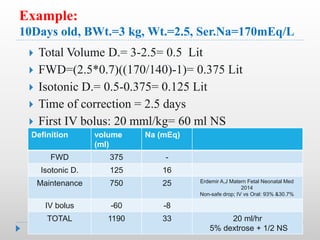
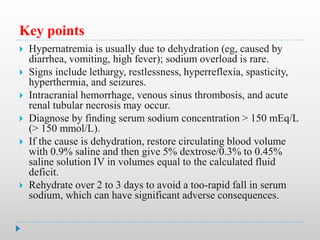
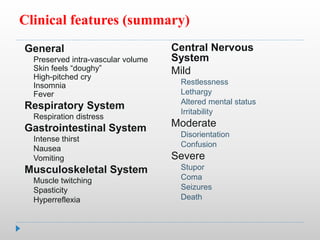
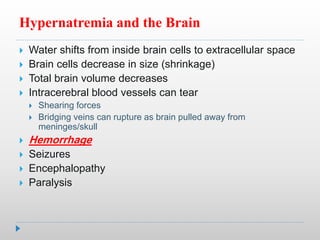
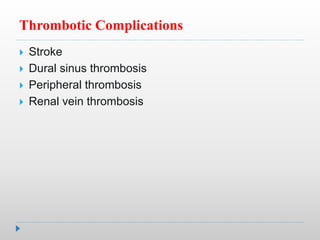
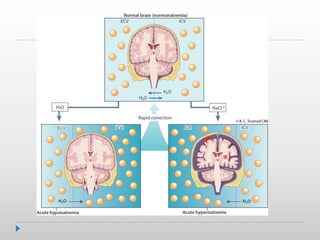
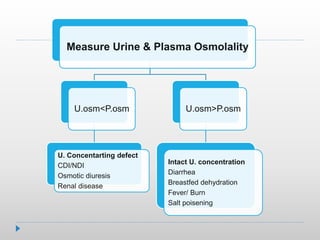
Hypernatremia in neonates is potentially lethal and can cause neurological damage. It is commonly caused by water loss exceeding sodium loss due to greater insensible losses and inability of neonates to communicate thirst. Treatment involves stabilizing the infant, determining the rapidity and rate of sodium correction to avoid cerebral edema, and rehydrating over 2-3 days with IV saline and dextrose solutions to slowly lower the serum sodium level.


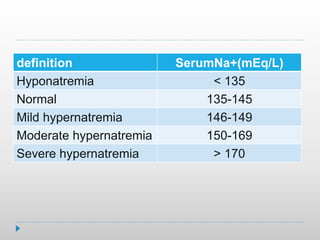










![Treatment of hypernatremic dehydration:
correction phase
Step1:Estimate volume deficit (VD)
Body wt. is best marker
= free water loss + isotonic fluid deficit
Step 2: calculate Free water deficit
FWD= TBW(p)[(P.ser.Na/140)-1] (No Na)
Isotonic F. loss= VD - FWD (140mEq Na/Lit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drkhazaei-210520044159/85/Dr-khazaei-19-320.jpg)