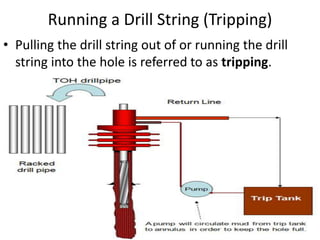
This document discusses drill string and bottom hole assembly (BHA) design. It describes the components of the drill string, including drill pipe, transition pipe, and BHA. The BHA contains components like the drill bit, drill collars, and stabilizers. Drill string design must account for loads, wellbore trajectory, and hydraulic requirements. BHA design depends on factors like directional needs, measurement tools, and drilling conditions. The document also discusses drill string failures, deepest drill strings achieved, and components like subs, motors, and stabilizers.