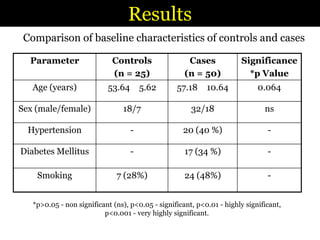
1) The study assessed lipid profiles and blood glucose levels in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke within 24 hours of onset and compared them to healthy controls.
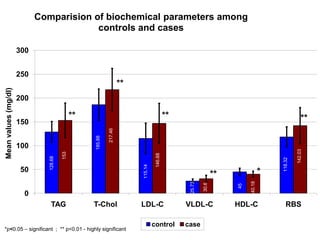
2) It found that ischemic stroke was associated with elevated triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, and low HDL cholesterol levels.
3) Hyperglycemia and hypertension may also be risk factors involved in the etiology of cerebral ischemic stroke.