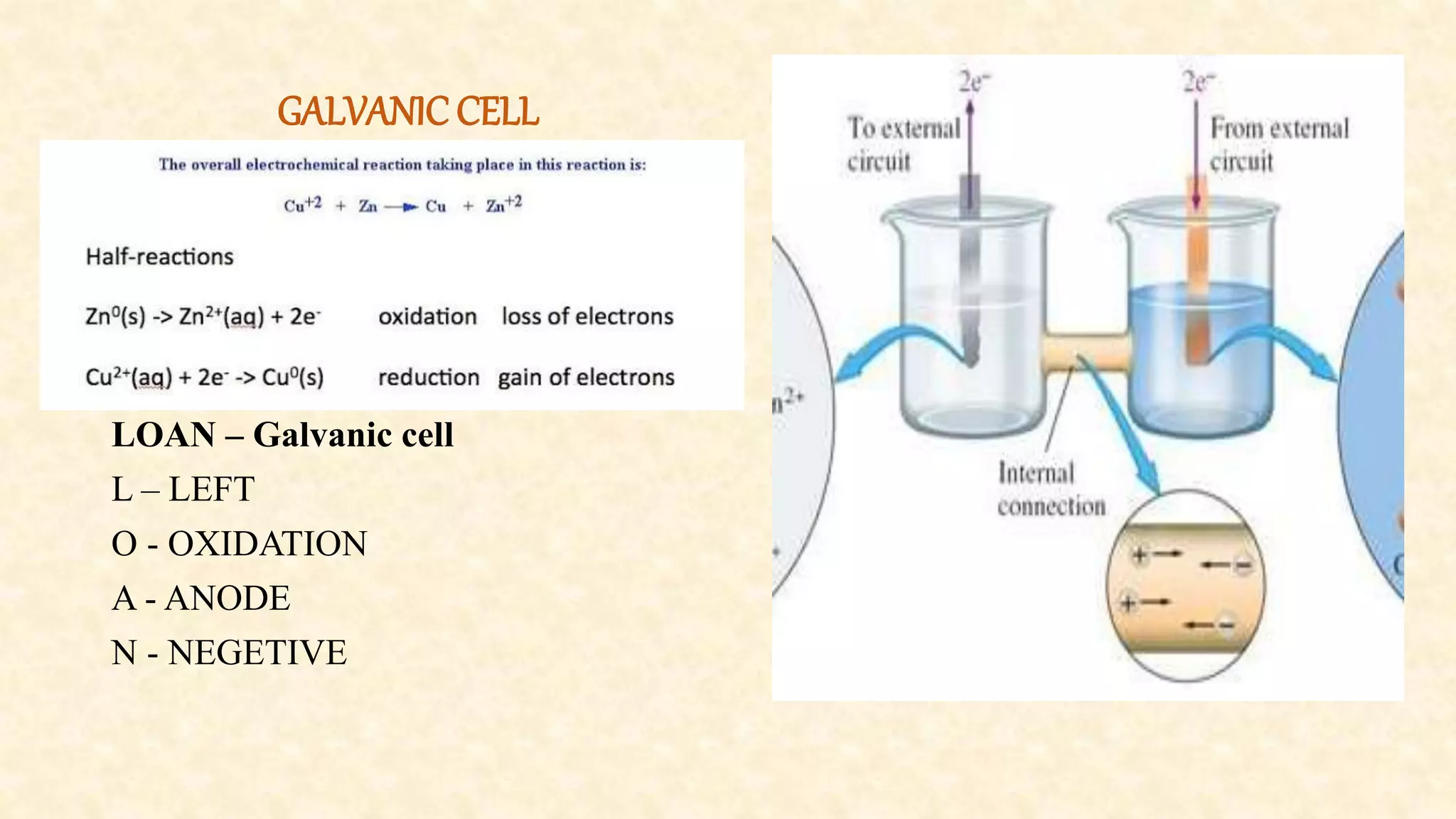

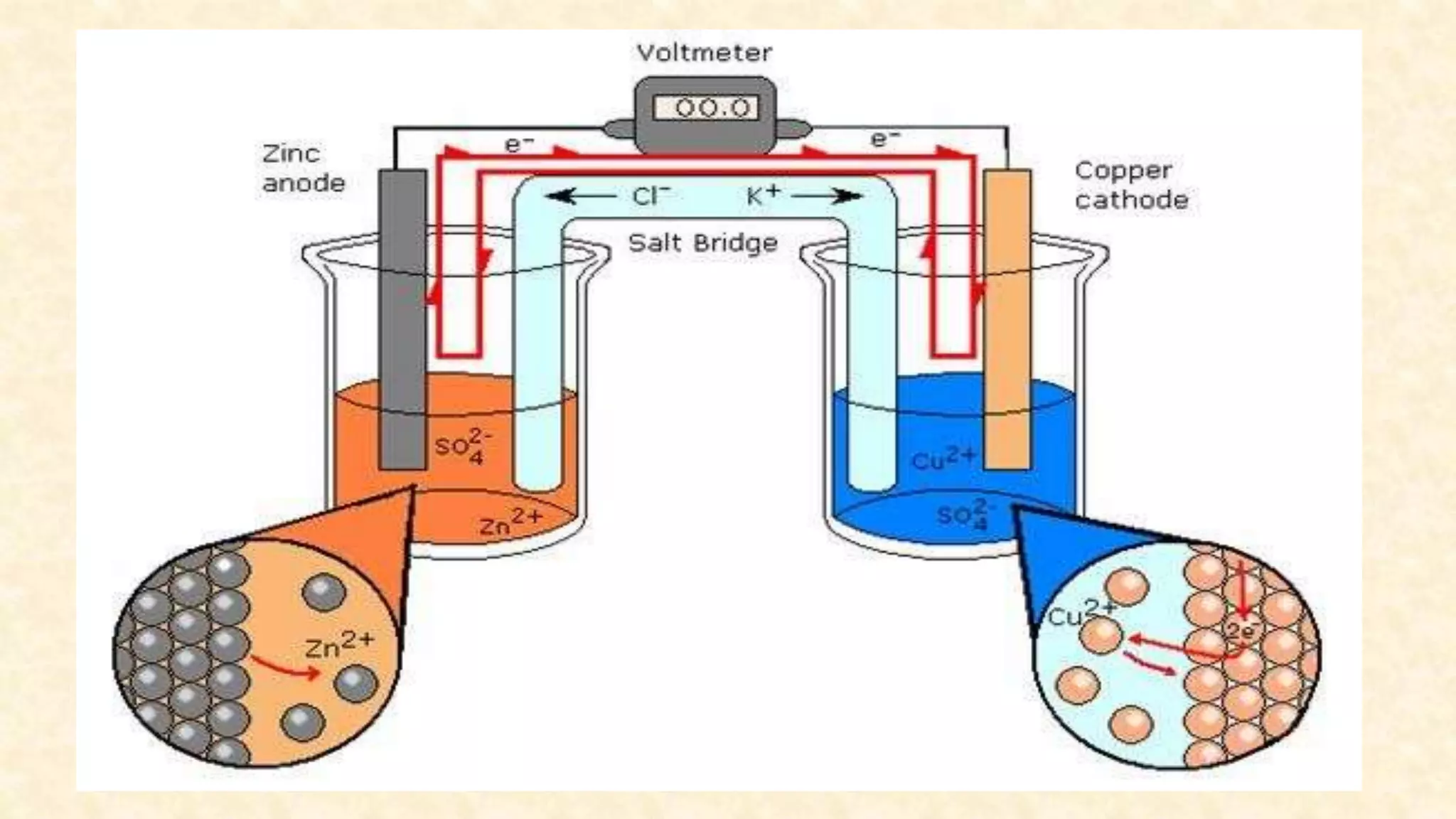
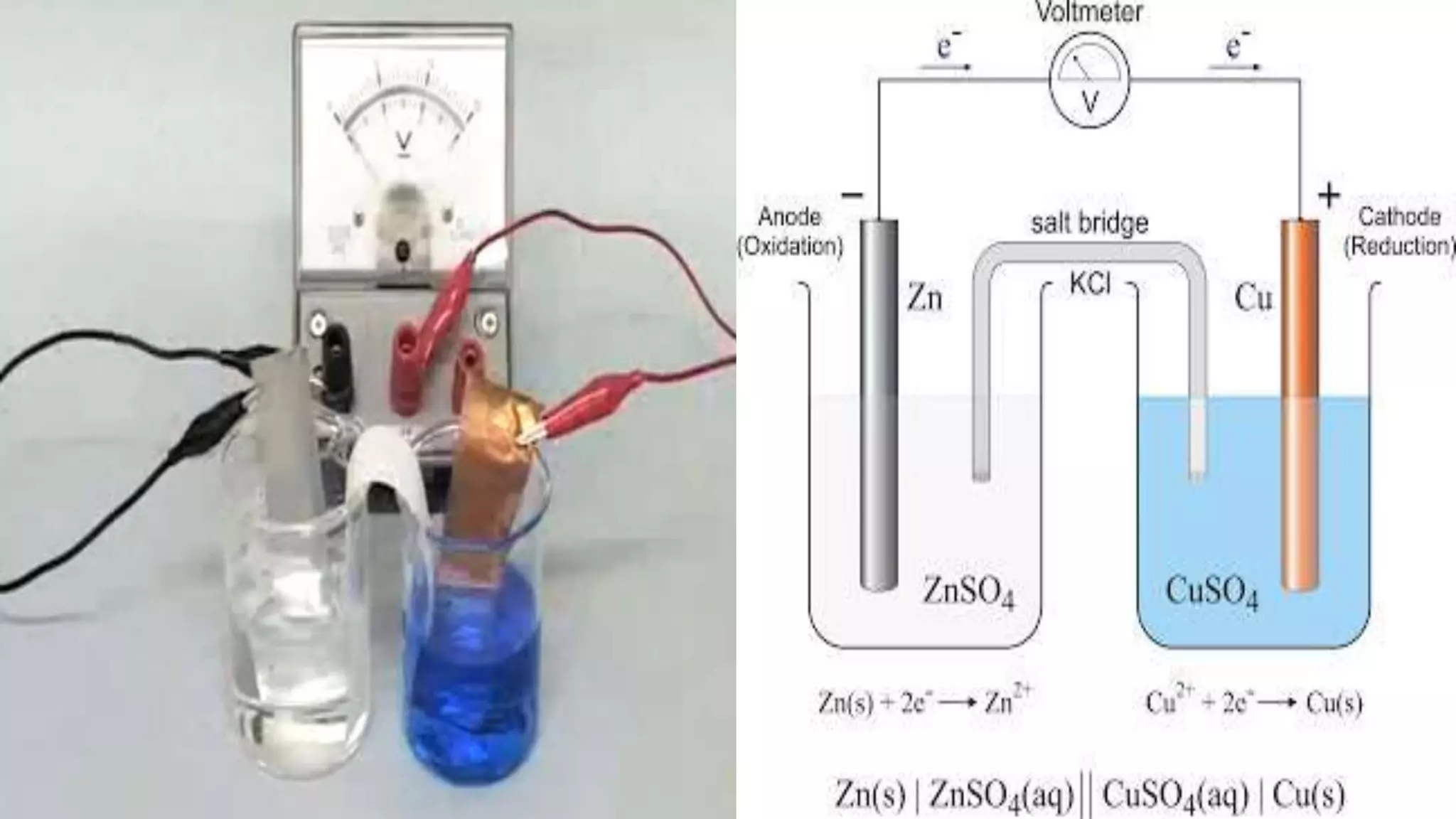

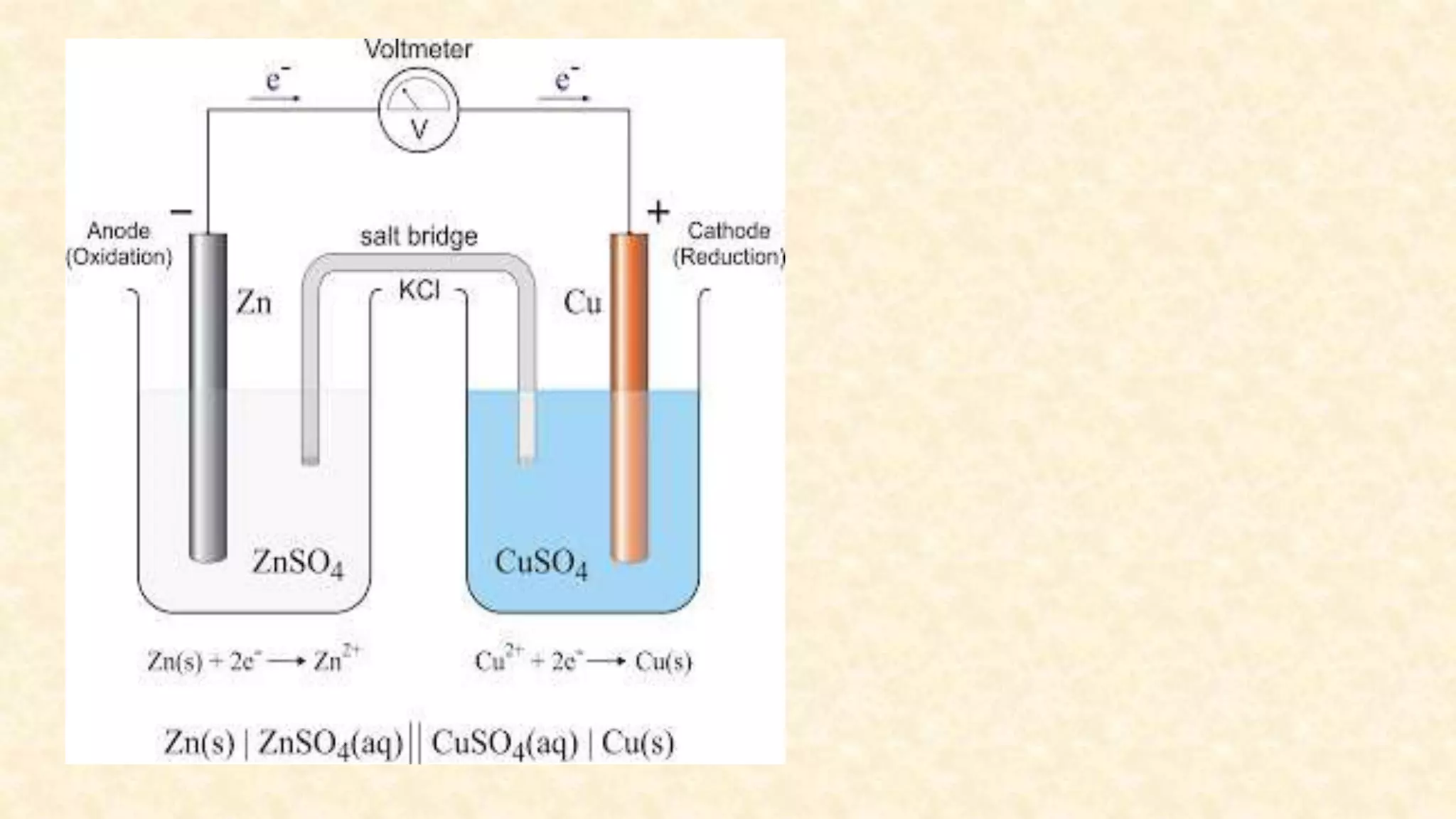


Electrochemistry involves redox reactions in galvanic cells that convert chemical energy to electrical energy. In a galvanic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction occurs at the cathode. A salt bridge completes the circuit between the two half cells and maintains electrical neutrality. When a zinc rod is used as the anode in a copper sulfate solution with a copper cathode, the zinc rod loses weight as it oxidizes while copper precipitates and the solution warms due to heat released, demonstrating the spontaneous conversion of chemical to electrical energy in a galvanic cell.












