The document provides an overview of the subprime mortgage crisis, including:
1) It explains what subprime and prime loans are and defines what a crisis is.
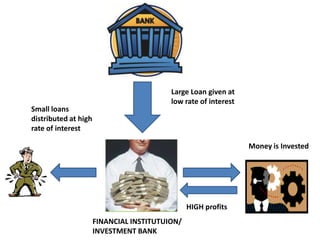
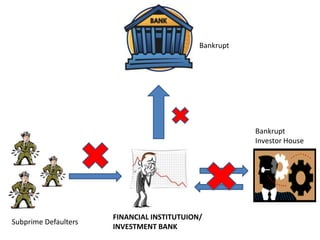
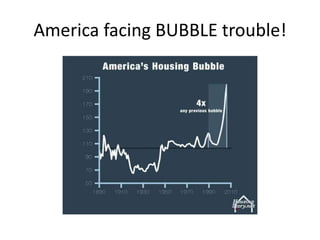
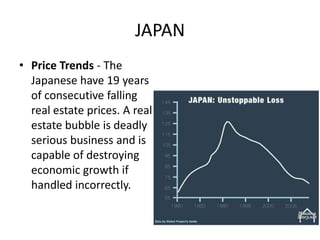
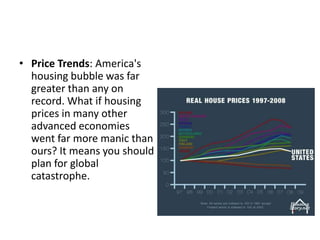
2) The housing bubble burst as home prices declined after peaking in 2006, increasing foreclosures.
3) This sent a shock through the financial system as investment banks and other institutions incurred major losses on mortgage-backed securities.