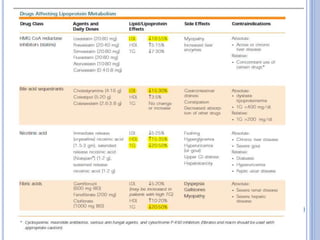
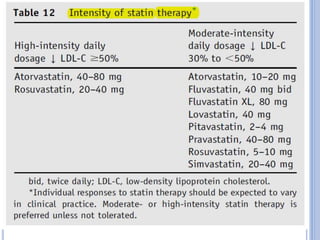
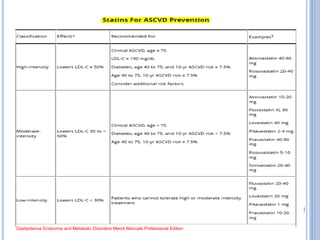
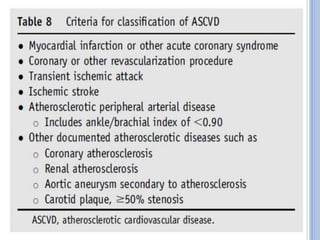
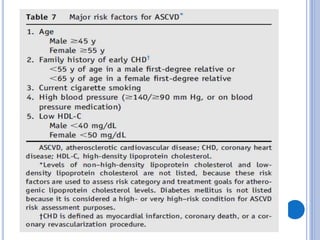
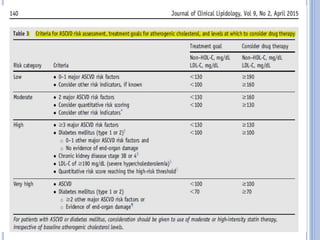
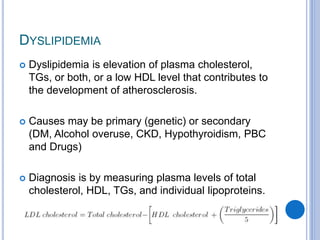
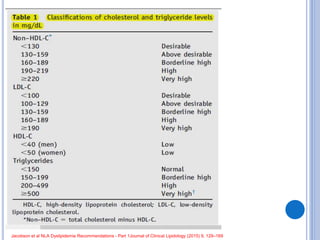
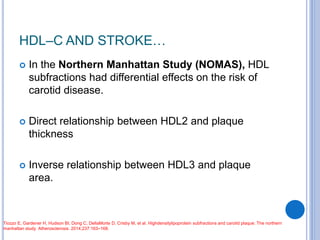
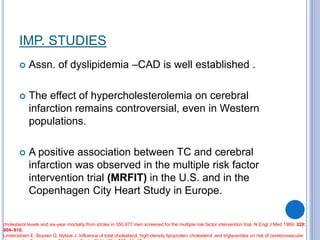
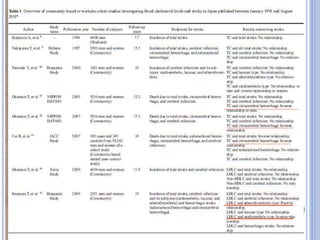
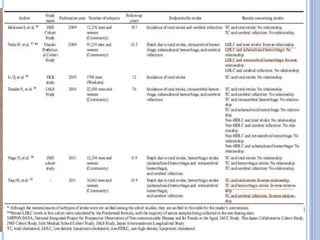
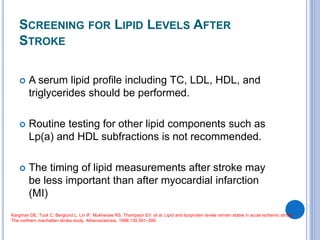
This document discusses dyslipidemia and its relationship to stroke risk. It defines dyslipidemia as abnormal lipid levels that can contribute to atherosclerosis. While dyslipidemia is a risk factor for ischemic stroke, the relationship is complex as lipid levels also influence risks of hemorrhagic stroke. Studies show LDL cholesterol in particular is strongly associated with increased ischemic stroke risk, while low cholesterol may raise risks of hemorrhage. Triglycerides and lipoprotein(a) levels also influence stroke risk. Screening lipid profiles after stroke is recommended to guide treatment and reduce future risks.























![The Long- Term Intervention with Pravastatin in
Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) study-
investigated cholesterol lowering with Pravastatin in
patients with a previous myocardial infarction (MI) or
unstable angina who had cholesterol levels between
155 and 271 mg/dL
A remarkable reduction in MI, cardiac
revascularizations, and cardiovascular deaths, as
well as a 20% reduction in the risk for stroke
(Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease [LIPID] Study Group, 1998).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyslipidemiainstroke06-171102154855/85/Dyslipidemia-in-stroke-32-320.jpg)