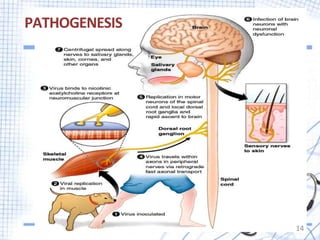
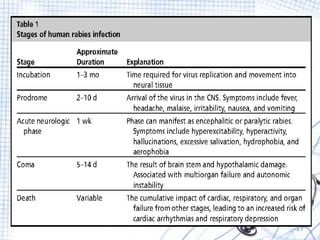
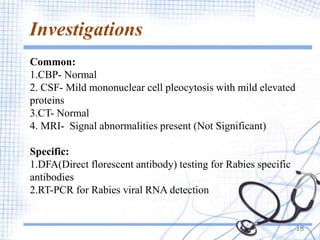
This document provides an overview of rabies, including its definition, epidemiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Rabies is an acute viral infection of the brain that is nearly always fatal once symptoms appear. It is transmitted through the bites or scratches of infected animals, with dogs accounting for 99% of human rabies cases. The virus travels through nerves to the brain, where it causes inflammation. Treatment involves thorough wound cleansing, rabies vaccine, and possibly rabies immunoglobulin. Prevention focuses on vaccinating animals and seeking medical care after potential exposures.