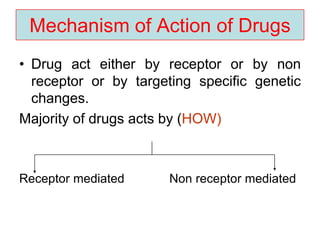
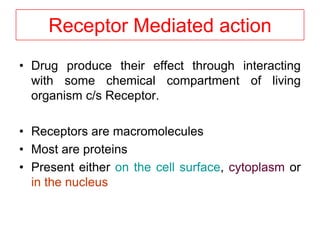
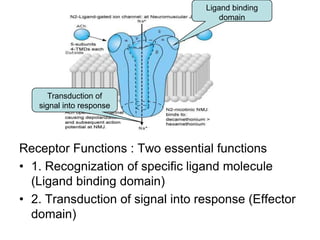
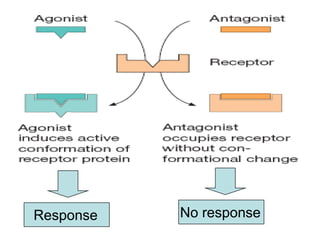
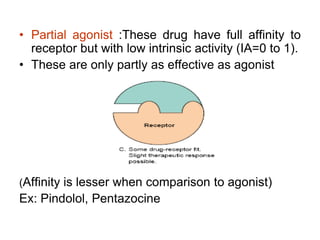
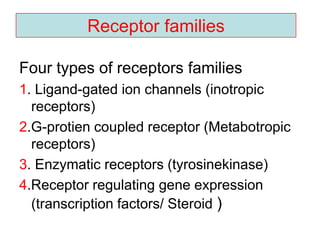
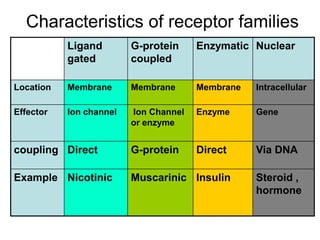
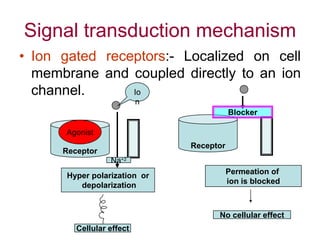
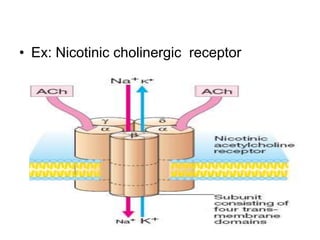
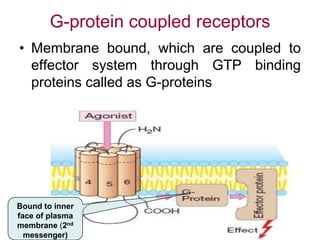
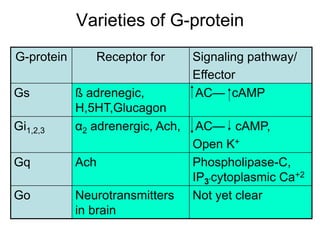
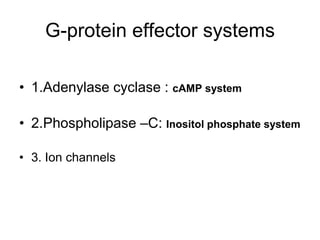
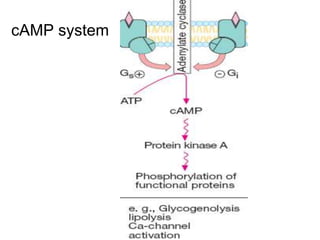
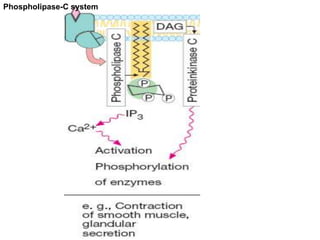
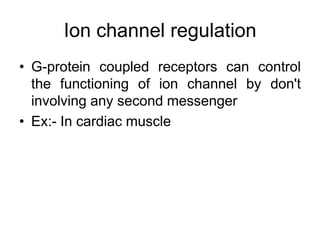
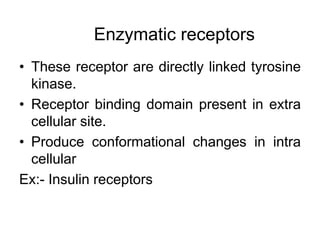
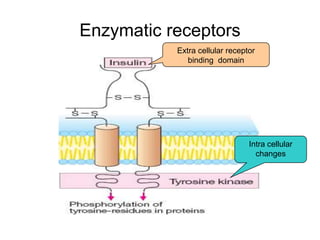
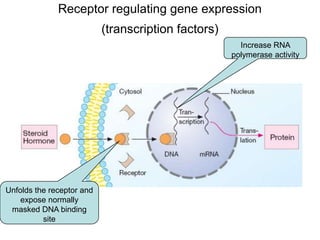
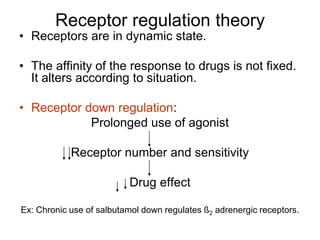
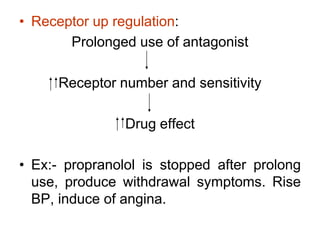
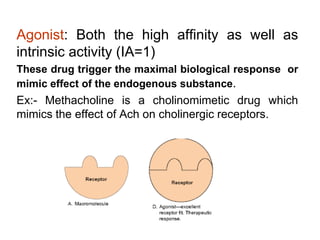
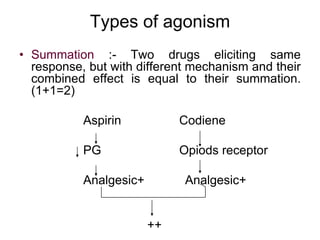
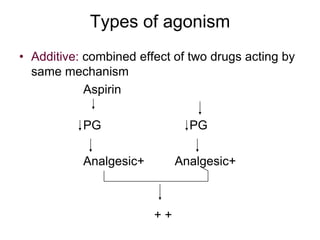
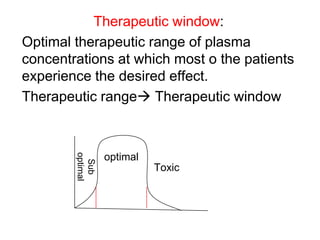
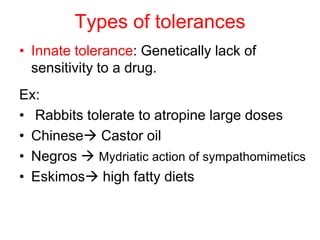
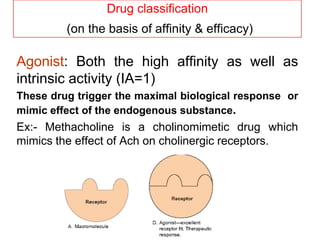
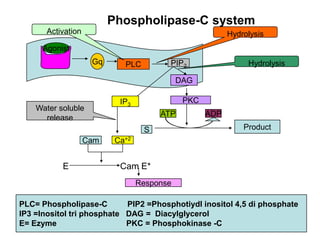
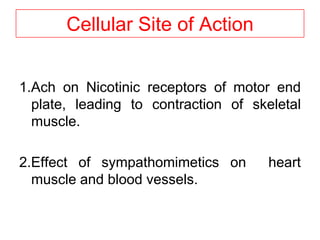
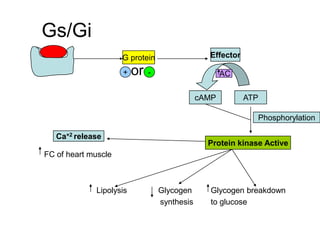
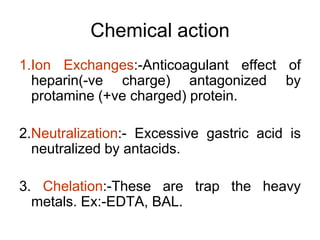
Pharmacodynamics covers how drugs act on the body. Drugs can act through receptor-mediated or non-receptor mediated mechanisms. Receptor-mediated actions involve drug binding to receptors, which then trigger signal transduction pathways. There are various types of receptors including ion channels, G-protein coupled receptors, and nuclear receptors. Drug effects are determined by factors like affinity, efficacy, and intrinsic activity. Individual drug responses can be modified by pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic factors such as age, weight, disease states, genetic differences, and drug interactions.