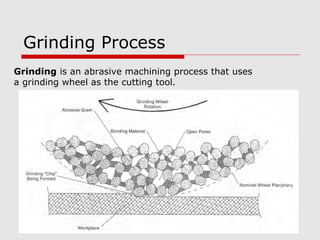
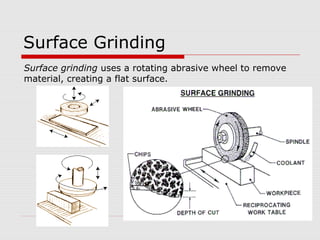
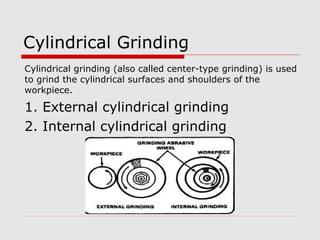
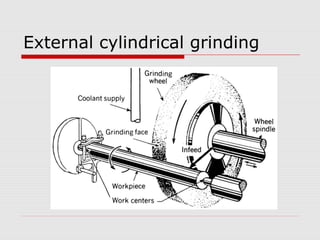
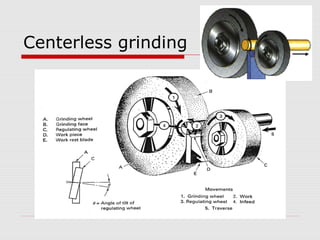
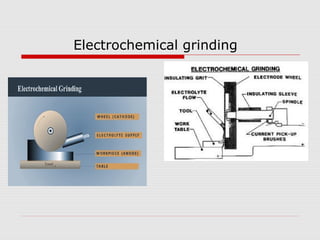
This document provides an overview of various grinding operations and processes. It describes how grinding is used to machine hard materials by producing a smooth surface with minimal surface pressure. The types of grinding operations discussed include rough and precision grinding, as well as specific processes like surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding, form and profile grinding, and plunge cut grinding. Electrochemical grinding is also summarized as a process that removes metal primarily through electrolysis rather than abrasion.