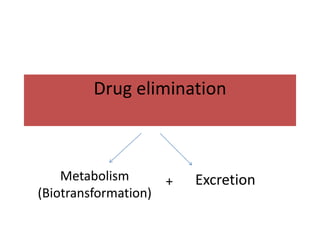
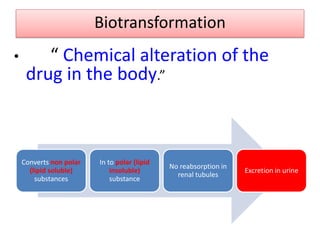
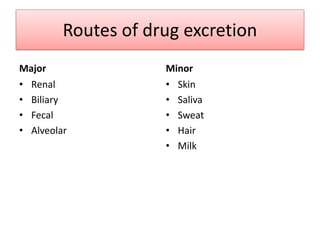
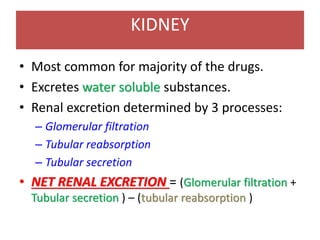
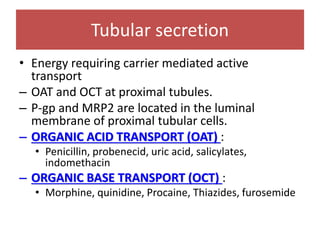
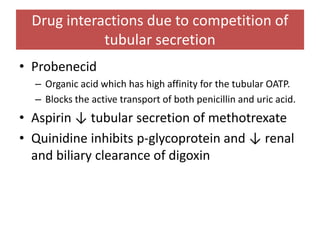
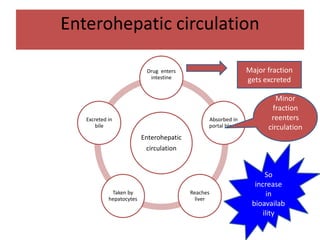
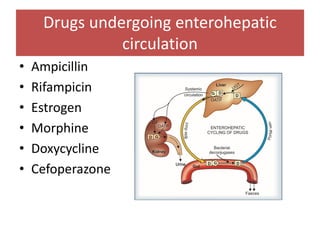
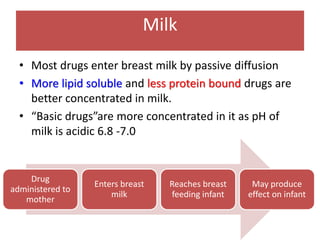
Drugs are eliminated from the body through metabolism and excretion. The major routes of excretion include renal (kidney), biliary (bile), fecal, alveolar (lungs), and minor routes like skin, saliva, sweat, hair, and milk. The kidney is the most common route and filters drugs through glomerular filtration while tubular secretion and reabsorption also influence renal excretion. Certain drugs can interact by competing for tubular secretion. Biliary excretion and enterohepatic circulation recirculate some drugs through the liver and intestines. Adjusting urine pH can enhance the excretion of acidic or alkaline drugs. Accumulation may occur if drugs rely on renal excretion and