This document discusses hypernatremia (high sodium levels) and its treatment using peritoneal dialysis (PD). It provides details on:
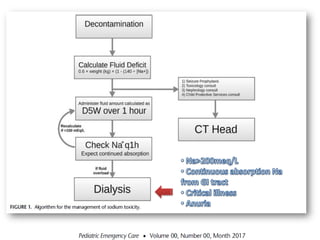
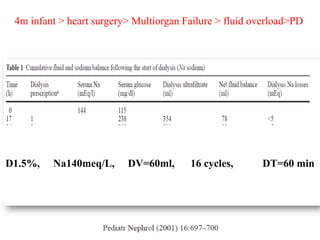
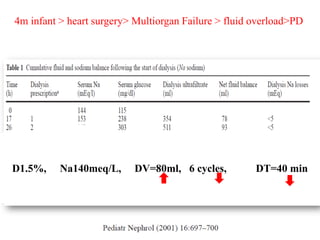
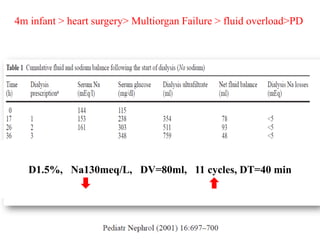
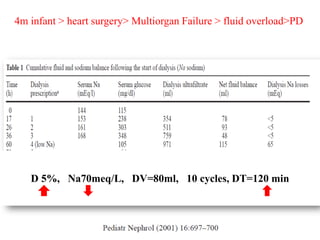
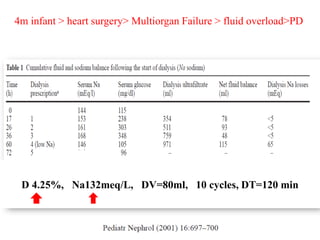
1) An infant who developed hypernatremia after heart surgery and was treated with various PD prescriptions using dialysate with different sodium concentrations and dwell times to gradually reduce the sodium level.
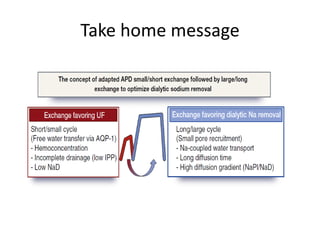
2) How rapid cycling with hypertonic dialysis solutions can cause hypernatremia due to enhanced free water clearance, and how extending dwell time or using hypotonic fluids can help if it develops.
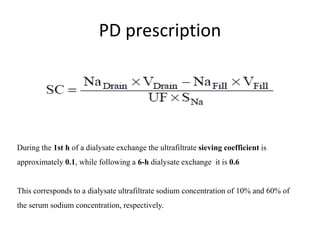
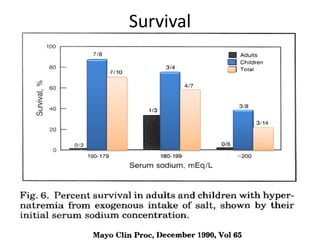
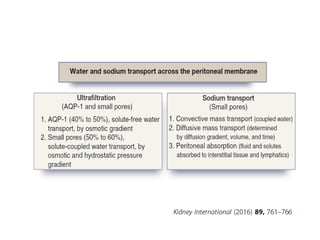
3) How the sieving coefficient for ultrafiltrate sodium concentration is about 10% during the first hour and 60% after a 6-hour dwell,







![• [DNa ] =132 – 134 mmol/L.
• with acute PD, rapid cycling with hypertonic dialysis
solutions to promote UF can result in hyperNa as a
result of enhanced free water clearance secondary
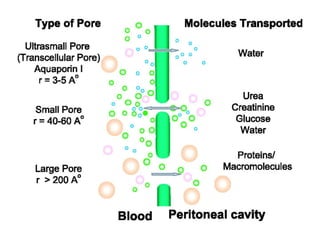
to sodium sieving and transport of water through
aquaporin channels
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 34, pp. 494–517](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drhuman-210520044757/85/PD-hypernatremia-19-320.jpg)